

DEV Community
Posted on Feb 9, 2020
JavaScript OR Assignment Operator
In JavaScript, there may be times when you want to assign one variable to a non-null value. The JavaScript OR assignment operator can be used to quickly assign the value of a variable to one of two options based on one value and if it is null or undefined.
The below code shows a function called 'getNotNull' which takes two parameters 'a' and 'b'. If the value of 'a' is defined and isn't null, it is returned, otherwise, the variable 'b' is returned. This doesn't prevent a null value being returned though, as if both 'a' and 'b' are null then the value of 'b' will be returned and therefore a null value will be returned.
A ternary operator can also be used to the same effect. In the below code a ternary operator is used to set the value of the variable 'result' to either the value of 'a' if it defined and not null otherwise it will be set to the value 'b'. Again, this does not prevent a null value if both variables are null or undefined.
The JavaScript OR assignment operator is represented with two pipe '|' symbols. This can be used to achieve the same effect as the above two code snippets. The value of the 'result' variable will be assigned to the value of 'a' if it is defined or not null otherwise it will be assigned to the value of 'b'.
The OR assignment operator does not need to be used with variables, it can be used with raw values too. The below code snippet shows using the OR operator to set the value of the 'result' variable uses raw values, 'null' or the number '2'. The value of the 'result' variable will be 2 as the left side of the OR assignment operator is null.
The OR assignment operator can be used to assign the value of one variable to either one or another value based on if the first value is null or undefined. Using the OR assignment operator does not prevent the variable from being assigned a null or undefined value, if both sides of the OR assignment operator are null then the resulting value will also be null.
This post was originally published on https://acroynon.com
Top comments (14)
Templates let you quickly answer FAQs or store snippets for re-use.
- Joined Feb 5, 2018
You should replace "null" / "null or undefined" by "falsy".
And also have a look at the "??" operator.
Keep writing it is a good way to improve!
- Location United Kingdom
- Education Computer Science Bsc
- Work Senior Software Engineer
- Joined Nov 7, 2019
Yeah, you're correct, it is a "falsely" value that is evaluated, I didn't want to make this post too complicated, but great to mention this for the curious readers. Thanks
I am not sure what you mean by "??" operator, I have written a post on the ternary operator and I plan to write a post about the optional chaining operator ('?.') in the future.
Here is the related documentation:
developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/W...
Thanks, it seems like a more strict version of the OR assignment operator. Perhaps I shall create a post comparing the two
I think that you should point out the differences between falsy values (cf. developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/G... ) and null/undefined checks (with ??). I think that will add value to your post.
I think I shall leave this post as it is for now and cover the falsy values and the coalescing operator in separate posts, thank you for the feedback and ideas
Up to you, I just recommend you to be careful with the terms that you use in your post and in my opinion it is a good to support your posts with official references.
For example you function:
Doesn't work if you pass to it a falsy value like 0 or an empty string.
By being not precise you will assume wrong things (I have been there so many times, and it is still happening).
I would recommend the "you don't know js" by Kyle Simpson ( @getify ), to expand your knowledge.
Thanks for all the feedback. My plan isn't to fill every post with all the detail needed, at least not right now (I don't have the time to put that much time into each post). I mainly want to encourage people to begin to learn how to code, or experiment with something they haven't used before. I don't admit to knowing everything, but I don't want to overload the reader with too much information that reduces their interest in code. Again, thank you for all the feedback, I super appreciate it and I guarantee some readers will benefit from some of the links you've posted.
- Joined May 7, 2020
You’re talking about the regular OR-operator; the OR assignment -operator doesn’t exist in Javascript (unfortunately)
I consider the standard or operator the one used in if statement, for boolean logic. Then the or assignment operator being used to assign values to variables (assign this value, if its falsey assign this value instead). I could be completely wrong in my phrasing, but I think it makes a nice distinction between the two use cases
You can consider a melon a nail when you hit it with a hammer, but it’s not going to make sense to anybody.
I’m afraid the long and short of it is just that the OR-assignment operator ( ||= ) is not the OR-operator ( || ), sorry man.
Okay, thanks for the clarification
Okay thank you
Great stuff, do you think my explanation in this post is good?
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink .
Hide child comments as well
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse

REAP Method Enhances LLM Complex Problem-Solving with Reflection and Advanced Prompting
Mike Young - Sep 17

Boost Software Development Success: Integrating Cross-Disciplinary Skill Sets for Better Results
Parth Dadhaniya - Sep 17

Introducing HTPX: A Lightweight and Versatile HTTP Client for JavaScript and Node.js
Krrish Paul - Sep 17

Introducing simpledev.css
Javier Alvarado - Sep 16

We're a place where coders share, stay up-to-date and grow their careers.

JAVASCRIPT ASSIGNMENT OPERATORS
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different assignment operators in javascript and how to use them in javascript.
Assignment Operators
In javascript, there are 16 different assignment operators that are used to assign value to the variable. It is shorthand of other operators which is recommended to use.
The assignment operators are used to assign value based on the right operand to its left operand.
The left operand must be a variable while the right operand may be a variable, number, boolean, string, expression, object, or combination of any other.
One of the most basic assignment operators is equal = , which is used to directly assign a value.
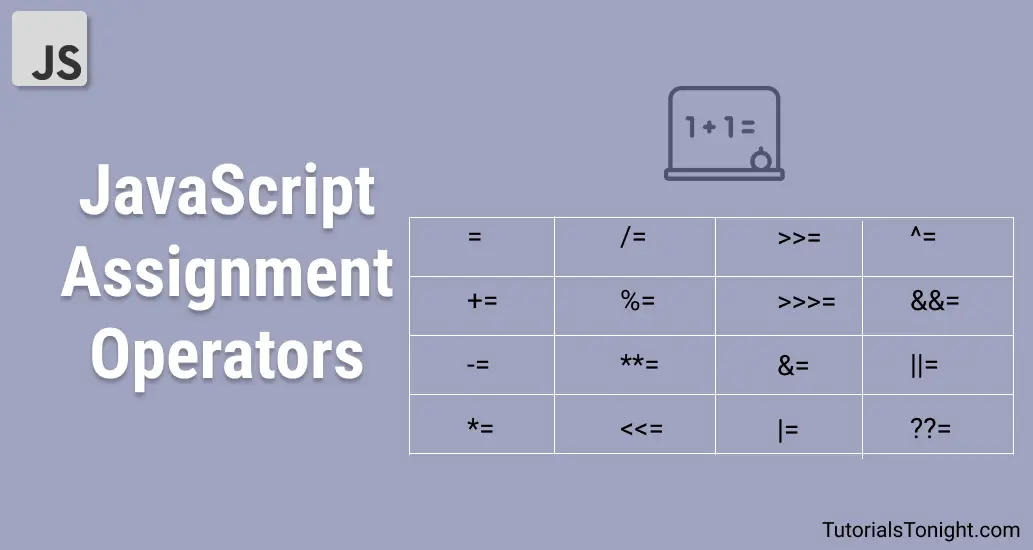
Assignment Operators List
Here is the list of all assignment operators in JavaScript:
In the following table if variable a is not defined then assume it to be 10.
