Assessment by Case Studies and Scenarios
Case studies depict real-life situations in which problems need to be solved. Scenario-based teaching may be similar to case studies, or may be oriented toward developing communication or teamwork skills. Both case studies and scenarios are commonly used methods of problem-based learning. Typically, using these methods, teachers aim to develop student reasoning, problem-solving and decision-making skills. Case studies differ from role plays in that in the former, learning takes place largely through discussion and analysis, whereas in the latter, students assume a character or role and "act out" what that character would do in the scenario (The Teaching Gateway page Assessing with Role Plays and Simulations contains more information on using role plays for assessments.) Like role plays and simulations, case studies and scenarios aim for authenticity: allowing students to get a sense of the situations they might face in the real world upon graduation. Students can see how their learning and skills can be applied in a real-world situation, without the pressure of being actually involved in that situation with the associated constraints on research, discussion and reflection time.
Case studies and scenarios are particularly useful when they present situations are complex and solutions are uncertain. Ideally, their complexity requires group members to draw from and share their experiences, work together, and learn by doing to understand and help solve the case-study problem.
You can present a single case to several groups in a class and require each group to offer its solutions, or you can give a different case to each group or individual.
Case studies' effectiveness comes from their abiliity to:
- engage students in research and reflective discussion
- encourage clinical and professional reasoning in a safe environment
- encourage higher-order thinking
- facilitate creative problem solving and the application of different problem-solving theories without risk to third parties or projects
- allow students to develop realistic solutions to complex problems
- develop students' ability to identify and distinguish between critical and extraneous factors
- enable students to apply previously acquired skills
- allow students to learn from one another
- provide an effective simulated learning environment
- encourage practical reasoning
- allow you to assess individuals or teams.
You can use case studies to bridge the gap between teacher-centred lectures and pure problem-based learning. They leave room for you to guide students directly, while the scenarios themselves suggest how students should operate, and provide parameters for their work.
Although some students have reported greater satisfaction with simulations as learning tools than with case studies (Maamari & El-Nakla, 2023), case studies generally require less up-front preparation time, and can be less intimidating for students.
To make case studies an effective form of assessment, instructors and tutors need to be familiar with their use in both teaching and assessment. This applies whether teachers are developing the case studies for their courses themselves or using those developed by others.
Case studies reach their highest effectiveness as a teaching and assessment tool when they are authentic; ensuring that case studies accurately reflect the circumstances in which a student will eventually be practising professionally can require a considerable amount of research, as well as the potential involvement of industry professionals.
Students may need scaffolding as they learn how to problem-solve in the context of case studies; using case studies as low-stakes, formative assessments can prepare them for summative assessment by case study at the end of the course.
Learning outcomes, course outlines, and marking rubrics need to be entirely clear about how case studies will be used in the course and how students will be expected to demonstrate their learning through thee way they analyse and problem-solve in the context of case studies.

Assessment preparation
Typically, the product assessed after case study or scenario work is a verbal presentation or a written submission. Decide who will take part in the assessment: the tutor, an industry specialist, a panel, peer groups or students themselves by self-evaluation? Choose whether to give a class or group mark or to assess individual performance; and whether to assess the product yourself or have it assessed by peers.
Assessment strategies
You can assess students’ interaction with other members of a group by asking open-ended questions, and setting tasks that require teamwork and sharing resources.
Assess the process of analysis
Case studies allow you to assess a student’s demonstration of deeper understanding and cognitive skills as they address the case. These skills include, for example:
- identification of a problem
- hypotheses generation
- construction of an enquiry plan
- interpretation of findings
- investigation of results collected for evidence to refine a hypothesis and construction of a management plan.
During the problem-solving process, you can also observe and evaluate:
- quality of research
- structural issues in written material
- organisation of arguments
- feasibility of solutions presented
- intra-group dynamics
- evidence of consideration of all case factors
- multiple resolutions of the same scenario issue.
Use a variety of questions in case analysis
The Questioning page discusses in detail various ways to use questions in teaching . If your students are using the Harvard Business School case study method for their analysis, use a range of question types to enable the class to move through the stages of analysis:
- clarification/information seeking ( What? )
- analysis/diagnosis ( Why? )
- conclusion/recommendation ( What now? )
- implementation ( How? ) and
- application/reflection ( So what? What does it mean to you?)
Use technology
Learning-management systems such as Moodle can help you track contributions to case discussions . You can assess students' interactions with other members of a group by viewing their responses to open-ended questions or observing their teamwork and sharing of resources as part of the discussion. You can incorporate the use of various tools in these systems, or others such as Survey Monkey, into students' assessment of their peers, or of their group members' contribution to exploring and presenting case studies. You can also set this peer assessment up so that it takes place anonymously.
Assessing by Case Studies: UNSW examples
These videos show examples of how UNSW faculty have implemented case studies in their own courses.