| Operator | Description | Example | Equivalent to |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | a = 10 | a = 10 | |
| += | a += 10 | a = a + 10 | |
| -= | a -= 10 | a = a - 10 | |
| *= | a *= 10 | a = a * 10 | |
| /= | a /= 10 | a = a / 10 | |
| %= | a %= 10 | a = a % 10 | |
| **= | a **= 2 | a = a ** 2 | |
| <<= | a <<= 1 | a = a << 1 | |
| >>= | a >>= 2 | a = a >> 2 | |
| >>>= | a >>>= 1 | a = a >>> 1 | |
| &= | a &= 4 | a = a & 4 | |
| |= | a |= 2 | a = a | 2 | |
| ^= | a ^= 5 | a = a ^ 5 | |
| &&= | a &&= 3 | a = a && 3 | |
| ||= | a ||= 4 | a = a || 4 | |
| ??= | a ??= 2 | a = a ?? 2 |
Assignment operator
The assignment operator = is the simplest value assigning operator which assigns a given value to a variable.
The assignment operators support chaining, which means you can assign a single value in multiple variables in a single line.
Addition assignment operator
The addition assignment operator += is used to add the value of the right operand to the value of the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
On the basis of the data type of variable, the addition assignment operator may add or concatenate the variables.
Subtraction assignment operator
The subtraction assignment operator -= subtracts the value of the right operand from the value of the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
If the value can not be subtracted then it results in a NaN .
Multiplication assignment operator
The multiplication assignment operator *= assigns the result to the left operand after multiplying values of the left and right operand.
Division assignment operator
The division assignment operator /= divides the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
Remainder assignment operator
The remainder assignment operator %= assigns the remainder to the left operand after dividing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Exponentiation assignment operator
The exponential assignment operator **= assigns the result of exponentiation to the left operand after exponentiating the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Left shift assignment
The left shift assignment operator <<= assigns the result of the left shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Right shift assignment
The right shift assignment operator >>= assigns the result of the right shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Unsigned right shift assignment
The unsigned right shift assignment operator >>>= assigns the result of the unsigned right shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise AND assignment
The bitwise AND assignment operator &= assigns the result of bitwise AND to the left operand after ANDing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise OR assignment
The bitwise OR assignment operator |= assigns the result of bitwise OR to the left operand after ORing the value of left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise XOR assignment
The bitwise XOR assignment operator ^= assigns the result of bitwise XOR to the left operand after XORing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Logical AND assignment
The logical AND assignment operator &&= assigns value to left operand only when it is truthy .
Note : A truthy value is a value that is considered true when encountered in a boolean context.
Logical OR assignment
The logical OR assignment operator ||= assigns value to left operand only when it is falsy .
Note : A falsy value is a value that is considered false when encountered in a boolean context.
Logical nullish assignment
The logical nullish assignment operator ??= assigns value to left operand only when it is nullish ( null or undefined ).
Popular Tutorials
Popular examples, reference materials, learn python interactively, js introduction.
- Getting Started
- JS Variables & Constants
- JS console.log
- JavaScript Data types
JavaScript Operators
- JavaScript Comments
- JS Type Conversions
JS Control Flow
- JS Comparison Operators
- JavaScript if else Statement
- JavaScript for loop
- JavaScript while loop
- JavaScript break Statement
- JavaScript continue Statement
- JavaScript switch Statement
JS Functions
- JavaScript Function
- Variable Scope
- JavaScript Hoisting
- JavaScript Recursion
- JavaScript Objects
- JavaScript Methods & this
- JavaScript Constructor
- JavaScript Getter and Setter
- JavaScript Prototype
- JavaScript Array
- JS Multidimensional Array
- JavaScript String
- JavaScript for...in loop
- JavaScript Number
- JavaScript Symbol
Exceptions and Modules
- JavaScript try...catch...finally
- JavaScript throw Statement
- JavaScript Modules
- JavaScript ES6
- JavaScript Arrow Function
- JavaScript Default Parameters
- JavaScript Template Literals
- JavaScript Spread Operator
- JavaScript Map
- JavaScript Set
- Destructuring Assignment
- JavaScript Classes
- JavaScript Inheritance
- JavaScript for...of
- JavaScript Proxies
JavaScript Asynchronous
- JavaScript setTimeout()
- JavaScript CallBack Function
- JavaScript Promise
- Javascript async/await
- JavaScript setInterval()
Miscellaneous
- JavaScript JSON
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript Closure
- JavaScript this
- JavaScript use strict
- Iterators and Iterables
- JavaScript Generators
- JavaScript Regular Expressions
- JavaScript Browser Debugging
- Uses of JavaScript
JavaScript Tutorials
JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators
JavaScript Ternary Operator
JavaScript Booleans
JavaScript Bitwise Operators
- JavaScript Object.is()
- JavaScript typeof Operator
JavaScript operators are special symbols that perform operations on one or more operands (values). For example,
Here, we used the + operator to add the operands 2 and 3 .
JavaScript Operator Types
Here is a list of different JavaScript operators you will learn in this tutorial:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- String Operators
- Miscellaneous Operators
1. JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
We use arithmetic operators to perform arithmetic calculations like addition, subtraction, etc. For example,
Here, we used the - operator to subtract 3 from 5 .
Commonly Used Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | ||
| Subtraction | ||
| Multiplication | ||
| Division | ||
| Remainder | ||
| Increment (increments by ) | or | |
| Decrement (decrements by ) | or | |
| Exponentiation (Power) |
Example 1: Arithmetic Operators in JavaScript
Note: The increment operator ++ adds 1 to the operand. And, the decrement operator -- decreases the value of the operand by 1 .
To learn more, visit Increment ++ and Decrement -- Operators .
2. JavaScript Assignment Operators
We use assignment operators to assign values to variables. For example,
Here, we used the = operator to assign the value 5 to the variable x .
Commonly Used Assignment Operators
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Assignment Operator | ||
| Addition Assignment | ||
| Subtraction Assignment | ||
| Multiplication Assignment | ||
| Division Assignment | ||
| Remainder Assignment | ||
| Exponentiation Assignment |
Example 2: Assignment Operators in JavaScript
3. javascript comparison operators.
We use comparison operators to compare two values and return a boolean value ( true or false ). For example,
Here, we have used the > comparison operator to check whether a (whose value is 3 ) is greater than b (whose value is 2 ).
Since 3 is greater than 2 , we get true as output.
Note: In the above example, a > b is called a boolean expression since evaluating it results in a boolean value.
Commonly Used Comparison Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Equal to | gives us | |
| Not equal to | gives us | |
| Greater than | gives us | |
| Less than | gives us | |
| Greater than or equal to | gives us | |
| Less than or equal to | gives us | |
| Strictly equal to | gives us | |
| Strictly not equal to | gives us |
Example 3: Comparison Operators in JavaScript
The equality operators ( == and != ) convert both operands to the same type before comparing their values. For example,
Here, we used the == operator to compare the number 3 and the string 3 .
By default, JavaScript converts string 3 to number 3 and compares the values.
However, the strict equality operators ( === and !== ) do not convert operand types before comparing their values. For example,
Here, JavaScript didn't convert string 4 to number 4 before comparing their values.
Thus, the result is false , as number 4 isn't equal to string 4 .
4. JavaScript Logical Operators
We use logical operators to perform logical operations on boolean expressions. For example,
Here, && is the logical operator AND . Since both x < 6 and y < 5 are true , the combined result is true .
Commonly Used Logical Operators
| Operator | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (Logical AND) | only if both and are | |
| (Logical OR) | if either or is | |
| (Logical NOT) | if is and vice versa |
Example 4: Logical Operators in JavaScript
Note: We use comparison and logical operators in decision-making and loops. You will learn about them in detail in later tutorials.
More on JavaScript Operators
We use bitwise operators to perform binary operations on integers.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND | |
| | | Bitwise OR | |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR | |
| ~ | Bitwise NOT | |
| << | Left shift | |
| >> | Sign-propagating right shift | |
| >>> | Zero-fill right shift |
Note: We rarely use bitwise operators in everyday programming. If you are interested, visit JavaScript Bitwise Operators to learn more.
In JavaScript, you can also use the + operator to concatenate (join) two strings. For example,
Here, we used the + operator to concatenate str1 and str2 .
JavaScript has many more operators besides the ones we listed above. You will learn about them in detail in later tutorials.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| : Evaluates multiple operands and returns the value of the last operand. | ||
| : Returns value based on the condition. | ||
| Returns the data type of the variable. | ||
| Returns t if the specified object is a valid object of the specified class. | ||
| Discards any expression's return value. |
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
- JavaScript Assignment Operators
- JavaScript Comparison Operators
- JavaScript Logical Operators
Before we wrap up, let’s put your knowledge of JavaScript Operators to the test! Can you solve the following challenge?
Write a function to perform basic arithmetic operations.
- The operations are: + for Addition, - for Subtraction, * for Multiplication and / for Division.
- Given num1 , num2 , and op specifying the operation to perform, return the result.
- For example, if num1 = 5 , op = "+" and num2 = 3 , the expected output is 8 .
Video: JavaScript Operators
Sorry about that.
Our premium learning platform, created with over a decade of experience and thousands of feedbacks .
Learn and improve your coding skills like never before.
- Interactive Courses
- Certificates
- 2000+ Challenges
Related Tutorials
JavaScript Tutorial
Home » JavaScript Tutorial » JavaScript Assignment Operators
JavaScript Assignment Operators
Summary : in this tutorial, you will learn how to use JavaScript assignment operators to assign a value to a variable.

Introduction to JavaScript assignment operators
An assignment operator ( = ) assigns a value to a variable. The syntax of the assignment operator is as follows:
In this syntax, JavaScript evaluates the expression b first and assigns the result to the variable a .
The following example declares the counter variable and initializes its value to zero:
The following example increases the counter variable by one and assigns the result to the counter variable:
When evaluating the second statement, JavaScript evaluates the expression on the right-hand first ( counter + 1 ) and assigns the result to the counter variable. After the second assignment, the counter variable is 1 .
To make the code more concise, you can use the += operator like this:
In this syntax, you don’t have to repeat the counter variable twice in the assignment.
The following table illustrates assignment operators that are shorthand for another operator and the assignment:
| Operator | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Assigns the value of to . | ||
| Assigns the result of plus to . | ||
| Assigns the result of minus to . | ||
| Assigns the result of times to . | ||
| Assigns the result of divided by to . | ||
| Assigns the result of modulo to . | ||
| Assigns the result of AND to . | ||
| Assigns the result of OR to . | ||
| Assigns the result of XOR to . | ||
| Assigns the result of shifted left by to . | ||
| Assigns the result of shifted right (sign preserved) by to . | ||
| Assigns the result of shifted right by to . |
Chaining JavaScript assignment operators
If you want to assign a single value to multiple variables, you can chain the assignment operators. For example:
In this example, JavaScript evaluates from right to left. Therefore, it does the following:
- Use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign a value to a variable.
- Chain the assignment operators if you want to assign a single value to multiple variables.
A Guide to Variable Assignment and Mutation in JavaScript
Share this article

Variable Assignment
Variable reassignment, variable assignment by reference, copying by reference, the spread operator to the rescue, are mutations bad, frequently asked questions (faqs) about javascript variable assignment and mutation.
Mutations are something you hear about fairly often in the world of JavaScript, but what exactly are they, and are they as evil as they’re made out to be?
In this article, we’re going to cover the concepts of variable assignment and mutation and see why — together — they can be a real pain for developers. We’ll look at how to manage them to avoid problems, how to use as few as possible, and how to keep your code predictable.
If you’d like to explore this topic in greater detail, or get up to speed with modern JavaScript, check out the first chapter of my new book Learn to Code with JavaScript for free.