- Boston University. Using Case Studies to Teach
- Columbia University. Case Method Teaching and Learning
- Science Education Resource Center, Carleton College. Starting Point: What is Investigative Case-Based Learning?
Maamari, B. E., & El-Nakla, D. (2023). From case studies to experiential learning. Is simulation an effective tool for student assessment? Arab Economic and Business Journal, 15(1), Article 2. https://doi.org/10.38039/2214-4625.1023
Merret, C. (2020). Using case studies and build projects as authentic assessments in cornerstone courses. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education , 50 (1), 20-50. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306419020913286
Porzecanski, A. L., Bravo, A., Groom, M. J., Dávalos, L. M., Bynum, N., Abraham, B. J., Cigliano, J. A., Griffiths, C., Stokes, D. L., Cawthorn, M., Fernandez, D. S., Freeman, L., Leslie, T., Theodose, T., Vogler, D., & Sterling, E. J. (2021). Using case studies to improve the critical thinking skills of undergraduate conservation biology students. Case Studies in the Environment , 5 (1), 1536396. https://doi.org/10.1525/cse.2021.1536396
- Teaching for learning
- Assessment Toolkit
- Digital Assessment at UNSW
- Designing Assessment
- Selecting Assessment Methods
- Selecting Assessment Technologies
- Oral Assessment
- Capstone Project
- Case Studies & Scenarios
- Oral Presentations
- Role Play & Simulation
- Competency Assessment and Grading
- Grading & Giving Feedback
- Reviewing Assessment Quality
- Spotlight on Assessment
- Assessment Development Framework
- Teaching Settings
Events & news
- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Situational Judgement
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Watson Glaser Critical thinking
- Deductive reasoning
- Abstract reasoning
- Spatial reasoning
- Error checking
- Verbal comprehension
- Reading comprehension
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Psychometric tests
- Personality test
- In-Tray exercise
- E-Tray exercise
- Competency based assessment
- Game based assessments
- Analysis exercise
- Group exercise
- Presentation exercise
- Video interview
- Strengths based assessment
- Strengths based interviews
- Saville Assessment
- Talent Q / Korn Ferry
- Watson Glaser
- Criterion Partnership
- Test Partnership
- Cut-e / Aon
- Team Focus PFS
- Sova Assessment
Chapter 6: Case Study Exercises

A resource guide to help you master case study exercises
Page contents:
What is a case study exercise, how to answer a case study exercise, what skills does a case-study exercise assess, what questions will be asked in a case study exercise, case study exercise tips to succeed, key takeaways.
Case-study exercises are a very popular part of an assessment centre. But don't worry, with a bit of preparation and understanding, you can ace this part of the assessment.
Case study exercises are a popular tool used by employers to evaluate candidates' problem-solving skills, analytical thinking, and decision-making abilities. These exercises can be in the form of a written report, a presentation, or a group discussion, and typically involve a hypothetical business problem that requires a solution.
The case study presents the candidate with a series of fictional documents such as company reports, a consultant’s report, results from new product research etc. (i.e. similar to the in-tray exercise except these documents will be longer). You will then be asked to make business decisions based on the information. This can be done as an individual exercise, or more likely done in a group discussion so that assessors can also score your teamworking ability.
Before you start the exercise, it's important to carefully read and understand the instructions. Make sure you know what you're being asked to do, what resources you have available to you, and how your performance will be assessed. If you're unsure about anything, don't be afraid to ask for clarification.
Once you've read the case study, it's time to start analysing the problem. This involves breaking down the problem into its component parts, identifying the key issues, and considering different options for addressing them. It's important to approach the problem from different angles and to consider the implications of each possible solution.
During the exercise, you'll need to demonstrate your ability to work well under pressure, to think on your feet, and to communicate your ideas effectively. Make sure to use clear and concise language, and to back up your arguments with evidence and examples.
If you're working on a group case study exercise, it's important to listen to the ideas of others and to contribute your own ideas in a constructive and respectful way. Remember that the assessors are not only evaluating your individual performance but also how well you work as part of a team.
When it comes to presenting your solution, make sure to structure your presentation in a clear and logical way. Start with an introduction that sets out the problem and your approach, then move onto your analysis and recommendations, and finish with a conclusion that summarizes your key points. Make sure to keep to time and to engage your audience with your presentation.
A case study exercise is designed to assess several core competencies that are critical for success in the role you are applying for. There will be many common competencies that will be valuable across most roles in the professional world, these competencies typically include:
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and analyse problems, and to develop and implement effective solutions.
- Analytical Thinking: The capacity to break down complex information into smaller parts, evaluate it systematically, and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Decision-Making Abilities: The ability to make well-informed and timely decisions, considering all relevant information and potential outcomes.
- Communication Skills: The capacity to convey ideas clearly and concisely, and to listen actively to others.
- Teamwork Skills: The ability to collaborate effectively with others, and to work towards a shared goal.