Let’s start by going back to the very basics of value types …
Every value in JavaScript is either a primitive value or an object. There are seven different primitive data types:
- numbers, such as 3 , 0 , -4 , 0.625
- strings, such as 'Hello' , "World" , `Hi` , ''
- Booleans, true and false
- symbols — a unique token that’s guaranteed never to clash with another symbol
- BigInt — for dealing with large integer values
Anything that isn’t a primitive value is an object , including arrays, dates, regular expressions and, of course, object literals. Functions are a special type of object. They are definitely objects, since they have properties and methods, but they’re also able to be called.
Variable assignment is one of the first things you learn in coding. For example, this is how we would assign the number 3 to the variable bears :
A common metaphor for variables is one of boxes with labels that have values placed inside them. The example above would be portrayed as a box containing the label “bears” with the value of 3 placed inside.

An alternative way of thinking about what happens is as a reference, that maps the label bears to the value of 3 :
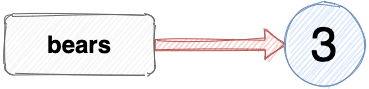
If I assign the number 3 to another variable, it’s referencing the same value as bears:
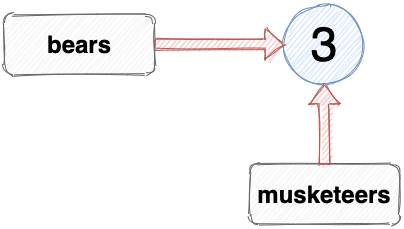
The variables bears and musketeers both reference the same primitive value of 3. We can verify this using the strict equality operator, === :
The equality operator returns true if both variables are referencing the same value.
Some gotchas when working with objects
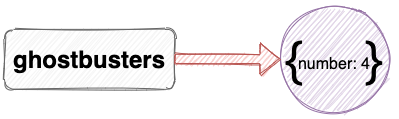
The previous examples showed primitive values being assigned to variables. The same process is used when assigning objects:
This assignment means that the variable ghostbusters references an object:
A big difference when assigning objects to variables, however, is that if you assign another object literal to another variable, it will reference a completely different object — even if both object literals look exactly the same! For example, the assignment below looks like the variable tmnt (Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles) references the same object as the variable ghostbusters :
Even though the variables ghostbusters and tmnt look like they reference the same object, they actually both reference a completely different object, as we can see if we check with the strict equality operator:

When the const keyword was introduced in ES6, many people mistakenly believed that constants had been introduced to JavaScript, but this wasn’t the case. The name of this keyword is a little misleading.
Any variable declared with const can’t be reassigned to another value. This goes for primitive values and objects. For example, the variable bears was declared using const in the previous section, so it can’t have another value assigned to it. If we try to assign the number 2 to the variable bears , we get an error:
The reference to the number 3 is fixed and the bears variable can’t be reassigned another value.
The same applies to objects. If we try to assign a different object to the variable ghostbusters , we get the same error:
Variable reassignment using let
When the keyword let is used to declare a variable, it can be reassigned to reference a different value later on in our code. For example, we declared the variable musketeers using let , so we can change the value that musketeers references. If D’Artagnan joined the Musketeers, their number would increase to 4:
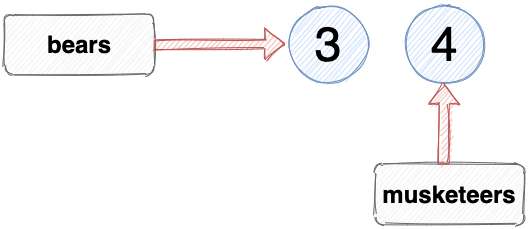
This can be done because let was used to declare the variable. We can alter the value that musketeers references as many times as we like.
The variable tmnt was also declared using let , so it can also be reassigned to reference another object (or a different type entirely if we like):
Note that the variable tmnt now references a completely different object ; we haven’t just changed the number property to 5.
In summary , if you declare a variable using const , its value can’t be reassigned and will always reference the same primitive value or object that it was originally assigned to. If you declare a variable using let , its value can be reassigned as many times as required later in the program.
Using const as often as possible is generally considered good practice, as it means that the value of variables remains constant and the code is more consistent and predictable, making it less prone to errors and bugs.
In native JavaScript, you can only assign values to variables. You can’t assign variables to reference another variable, even though it looks like you can. For example, the number of Stooges is the same as the number of Musketeers, so we can assign the variable stooges to reference the same value as the variable musketeers using the following:
This looks like the variable stooges is referencing the variable musketeers , as shown in the diagram below:
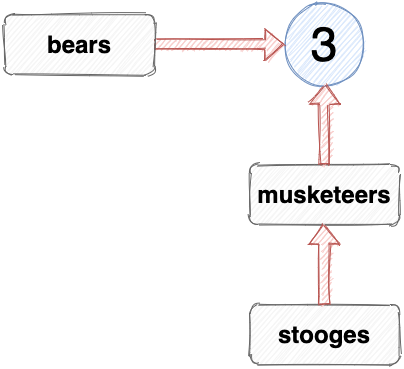
However, this is impossible in native JavaScript: a variable can only reference an actual value; it can’t reference another variable . What actually happens when you make an assignment like this is that the variable on the left of the assignment will reference the value the variable on the right references, so the variable stooges will reference the same value as the musketeers variable, which is the number 3. Once this assignment has been made, the stooges variable isn’t connected to the musketeers variable at all.
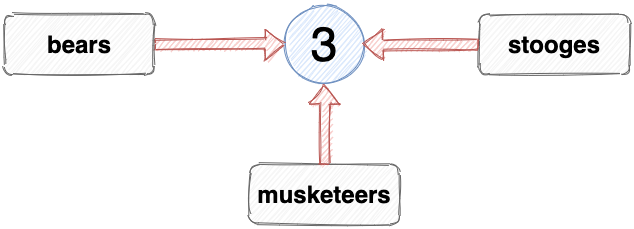
This means that if D’Artagnan joins the Musketeers and we set the value of the musketeers to 4, the value of stooges will remain as 3. In fact, because we declared the stooges variable using const , we can’t set it to any new value; it will always be 3.
In summary : if you declare a variable using const and set it to a primitive value, even via a reference to another variable, then its value can’t change. This is good for your code, as it means it will be more consistent and predictable.
A value is said to be mutable if it can be changed. That’s all there is to it: a mutation is the act of changing the properties of a value.
All primitive value in JavaScript are immutable : you can’t change their properties — ever. For example, if we assign the string "cake" to variable food , we can see that we can’t change any of its properties:
If we try to change the first letter to “f”, it looks like it has changed:
But if we take a look at the value of the variable, we see that nothing has actually changed:
The same thing happens if we try to change the length property:
Despite the return value implying that the length property has been changed, a quick check shows that it hasn’t:
Note that this has nothing to do with declaring the variable using const instead of let . If we had used let , we could set food to reference another string, but we can’t change any of its properties. It’s impossible to change any properties of primitive data types because they’re immutable .
Mutability and objects in JavaScript
Conversely, all objects in JavaScript are mutable, which means that their properties can be changed, even if they’re declared using const (remember let and const only control whether or not a variable can be reassigned and have nothing to do with mutability). For example, we can change the the first item of an array using the following code:
Note that this change still occurred, despite the fact that we declared the variable food using const . This shows that using const does not stop objects from being mutated .
We can also change the length property of an array, even if it has been declared using const :
Remember that when we assign variables to object literals, the variables will reference completely different objects, even if they look the same:
But if we assign a variable fantastic4 to another variable, they will both reference the same object:
This assigns the variable fantastic4 to reference the same object that the variable tmnt references, rather than a completely different object.
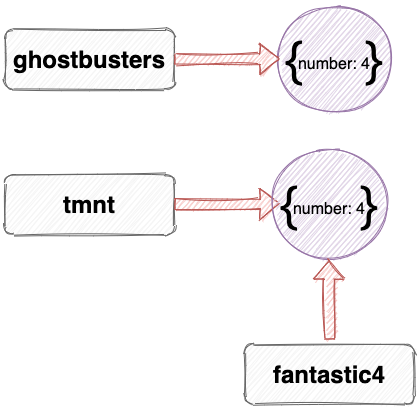
This is often referred to as copying by reference , because both variables are assigned to reference the same object.
This is important, because any mutations made to this object will be seen in both variables.
So, if Spider-Man joins The Fantastic Four, we might update the number value in the object:
This is a mutation, because we’ve changed the number property rather than setting fantastic4 to reference a new object.
This causes us a problem, because the number property of tmnt will also also change, possibly without us even realizing:
This is because both tmnt and fantastic4 are referencing the same object, so any mutations that are made to either tmnt or fantastic4 will affect both of them.
This highlights an important concept in JavaScript: when objects are copied by reference and subsequently mutated, the mutation will affect any other variables that reference that object. This can lead to unintended side effects and bugs that are difficult to track down.
So how do you make a copy of an object without creating a reference to the original object? The answer is to use the spread operator !
The spread operator was introduced for arrays and strings in ES2015 and for objects in ES2018. It allows you to easily make a shallow copy of an object without creating a reference to the original object.
The example below shows how we could set the variable fantastic4 to reference a copy of the tmnt object. This copy will be exactly the same as the tmnt object, but fantastic4 will reference a completely new object. This is done by placing the name of the variable to be copied inside an object literal with the spread operator in front of it:
What we’ve actually done here is assign the variable fantastic4 to a new object literal and then used the spread operator to copy all the enumerable properties of the object referenced by the tmnt variable. Because these properties are values, they’re copied into the fantastic4 object by value, rather than by reference.
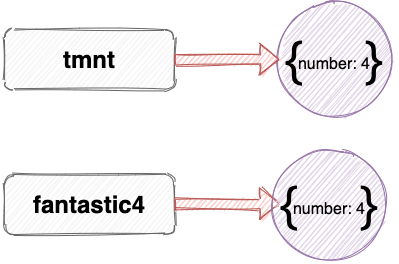
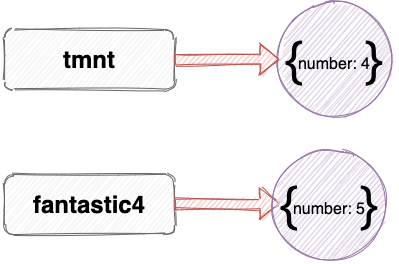
Now any changes that are made to either object won’t affect the other. For example, if we update the number property of the fantastic4 variable to 5, it won’t affect the tmnt variable:
The spread operator also has a useful shortcut notation that can be used to make copies of an object and then make some changes to the new object in a single line of code.
For example, say we wanted to create an object to model the Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles. We could create the first turtle object, and assign the variable leonardo to it:
The other turtles all have the same properties, except for the weapon and color properties, that are different for each turtle. It makes sense to make a copy of the object that leonardo references, using the spread operator, and then change the weapon and color properties, like so:
We can do this in one line by adding the properties we want to change after the reference to the spread object. Here’s the code to create new objects for the variables donatello and raphael :
Note that using the spread operator in this way only makes a shallow copy of an object. To make a deep copy, you’d have to do this recursively, or use a library. Personally, I’d advise that you try to keep your objects as shallow as possible.
In this article, we’ve covered the concepts of variable assignment and mutation and seen why — together — they can be a real pain for developers.
Mutations have a bad reputation, but they’re not necessarily bad in themselves. In fact, if you’re building a dynamic web app, it must change at some point. That’s literally the meaning of the word “dynamic”! This means that there will have to be some mutations somewhere in your code. Having said that, the fewer mutations there are, the more predictable your code will be, making it easier to maintain and less likely to develop any bugs.
A particularly toxic combination is copying by reference and mutations. This can lead to side effects and bugs that you don’t even realize have happened. If you mutate an object that’s referenced by another variable in your code, it can cause lots of problems that can be difficult to track down. The key is to try and minimize your use of mutations to the essential and keep track of which objects have been mutated.
In functional programming, a pure function is one that doesn’t cause any side effects, and mutations are one of the biggest causes of side effects.
A golden rule is to avoid copying any objects by reference. If you want to copy another object, use the spread operator and then make any mutations immediately after making the copy.
Next up, we’ll look into array mutations in JavaScript .
Don’t forget to check out my new book Learn to Code with JavaScript if you want to get up to speed with modern JavaScript. You can read the first chapter for free. And please reach out on Twitter if you have any questions or comments!
What is the difference between variable assignment and mutation in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, variable assignment refers to the process of assigning a value to a variable. For example, let x = 5; Here, we are assigning the value 5 to the variable x. On the other hand, mutation refers to the process of changing the value of an existing variable. For example, if we later write x = 10; we are mutating the variable x by changing its value from 5 to 10.
How does JavaScript handle variable assignment and mutation differently for primitive and non-primitive data types?
JavaScript treats primitive data types (like numbers, strings, and booleans) and non-primitive data types (like objects and arrays) differently when it comes to variable assignment and mutation. For primitive data types, when you assign a variable, a copy of the value is created and stored in a new memory location. However, for non-primitive data types, when you assign a variable, both variables point to the same memory location. Therefore, if you mutate one variable, the change is reflected in all variables that point to that memory location.