- Time Management: The capacity to prioritise tasks and to manage time effectively, while maintaining quality and meeting deadlines.
By assessing these competencies, employers can gain valuable insights into how candidates approach problems, how they think critically, and how they work with others to achieve goals. Ultimately, the aim is to identify candidates who can add value to the organisation, and who have the potential to become successful and productive members of the team.
Different companies will prioritise certain competencies; the original job description is a great place to look for finding out what competencies the employer desires and so will likely be scoring you against during the assessment centre activities.
The type of questions that may be asked can vary, but here are some examples of the most common types:
- Analytical Questions: These questions require the candidate to analyse a set of data or information and draw conclusions based on their findings. For example: "You have been given a dataset on customer behaviour. What insights can you draw from the data to improve sales performance?"
- Decision-Making Questions: These questions ask the candidate to make a decision based on a given scenario. For example: "You are the CEO of a company that is considering a merger. What factors would you consider when making the decision to proceed with the merger?"
- Group Discussion Questions: In a group case study exercise, candidates may be asked to work together to analyse a problem and present their findings to the assessors. For example: "As a team, analyse the strengths and weaknesses of our company's current marketing strategy and recommend improvements."
The questions are designed to test the candidate's problem-solving, analytical thinking, decision-making, and communication skills. It's important to carefully read and understand the questions, and to provide well-reasoned and evidence-based responses.
It has been known for employers to use real live projects for the case study exercise with sensitive information swapped for fictional examples.
Information from the case study exercise lends itself to be used as scene-setting for other exercises at the assessment centre. It is common to have the same fictional setting running through the assessment centre, to save time on having to describe a new scenario for each task. You will be told in each exercise if you are expected to remember the information from a previous exercise, but this is rarely the case. Usually the only information common to multiple exercises is the fictional scenario; all data to be used in each exercise will be part of that exercise.
Start practising quality tests with a free account
Practice makes perfect
- Learn from detailed solutions
- Track your progress
Here are some key tips to help you prepare for and successfully pass a case study exercise at an assessment centre:
- Understand the Brief: Carefully read and analyse the case study brief, making sure you understand the problem or scenario being presented, and the information and data provided. Take notes and identify key issues and opportunities.
- Plan Your Approach: Take some time to plan your approach to the case study exercise. Consider the key challenges and opportunities, and identify potential solutions and recommendations. This will help you structure your thoughts and prioritise your ideas.
- Use Evidence: Use evidence from the case study, as well as your own research and knowledge, to support your ideas and recommendations. This will demonstrate your analytical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Stay Focused: During the exercise, stay focused on the task at hand and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information or details. Keep the objective of the exercise in mind, and stay on track with your analysis and recommendations.
- Collaborate Effectively: If the case study exercise involves group work, make sure to communicate clearly and effectively with your team members. Listen actively to their ideas, and contribute constructively to the discussion.
- Be Confident: Have confidence in your ideas and recommendations, and be prepared to defend your positions if challenged. Speak clearly and confidently, and use evidence and data to support your arguments.
Here is the summary of what case-study exercises are and how to pass them:
- A case study exercise is a type of assessment where candidates are presented with a hypothetical business scenario and asked to provide solutions or recommendations.
- These exercises assess a range of competencies such as problem-solving, analytical thinking, decision-making, communication, teamwork, and time management.
- To pass a case study exercise, it's important to carefully read and understand the brief, plan your approach, use evidence to support your ideas, stay focused, collaborate effectively, be confident, and manage your time effectively.
Fully understanding the format of the exercise, taking practice case-study exercises and following our tips outlined above will drastically improve the chances of you standing out as a star candidate at the assessment centre.

Why Do Employers Use Case Studies at Assessment Centers?
What to expect from a case study exercise, how to prepare for the case study exercise in 2024, how to approach a group exercise, how to approach a presentation, case study exercises at assessment centers (2024 guide).
Updated November 21, 2023

Should you be invited to be tested at an assessment center as part of an employer's recruitment process, one of the exercises you may face is a case study .
A case study exercise presents you with a scenario similar to what you would experience in the job you have applied for.
It will generally be accompanied by documents, emails or other forms of information.
You are asked to make business decisions based on the data you have been provided with, either alone or as part of a group of candidates.
A case study enables employers to assess your skill-base and likely performance in the job, providing them with a more rounded view of the type of employee you would be and the value you would bring to the company.
Commonly used in the finance, banking, legal and business management industries, the main advantage to employers of using case study exercises is to see candidates in action, demonstrating the skills they would be expected to use at work.
The skills assessed when participating in a case study exercise will vary depending on the employer, the industry and the job applied for, but may include:
- Analytical skills
- Strategic thinking
- Decision making
- Problem-solving
- Communication
- Stress tolerance
- The ability to assimilate information quickly and effectively
- Organisational skills
- Situational judgment
- Commercial awareness
- Time management
- Team working
- Knowledge pertinent to the industry or job, for example, marketing skills
Despite the skills that the employer is actively assessing, such as those mentioned above, success in a case study exercise relies on your ability to:
- Interpret and analyze the information provided
- Reach a decision
- Use commercial awareness
- Manage your time
- Communicate well
Practice Case Study Exercises with JobTestPrep
There are generally two types of case study exercise that you may face as part of a selection process:
- Subject-related case studies pertinent to the job you are applying for and the related industry
- General case studies that assess your overall aptitude and skills
The actual scenario of the case study exercise you face will vary, but examples of typical case studies include:
- Expanding a team or department
- Deciding whether an acquisition or merger is advisable
- Investigating whether to begin a new product line
- Re-organisation of management structure
- The creation of an advertising campaign
- Responding to negative publicity
- Choosing from three business proposals
- Developing a social media presence
Prepare for Case Study Exercises with JobTestPrep
For example: You are presented with the scenario of an IT company that went through an expensive re-brand one year ago. At that time, the company moved to bigger premises in a better area, and two new teams of developers were recruited to work with two new clients. The IT company has recently lost one of those clients and is facing increasing costs as the rent is raised for their premises. The company's directors have concluded that they must make one of the following changes: Make staff redundancies and offer the chance to several employees to change to part-time hours Move to less expensive premises in a less desirable area Combine a move to a flexible working business model where employees work part of the week from home and desk-share in the office along with a physical move to smaller premises in the same area where the IT company is currently based
You are asked to advise the directors on which change would provide the greatest benefit.
Here is another example:
A multi-national environmental testing organization buys out an oil-testing laboratory. A gap test is carried out on whether: The oil-testing lab should be brought in line with the rest of the organization concerning its processes, customer interface, and testing procedures The oil-testing lab should be closed down and its clients absorbed into the rest of the organization The oil-testing lab should be allowed to continue as it is, but new processes put in place between it and the larger organization
You are asked to consider the findings of the gap test and suggest the best course of action.
Just as you would prepare before a job interview, it is always in your best interests to prepare before facing a case study exercise at an assessment center.
Step 1 . Do the Research
There is a whole range of research you can look into to prepare yourself for the case study exercise:
- The job description and any other literature or documents forwarded to you
- The employer's website and social media
- Industry related news stories and developments
Any of the above should provide you with a better understanding of the job you have applied for, the industry you will work within, and the culture and values of the employer.
Step 2 . Use Practice Case Studies
Practicing case study exercises in the run-up to the assessment day is one of the best ways you can prepare for the real thing.
Unless the employer provides sample case studies on their website or as part of their recruitment pack, you will not know the exact format that the exercise will take; however, you can build familiarity with the overall process of a case study through practice.
You can find plenty of practice case study exercises online. Most of these come at a cost, but you may also be able to find free sample case studies too.
For case study resources at a cost, have a look at JobTestPrep .
For two free sample case study exercises, you might like to visit Bain & Company's website .
Scroll down to the Associate Consultant Case Library. Europa also offers an extensive and detailed sample case study .
Step 3 . Timed Practice
Once you have sourced one or more practice case studies, take the opportunity to practice to a time limit.
The case study may come with a time limit, or the employer may have already told you how long you will have to complete the real case study exercise on the day.
Alternatively, set your reasonable time limit.
Timed practice will improve your response time and explain exactly how much time you should allocate to each stage of the case study process.
Step 4 . Improve Your Reading Comprehension
One skill that is key to handle a case study exercise successfully is your reading comprehension, that is, your ability to understand written information, interpret it and describe it in your own words.
In the context of a case study, this skill will help you to assimilate the information provided to you quickly, analyze it and ultimately reach a decision.
In the run-up to your assessment day, put aside time to improve your reading comprehension by reading a wide variety of material and picking out the key points of each passage.
You might find it especially helpful to read professional journals and news articles related to the job you have applied for and the related industry.
Try to improve the speed at which you can read but still retain information too. This will prove helpful during the real case study exercise.
Step 5 . Practice Mental Math
The case study exercise may include prices, area measurements, staff numbers, salaries and other numeric values.
It is important that you can complete basic mental math calculations, such as multiplication and percentages.
Practice your mental math using puzzle books, online math resources and math problems that you create yourself.
You can find plenty of online business math resources, for example:
- The University of Alabama at Birmingham Math and Business Guide
- Money Instructor
- Open Textbook Library
If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from JobTestPrep . You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
Get a Premium Package Now

Top Tips for Approaching Case Study Exercises
Now that you have prepared yourself, you can further improve your chances of a successful outcome by following our top tips on approaching case study exercises on the day.
Read the Information Carefully
Read all of the information provided as part of your case study exercise to understand what is being asked of you fully.