What is the concept of pass-by-value and pass-by-reference in JavaScript?
Pass-by-value and pass-by-reference are two ways that JavaScript can pass variables to a function. When JavaScript passes a variable by value, it creates a copy of the variable’s value and passes that copy to the function. Any changes made to the variable inside the function do not affect the original variable. However, when JavaScript passes a variable by reference, it passes a reference to the variable’s memory location. Therefore, any changes made to the variable inside the function also affect the original variable.
How can I prevent mutation in JavaScript?
There are several ways to prevent mutation in JavaScript. One way is to use the Object.freeze() method, which prevents new properties from being added to an object, existing properties from being removed, and prevents changing the enumerability, configurability, or writability of existing properties. Another way is to use the const keyword when declaring a variable. This prevents reassignment of the variable, but it does not prevent mutation of the variable’s value if the value is an object or an array.
What is the difference between shallow copy and deep copy in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, a shallow copy of an object is a copy of the object where the values of the original object and the copy point to the same memory location for non-primitive data types. Therefore, if you mutate the copy, the original object is also mutated. On the other hand, a deep copy of an object is a copy of the object where the values of the original object and the copy do not point to the same memory location. Therefore, if you mutate the copy, the original object is not mutated.
How can I create a deep copy of an object in JavaScript?
One way to create a deep copy of an object in JavaScript is to use the JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() methods. The JSON.stringify() method converts the object into a JSON string, and the JSON.parse() method converts the JSON string back into an object. This creates a new object that is a deep copy of the original object.
What is the MutationObserver API in JavaScript?
The MutationObserver API provides developers with a way to react to changes in a DOM. It is designed to provide a general, efficient, and robust API for reacting to changes in a document.
How does JavaScript handle variable assignment and mutation in the context of closures?
In JavaScript, a closure is a function that has access to its own scope, the scope of the outer function, and the global scope. When a variable is assigned or mutated inside a closure, it can affect the value of the variable in the outer scope, depending on whether the variable was declared in the closure’s scope or the outer scope.
What is the difference between var, let, and const in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, var, let, and const are used to declare variables. var is function scoped, and if it is declared outside a function, it is globally scoped. let and const are block scoped, meaning they exist only within the block they are declared in. The difference between let and const is that let allows reassignment, while const does not.
How does JavaScript handle variable assignment and mutation in the context of asynchronous programming?
In JavaScript, asynchronous programming allows multiple things to happen at the same time. When a variable is assigned or mutated in an asynchronous function, it can lead to unexpected results if other parts of the code are relying on the value of the variable. This is because the variable assignment or mutation may not have completed before the other parts of the code run. To handle this, JavaScript provides several features, such as promises and async/await, to help manage asynchronous code.
Darren loves building web apps and coding in JavaScript, Haskell and Ruby. He is the author of Learn to Code using JavaScript , JavaScript: Novice to Ninja and Jump Start Sinatra .He is also the creator of Nanny State , a tiny alternative to React. He can be found on Twitter @daz4126.

JS Tutorial
Js versions, js functions, js html dom, js browser bom, js web apis, js vs jquery, js graphics, js examples, js references, javascript variables, variables are containers for storing data.
JavaScript Variables can be declared in 4 ways:
- Automatically
- Using const
In this first example, x , y , and z are undeclared variables.
They are automatically declared when first used:
It is considered good programming practice to always declare variables before use.
From the examples you can guess:
- x stores the value 5
- y stores the value 6
- z stores the value 11
Example using var
The var keyword was used in all JavaScript code from 1995 to 2015.
The let and const keywords were added to JavaScript in 2015.
The var keyword should only be used in code written for older browsers.
Example using let
Example using const, mixed example.
The two variables price1 and price2 are declared with the const keyword.
These are constant values and cannot be changed.
The variable total is declared with the let keyword.
The value total can be changed.
When to Use var, let, or const?
1. Always declare variables
2. Always use const if the value should not be changed
3. Always use const if the type should not be changed (Arrays and Objects)
4. Only use let if you can't use const
5. Only use var if you MUST support old browsers.
Just Like Algebra
Just like in algebra, variables hold values:
Just like in algebra, variables are used in expressions:
From the example above, you can guess that the total is calculated to be 11.
Variables are containers for storing values.
Advertisement
JavaScript Identifiers
All JavaScript variables must be identified with unique names .
These unique names are called identifiers .
Identifiers can be short names (like x and y) or more descriptive names (age, sum, totalVolume).
The general rules for constructing names for variables (unique identifiers) are:
- Names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
- Names must begin with a letter.
- Names can also begin with $ and _ (but we will not use it in this tutorial).
- Names are case sensitive (y and Y are different variables).
- Reserved words (like JavaScript keywords) cannot be used as names.
JavaScript identifiers are case-sensitive.
The Assignment Operator
In JavaScript, the equal sign ( = ) is an "assignment" operator, not an "equal to" operator.
This is different from algebra. The following does not make sense in algebra:
In JavaScript, however, it makes perfect sense: it assigns the value of x + 5 to x.
(It calculates the value of x + 5 and puts the result into x. The value of x is incremented by 5.)
The "equal to" operator is written like == in JavaScript.
JavaScript Data Types
JavaScript variables can hold numbers like 100 and text values like "John Doe".
In programming, text values are called text strings.
JavaScript can handle many types of data, but for now, just think of numbers and strings.
Strings are written inside double or single quotes. Numbers are written without quotes.
If you put a number in quotes, it will be treated as a text string.
Declaring a JavaScript Variable
Creating a variable in JavaScript is called "declaring" a variable.
You declare a JavaScript variable with the var or the let keyword:
After the declaration, the variable has no value (technically it is undefined ).
To assign a value to the variable, use the equal sign:
You can also assign a value to the variable when you declare it:
In the example below, we create a variable called carName and assign the value "Volvo" to it.
Then we "output" the value inside an HTML paragraph with id="demo":
It's a good programming practice to declare all variables at the beginning of a script.
One Statement, Many Variables
You can declare many variables in one statement.
Start the statement with let and separate the variables by comma :
A declaration can span multiple lines:
Value = undefined
In computer programs, variables are often declared without a value. The value can be something that has to be calculated, or something that will be provided later, like user input.
A variable declared without a value will have the value undefined .