Quickly identify the key points in the task and the overall decision you have been asked to make, for example:
- Has the exercise provided you with a choice of outcomes you must decide between, or must you create the outcome yourself?
- What information do you need to make your decision?
- Are there calculations involved in the task?
- What character are you playing in the task (for example, HR manager or business consultant) and what are that character's motivations?
- Who is your character presenting their response to? Company directors, client or HR department?
Prioritize the Information
Prioritize the information by importance.
Which pieces of information are most pertinent to the task, and what key data do they provide?
Can any of the information be dismissed? Does any of the information contradict or sit in conflict with others?
Divide Up the Tasks and Allocate Time
You will generally be asked to come to a conclusion or advise a course of action regarding your case study exercise; however, you may have to carry out several tasks to arrive at this result.
Once you have read through the information, plan out what tasks the exercise will entail and allocate time for each one.
Do Not Be Distracted by Finding the Only 'Right' Answer
Where you are provided with several outcomes, and you must decide on one, do not assume that anyone's outcome is the only right answer to give.
It may be that any of the outcomes could be correct if you can sufficiently support your decision from the information provided.
Keep the Objective in Focus
- What does the task ask you to do?
- Must you choose between three business acquisitions?
- Are you providing advice on whether or not to invest?
- Are you putting together a plan for a staff redundancy situation?
Keep the objective of the case study exercise in mind at all times.
Support Your Decision With Evidence
The conclusion you come to may seem obvious to you, but you must be able to support your decision with evidence.
Why would it be better for the company to invest in property overstock? What is the benefit to the company of entering a new market?
It is not sufficient to know which outcome would be the best. As in the real-life business world, you must be able to support your claims.
If you are assessed as part of a group, you must arrive at a conclusion as a team and bear in mind your strengths.
For example, do you have a good eye for detail and would therefore be suited to the analytical part of the task?
Arrive at a list of tasks together and then assign the tasks to different members of the group.
Please make sure you contribute to the group discussions but do not dominate them.
Group assessments are generally used by employers who place value on leadership, teamwork and communication skills.
If you are asked to present your findings or conclusion as part of a case study exercise, bear in mind to whom the task has asked you to make that presentation.
For example, a business client or a marketing manager.
Make sure that you can fully support the reasons that you came to your conclusion.
If you are presenting as a group, make sure that each group member has their role to play in the presentation and that everyone knows why the group came to that conclusion.
Act professionally to suit the job you have applied for. Be polite, confident and well-spoken.
Case study exercises are just one of the many methods that employers use to assess job applicants, and as with any other aspect of the selection process, they require a degree of consideration and preparation.
The best way to improve your chances of a successful outcome and reduce exam tension is to research the job and the industry, practice case study exercises and improve your skills.
You might also be interested in these other Psychometric Success articles:

Or explore the Aptitude Tests / Test Types sections.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Definition and Introduction
Case analysis is a problem-based teaching and learning method that involves critically analyzing complex scenarios within an organizational setting for the purpose of placing the student in a “real world” situation and applying reflection and critical thinking skills to contemplate appropriate solutions, decisions, or recommended courses of action. It is considered a more effective teaching technique than in-class role playing or simulation activities. The analytical process is often guided by questions provided by the instructor that ask students to contemplate relationships between the facts and critical incidents described in the case.
Cases generally include both descriptive and statistical elements and rely on students applying abductive reasoning to develop and argue for preferred or best outcomes [i.e., case scenarios rarely have a single correct or perfect answer based on the evidence provided]. Rather than emphasizing theories or concepts, case analysis assignments emphasize building a bridge of relevancy between abstract thinking and practical application and, by so doing, teaches the value of both within a specific area of professional practice.
Given this, the purpose of a case analysis paper is to present a structured and logically organized format for analyzing the case situation. It can be assigned to students individually or as a small group assignment and it may include an in-class presentation component. Case analysis is predominately taught in economics and business-related courses, but it is also a method of teaching and learning found in other applied social sciences disciplines, such as, social work, public relations, education, journalism, and public administration.
Ellet, William. The Case Study Handbook: A Student's Guide . Revised Edition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2018; Christoph Rasche and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Analysis . Writing Center, Baruch College; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
How to Approach Writing a Case Analysis Paper
The organization and structure of a case analysis paper can vary depending on the organizational setting, the situation, and how your professor wants you to approach the assignment. Nevertheless, preparing to write a case analysis paper involves several important steps. As Hawes notes, a case analysis assignment “...is useful in developing the ability to get to the heart of a problem, analyze it thoroughly, and to indicate the appropriate solution as well as how it should be implemented” [p.48]. This statement encapsulates how you should approach preparing to write a case analysis paper.
Before you begin to write your paper, consider the following analytical procedures:
- Review the case to get an overview of the situation . A case can be only a few pages in length, however, it is most often very lengthy and contains a significant amount of detailed background information and statistics, with multilayered descriptions of the scenario, the roles and behaviors of various stakeholder groups, and situational events. Therefore, a quick reading of the case will help you gain an overall sense of the situation and illuminate the types of issues and problems that you will need to address in your paper. If your professor has provided questions intended to help frame your analysis, use them to guide your initial reading of the case.
- Read the case thoroughly . After gaining a general overview of the case, carefully read the content again with the purpose of understanding key circumstances, events, and behaviors among stakeholder groups. Look for information or data that appears contradictory, extraneous, or misleading. At this point, you should be taking notes as you read because this will help you develop a general outline of your paper. The aim is to obtain a complete understanding of the situation so that you can begin contemplating tentative answers to any questions your professor has provided or, if they have not provided, developing answers to your own questions about the case scenario and its connection to the course readings,lectures, and class discussions.
- Determine key stakeholder groups, issues, and events and the relationships they all have to each other . As you analyze the content, pay particular attention to identifying individuals, groups, or organizations described in the case and identify evidence of any problems or issues of concern that impact the situation in a negative way. Other things to look for include identifying any assumptions being made by or about each stakeholder, potential biased explanations or actions, explicit demands or ultimatums , and the underlying concerns that motivate these behaviors among stakeholders. The goal at this stage is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the situational and behavioral dynamics of the case and the explicit and implicit consequences of each of these actions.
- Identify the core problems . The next step in most case analysis assignments is to discern what the core [i.e., most damaging, detrimental, injurious] problems are within the organizational setting and to determine their implications. The purpose at this stage of preparing to write your analysis paper is to distinguish between the symptoms of core problems and the core problems themselves and to decide which of these must be addressed immediately and which problems do not appear critical but may escalate over time. Identify evidence from the case to support your decisions by determining what information or data is essential to addressing the core problems and what information is not relevant or is misleading.
- Explore alternative solutions . As noted, case analysis scenarios rarely have only one correct answer. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind that the process of analyzing the case and diagnosing core problems, while based on evidence, is a subjective process open to various avenues of interpretation. This means that you must consider alternative solutions or courses of action by critically examining strengths and weaknesses, risk factors, and the differences between short and long-term solutions. For each possible solution or course of action, consider the consequences they may have related to their implementation and how these recommendations might lead to new problems. Also, consider thinking about your recommended solutions or courses of action in relation to issues of fairness, equity, and inclusion.
- Decide on a final set of recommendations . The last stage in preparing to write a case analysis paper is to assert an opinion or viewpoint about the recommendations needed to help resolve the core problems as you see them and to make a persuasive argument for supporting this point of view. Prepare a clear rationale for your recommendations based on examining each element of your analysis. Anticipate possible obstacles that could derail their implementation. Consider any counter-arguments that could be made concerning the validity of your recommended actions. Finally, describe a set of criteria and measurable indicators that could be applied to evaluating the effectiveness of your implementation plan.
Use these steps as the framework for writing your paper. Remember that the more detailed you are in taking notes as you critically examine each element of the case, the more information you will have to draw from when you begin to write. This will save you time.
NOTE : If the process of preparing to write a case analysis paper is assigned as a student group project, consider having each member of the group analyze a specific element of the case, including drafting answers to the corresponding questions used by your professor to frame the analysis. This will help make the analytical process more efficient and ensure that the distribution of work is equitable. This can also facilitate who is responsible for drafting each part of the final case analysis paper and, if applicable, the in-class presentation.
Framework for Case Analysis . College of Management. University of Massachusetts; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Rasche, Christoph and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Study Analysis . University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center; Van Ness, Raymond K. A Guide to Case Analysis . School of Business. State University of New York, Albany; Writing a Case Analysis . Business School, University of New South Wales.
Structure and Writing Style
A case analysis paper should be detailed, concise, persuasive, clearly written, and professional in tone and in the use of language . As with other forms of college-level academic writing, declarative statements that convey information, provide a fact, or offer an explanation or any recommended courses of action should be based on evidence. If allowed by your professor, any external sources used to support your analysis, such as course readings, should be properly cited under a list of references. The organization and structure of case analysis papers can vary depending on your professor’s preferred format, but its structure generally follows the steps used for analyzing the case.
Introduction
The introduction should provide a succinct but thorough descriptive overview of the main facts, issues, and core problems of the case . The introduction should also include a brief summary of the most relevant details about the situation and organizational setting. This includes defining the theoretical framework or conceptual model on which any questions were used to frame your analysis.
Following the rules of most college-level research papers, the introduction should then inform the reader how the paper will be organized. This includes describing the major sections of the paper and the order in which they will be presented. Unless you are told to do so by your professor, you do not need to preview your final recommendations in the introduction. U nlike most college-level research papers , the introduction does not include a statement about the significance of your findings because a case analysis assignment does not involve contributing new knowledge about a research problem.