The variable carName will have the value undefined after the execution of this statement:
Re-Declaring JavaScript Variables
If you re-declare a JavaScript variable declared with var , it will not lose its value.
The variable carName will still have the value "Volvo" after the execution of these statements:
You cannot re-declare a variable declared with let or const .
This will not work:
JavaScript Arithmetic
As with algebra, you can do arithmetic with JavaScript variables, using operators like = and + :
You can also add strings, but strings will be concatenated:
Also try this:
If you put a number in quotes, the rest of the numbers will be treated as strings, and concatenated.
Now try this:
JavaScript Dollar Sign $
Since JavaScript treats a dollar sign as a letter, identifiers containing $ are valid variable names:
Using the dollar sign is not very common in JavaScript, but professional programmers often use it as an alias for the main function in a JavaScript library.
In the JavaScript library jQuery, for instance, the main function $ is used to select HTML elements. In jQuery $("p"); means "select all p elements".
JavaScript Underscore (_)
Since JavaScript treats underscore as a letter, identifiers containing _ are valid variable names:
Using the underscore is not very common in JavaScript, but a convention among professional programmers is to use it as an alias for "private (hidden)" variables.
Test Yourself With Exercises
Create a variable called carName and assign the value Volvo to it.
Start the Exercise

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- DSA with JS - Self Paced
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
JavaScript Logical AND assignment (&&=) Operator
This operator is represented by x &&= y, and it is called the logical AND assignment operator. It assigns the value of y into x only if x is a truthy value.
We use this operator x &&= y like this. Now break this expression into two parts, x && (x = y) . If the value of x is true, then the statement (x = y) executes, and the value of y gets stored into x but if the value of x is a falsy value then the statement (x = y) does not get executed.
is equivalent to
Example: This example shows the basic use of the Javascript Logical AND assignment(&&=) operator.
Example 2: This example shows the basic use of the Javascript Logical AND assignment(&&=) operator.
.png)
Javascript Logical AND assignment(&&=) operator
We have a complete list of Javascript Operators, to check those please go through the Javascript Operators Complete Reference article.
Supported Browsers:

Similar Reads
- Web Technologies
- javascript-operators
- JavaScript-Questions
Please Login to comment...
- How to Watch NFL on NFL+ in 2024: A Complete Guide
- Best Smartwatches in 2024: Top Picks for Every Need
- Top Budgeting Apps in 2024
- 10 Best Parental Control App in 2024
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
The Earthquake Event Page application supports most recent browsers, view supported browsers . Or, try our Real-time Notifications, Feeds, and Web Services .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Remember language
Logical AND assignment (&&=)
The logical AND assignment ( &&= ) operator only evaluates the right operand and assigns to the left if the left operand is truthy .
Description
Logical AND assignment short-circuits , meaning that x &&= y is equivalent to x && (x = y) , except that the expression x is only evaluated once.
No assignment is performed if the left-hand side is not truthy, due to short-circuiting of the logical AND operator. For example, the following does not throw an error, despite x being const :
Neither would the following trigger the setter:
In fact, if x is not truthy, y is not evaluated at all.
Using logical AND assignment
Specifications.
| Specification |
|---|
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
- Logical AND ( && )
- Nullish coalescing operator ( ?? )
- Bitwise AND assignment ( &= )
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
IF statement as assignment expression in JavaScript
The JSLint Error Explanations document ( https://jslinterrors.com/unexpected-assignment-expression ) says that if we evaluate an assignment expression (x = 0) the IF body will never be executed (y = 1).
"The body of the if statement will not be executed because the assignment expression results in undefined which is falsy."
But I could prove the opposite in if (x = 1) { y = 1; } . Is it a matter of JS version?
In fact I made a mistake assuming that is possible to use the result of an assignment as a test value. What I really could prove in the console was the assignment returning a value, as in x = 1 outputting 1.
- 1 Yes, this is wrong. This assignment expression does not result in undefined. Consider leaving a comment on that page. )) – georg Commented Dec 16, 2014 at 17:25
- 2 LOL, we both commented on the article. :-) – T.J. Crowder Commented Dec 16, 2014 at 17:56
That article excerpt is both correct and incorrect. It's correct that the body of the if will not be entered with if (x = 0) , but it's incorrect when it says why.
The incorrect part is highlighted:
Instead of checking whether the variable x has the value 0 the example above will assign the value 0 to x . The body of the if statement will not be executed because the assignment expression results in undefined which is falsy (sic) .
That's just plain wrong. The result of an assignment expression is the value that was assigned, not undefined , so if (x = 0) won't enter the body of the if (because 0 is falsey), but if (x = 1) will (because 1 is truthy).
Is it a matter of JS version?
No, it's always been this way. Someone just got it wrong in those docs.
In fact I made a mistake assuming that is possible to use the result of an assignment as a test value.
It wasn't a mistake, you can — and sometimes, you want to. This is fairly common, for instance:
That's also using the result of an assignment as a test. Sometimes people even write it like this:
...although I never do, because it's just too easy to see that as an == and mess something up.
Note that it's very, very rare to want to assign to a variable within an if statement. It does happen, but it's really rare, and most style guides will suggest you break up the assignment and the branch.
Almost always, when you see if (x = 0) , what the author meant to write was if (x == 0) or if (x === 0) . That is, they meant to test the value of x , not assign a new value to x .
Example of what the JSLint docs mean about assigning zero:
var x; snippet.log("first test: using 0"); if (x = 0) { snippet.log("entered if body"); } else { snippet.log("entered else body"); } snippet.log("second test: using 1"); if (x = 1) { snippet.log("entered if body"); } else { snippet.log("entered else body"); } <!-- Script provides the `snippet` object, see http://meta.stackexchange.com/a/242144/134069 --> <script src="http://tjcrowder.github.io/simple-snippets-console/snippet.js"></script>
- 1 @Crowder, you got the point and your answer was very clarifying! Thanks! – Igor de Lorenzi Commented Dec 16, 2014 at 17:37
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged javascript or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Masked self-attention: How LLMs learn relationships between tokens
- Deedy Das: from coding at Meta, to search at Google, to investing with Anthropic
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
- Feedback Requested: How do you use the tagged questions page?
Hot Network Questions
- Why are METAR issued at 53 minutes of the hour?
- Choosing MCU for motor control
- Information about novel 'heavy weapons'
- Is my TOTP key secure on a free hosting provider server with FTP and .htaccess restrictions?
- In big band horn parts, should I write double flats (sharps) or the enharmonic equivalent?