Background Analysis
Background analysis can vary depending on any guiding questions provided by your professor and the underlying concept or theory that the case is based upon. In general, however, this section of your paper should focus on:
- Providing an overarching analysis of problems identified from the case scenario, including identifying events that stakeholders find challenging or troublesome,
- Identifying assumptions made by each stakeholder and any apparent biases they may exhibit,
- Describing any demands or claims made by or forced upon key stakeholders, and
- Highlighting any issues of concern or complaints expressed by stakeholders in response to those demands or claims.
These aspects of the case are often in the form of behavioral responses expressed by individuals or groups within the organizational setting. However, note that problems in a case situation can also be reflected in data [or the lack thereof] and in the decision-making, operational, cultural, or institutional structure of the organization. Additionally, demands or claims can be either internal and external to the organization [e.g., a case analysis involving a president considering arms sales to Saudi Arabia could include managing internal demands from White House advisors as well as demands from members of Congress].
Throughout this section, present all relevant evidence from the case that supports your analysis. Do not simply claim there is a problem, an assumption, a demand, or a concern; tell the reader what part of the case informed how you identified these background elements.
Identification of Problems
In most case analysis assignments, there are problems, and then there are problems . Each problem can reflect a multitude of underlying symptoms that are detrimental to the interests of the organization. The purpose of identifying problems is to teach students how to differentiate between problems that vary in severity, impact, and relative importance. Given this, problems can be described in three general forms: those that must be addressed immediately, those that should be addressed but the impact is not severe, and those that do not require immediate attention and can be set aside for the time being.
All of the problems you identify from the case should be identified in this section of your paper, with a description based on evidence explaining the problem variances. If the assignment asks you to conduct research to further support your assessment of the problems, include this in your explanation. Remember to cite those sources in a list of references. Use specific evidence from the case and apply appropriate concepts, theories, and models discussed in class or in relevant course readings to highlight and explain the key problems [or problem] that you believe must be solved immediately and describe the underlying symptoms and why they are so critical.
Alternative Solutions
This section is where you provide specific, realistic, and evidence-based solutions to the problems you have identified and make recommendations about how to alleviate the underlying symptomatic conditions impacting the organizational setting. For each solution, you must explain why it was chosen and provide clear evidence to support your reasoning. This can include, for example, course readings and class discussions as well as research resources, such as, books, journal articles, research reports, or government documents. In some cases, your professor may encourage you to include personal, anecdotal experiences as evidence to support why you chose a particular solution or set of solutions. Using anecdotal evidence helps promote reflective thinking about the process of determining what qualifies as a core problem and relevant solution .
Throughout this part of the paper, keep in mind the entire array of problems that must be addressed and describe in detail the solutions that might be implemented to resolve these problems.
Recommended Courses of Action
In some case analysis assignments, your professor may ask you to combine the alternative solutions section with your recommended courses of action. However, it is important to know the difference between the two. A solution refers to the answer to a problem. A course of action refers to a procedure or deliberate sequence of activities adopted to proactively confront a situation, often in the context of accomplishing a goal. In this context, proposed courses of action are based on your analysis of alternative solutions. Your description and justification for pursuing each course of action should represent the overall plan for implementing your recommendations.
For each course of action, you need to explain the rationale for your recommendation in a way that confronts challenges, explains risks, and anticipates any counter-arguments from stakeholders. Do this by considering the strengths and weaknesses of each course of action framed in relation to how the action is expected to resolve the core problems presented, the possible ways the action may affect remaining problems, and how the recommended action will be perceived by each stakeholder.
In addition, you should describe the criteria needed to measure how well the implementation of these actions is working and explain which individuals or groups are responsible for ensuring your recommendations are successful. In addition, always consider the law of unintended consequences. Outline difficulties that may arise in implementing each course of action and describe how implementing the proposed courses of action [either individually or collectively] may lead to new problems [both large and small].
Throughout this section, you must consider the costs and benefits of recommending your courses of action in relation to uncertainties or missing information and the negative consequences of success.
The conclusion should be brief and introspective. Unlike a research paper, the conclusion in a case analysis paper does not include a summary of key findings and their significance, a statement about how the study contributed to existing knowledge, or indicate opportunities for future research.
Begin by synthesizing the core problems presented in the case and the relevance of your recommended solutions. This can include an explanation of what you have learned about the case in the context of your answers to the questions provided by your professor. The conclusion is also where you link what you learned from analyzing the case with the course readings or class discussions. This can further demonstrate your understanding of the relationships between the practical case situation and the theoretical and abstract content of assigned readings and other course content.
Problems to Avoid
The literature on case analysis assignments often includes examples of difficulties students have with applying methods of critical analysis and effectively reporting the results of their assessment of the situation. A common reason cited by scholars is that the application of this type of teaching and learning method is limited to applied fields of social and behavioral sciences and, as a result, writing a case analysis paper can be unfamiliar to most students entering college.