- Does copying files from one drive to another also copy previously deleted data from the drive one?
- What is the role of this suffix for an opamp?
- Score the science points in 7 Wonders
- Does history possess the epistemological tools to establish the occurrence of an anomaly in the past that defies current scientific models?
- Will a Palm tree in Mars be approximately 2.5 times taller than the same tree on Earth?
- Used car dealership refused to let me use my OBDII on their car, is this a red flag?
- Is this a proof for energy conservation?
- Find the side lengths of a right triangle in terms of the distances of a point from its vertices,
- Lilypond Orchestral score: how to show duplicated tempo marking for violins?
- In a shell script, how do i wait for a volume to be available?
- Converting a set of reactions represented by strings separated by spaces to a list of similar strings
- Do pilots have to produce their pilot license to police when asked?
- Table Decimal Alignment using siunitx package
- Does Artifact negate Blasphemy's "Die next turn" effect?
- Switch or switches in the context of trains in American English? Is my assumption correct?
- Is it possible that the roots of a biquadratic equation will be in A.P. , G.P. , H.P.?
- is it correct to say "can you stop clinking the cup of coffee"?
- God the Father punished the Son as sin-bearer: how does that prove God’s righteousness?
- Where is this NPC's voice coming from?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is made to assign a default value, in this case the value of y, if the x variable is falsy. The boolean operators in JavaScript can return an operand, and not always a boolean result as in other languages. The Logical OR operator (||) returns the value of its second operand, if the first one is falsy, otherwise the value of the first ...
The logical OR assignment (||=) operator only evaluates the right operand and assigns to the left if the left operand is falsy. Logical OR assignment short-circuits, meaning that x ||= y is equivalent to x || (x = y), except that the expression x is only evaluated once. No assignment is performed if the left-hand side is not falsy, due to short ...
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.
Basically, the Logical AND operator (&&), will return the value of the second operand if the first is truthy, and it will return the value of the first operand if it is by itself falsy, for example: true && "foo"; // "foo" NaN && "anything"; // NaN 0 && "anything"; // 0. Note that falsy values are those that coerce to false when used in boolean ...
This chapter describes JavaScript's expressions and operators, including assignment, comparison, arithmetic, bitwise, logical, string, ternary and more. At a high level, an expression is a valid unit of code that resolves to a value. There are two types of expressions: those that have side effects (such as assigning values) and those that ...
The logical OR assignment operator (||=) accepts two operands and assigns the right operand to the left operand if the left operand is falsy: In this syntax, the ||= operator only assigns y to x if x is falsy. For example: console.log(title); Code language: JavaScript (javascript) Output: In this example, the title variable is undefined ...
The JavaScript OR assignment operator is represented with two pipe '|' symbols. This can be used to achieve the same effect as the above two code snippets. The value of the 'result' variable will be assigned to the value of 'a' if it is defined or not null otherwise it will be assigned to the value of 'b'. var result = a || b; The OR assignment ...
The assignment (=) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. ... JavaScript does not have implicit or undeclared variables. It just conflates the global object with the global scope and allows omitting the global object qualifier during property creation.
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different assignment operators in javascript and how to use them in javascript. Assignment Operators. In javascript, there are 16 different assignment operators that are used to assign value to the variable. It is shorthand of other operators which is recommended to use.
JavaScript operators are special symbols that perform operations on one or more operands (values). In this tutorial, you will learn about JavaScript operators with the help of examples. ... JavaScript Assignment Operators. We use assignment operators to assign values to variables. For example, let x = 5; Here, we used the = operator to assign ...
An assignment operator (=) assigns a value to a variable. The syntax of the assignment operator is as follows: let a = b; Code language: JavaScript (javascript) In this syntax, JavaScript evaluates the expression b first and assigns the result to the variable a. The following example declares the counter variable and initializes its value to zero:
JavaScript Exponentiation Assignment Operator in JavaScript is represented by "**=". This operator is used to raise the value of the variable to the power of the operand which is right. This can also be explained as the first variable is the power of the second operand. The exponentiation operator is equal to Math.pow(). Syntax: a **= b or a = a **
JavaScript Operators. Operators are used to assign values, compare values, perform arithmetic operations, and more. There are different types of JavaScript operators: Arithmetic Operators. Assignment Operators. Comparison Operators. Logical Operators. Conditional Operators. Type Operators.
Javascript operators are used to perform different types of mathematical and logical computations. Examples: The Assignment Operator = assigns values. The Addition Operator + adds values. The Multiplication Operator * multiplies values. The Comparison Operator > compares values
Here is an example: var a = 'quux'; a.foo = 'bar'; document.writeln(a.foo); This will output undefined: a holds a primitive value, which gets promoted to an object when assigning the property foo. But this new object is immediately discarded, so the value of foo is lost. Think of it like this: var a = 'quux';
In JavaScript, variable assignment refers to the process of assigning a value to a variable. For example, let x = 5; Here, we are assigning the value 5 to the variable x. On the other hand ...
The Assignment Operator. In JavaScript, the equal sign (=) is an "assignment" operator, not an "equal to" operator. This is different from algebra. The following does not make sense in algebra: x = x + 5 In JavaScript, however, it makes perfect sense: it assigns the value of x + 5 to x.
JavaScript Exponentiation Assignment Operator in JavaScript is represented by "**=". This operator is used to raise the value of the variable to the power of the operand which is right. This can also be explained as the first variable is the power of the second operand. The exponentiation operator is equal to Math.pow(). Syntax: a **= b or a = a **
Reference: JavaScript Tutorial: Comparison Operators. The == operator will compare for equality after doing any necessary type conversions. The === operator will not do the conversion, so if two values are not the same type === will simply return false. Both are equally quick.
The Earthquake Event Page application supports most recent browsers, view supported browsers.Or, try our Real-time Notifications, Feeds, and Web Services.Real-time Notifications, Feeds, and Web Services.
The logical AND assignment (&&=) operator only evaluates the right operand and assigns to the left if the left operand is truthy. Logical AND assignment short-circuits, meaning that x &&= y is equivalent to x && (x = y), except that the expression x is only evaluated once. No assignment is performed if the left-hand side is not truthy, due to ...
In fact I made a mistake assuming that is possible to use the result of an assignment as a test value. It wasn't a mistake, you can — and sometimes, you want to. This is fairly common, for instance: while ((thing = getMeTheNextThing()) != null) { // ...do something with `thing` } That's also using the result of an assignment as a test.