After you have drafted your paper, proofread the narrative flow and revise any of these common errors:
- Unnecessary detail in the background section . The background section should highlight the essential elements of the case based on your analysis. Focus on summarizing the facts and highlighting the key factors that become relevant in the other sections of the paper by eliminating any unnecessary information.
- Analysis relies too much on opinion . Your analysis is interpretive, but the narrative must be connected clearly to evidence from the case and any models and theories discussed in class or in course readings. Any positions or arguments you make should be supported by evidence.
- Analysis does not focus on the most important elements of the case . Your paper should provide a thorough overview of the case. However, the analysis should focus on providing evidence about what you identify are the key events, stakeholders, issues, and problems. Emphasize what you identify as the most critical aspects of the case to be developed throughout your analysis. Be thorough but succinct.
- Writing is too descriptive . A paper with too much descriptive information detracts from your analysis of the complexities of the case situation. Questions about what happened, where, when, and by whom should only be included as essential information leading to your examination of questions related to why, how, and for what purpose.
- Inadequate definition of a core problem and associated symptoms . A common error found in case analysis papers is recommending a solution or course of action without adequately defining or demonstrating that you understand the problem. Make sure you have clearly described the problem and its impact and scope within the organizational setting. Ensure that you have adequately described the root causes w hen describing the symptoms of the problem.
- Recommendations lack specificity . Identify any use of vague statements and indeterminate terminology, such as, “A particular experience” or “a large increase to the budget.” These statements cannot be measured and, as a result, there is no way to evaluate their successful implementation. Provide specific data and use direct language in describing recommended actions.
- Unrealistic, exaggerated, or unattainable recommendations . Review your recommendations to ensure that they are based on the situational facts of the case. Your recommended solutions and courses of action must be based on realistic assumptions and fit within the constraints of the situation. Also note that the case scenario has already happened, therefore, any speculation or arguments about what could have occurred if the circumstances were different should be revised or eliminated.
Bee, Lian Song et al. "Business Students' Perspectives on Case Method Coaching for Problem-Based Learning: Impacts on Student Engagement and Learning Performance in Higher Education." Education & Training 64 (2022): 416-432; The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Georgallis, Panikos and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching using Case-Based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Georgallis, Panikos, and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching Using Case-based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; .Dean, Kathy Lund and Charles J. Fornaciari. "How to Create and Use Experiential Case-Based Exercises in a Management Classroom." Journal of Management Education 26 (October 2002): 586-603; Klebba, Joanne M. and Janet G. Hamilton. "Structured Case Analysis: Developing Critical Thinking Skills in a Marketing Case Course." Journal of Marketing Education 29 (August 2007): 132-137, 139; Klein, Norman. "The Case Discussion Method Revisited: Some Questions about Student Skills." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 30-32; Mukherjee, Arup. "Effective Use of In-Class Mini Case Analysis for Discovery Learning in an Undergraduate MIS Course." The Journal of Computer Information Systems 40 (Spring 2000): 15-23; Pessoa, Silviaet al. "Scaffolding the Case Analysis in an Organizational Behavior Course: Making Analytical Language Explicit." Journal of Management Education 46 (2022): 226-251: Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Schweitzer, Karen. "How to Write and Format a Business Case Study." ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-write-and-format-a-business-case-study-466324 (accessed December 5, 2022); Reddy, C. D. "Teaching Research Methodology: Everything's a Case." Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 18 (December 2020): 178-188; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
Writing Tip
Ca se Study and Case Analysis Are Not the Same!
Confusion often exists between what it means to write a paper that uses a case study research design and writing a paper that analyzes a case; they are two different types of approaches to learning in the social and behavioral sciences. Professors as well as educational researchers contribute to this confusion because they often use the term "case study" when describing the subject of analysis for a case analysis paper. But you are not studying a case for the purpose of generating a comprehensive, multi-faceted understanding of a research problem. R ather, you are critically analyzing a specific scenario to argue logically for recommended solutions and courses of action that lead to optimal outcomes applicable to professional practice.
To avoid any confusion, here are twelve characteristics that delineate the differences between writing a paper using the case study research method and writing a case analysis paper:
- Case study is a method of in-depth research and rigorous inquiry ; case analysis is a reliable method of teaching and learning . A case study is a modality of research that investigates a phenomenon for the purpose of creating new knowledge, solving a problem, or testing a hypothesis using empirical evidence derived from the case being studied. Often, the results are used to generalize about a larger population or within a wider context. The writing adheres to the traditional standards of a scholarly research study. A case analysis is a pedagogical tool used to teach students how to reflect and think critically about a practical, real-life problem in an organizational setting.
- The researcher is responsible for identifying the case to study; a case analysis is assigned by your professor . As the researcher, you choose the case study to investigate in support of obtaining new knowledge and understanding about the research problem. The case in a case analysis assignment is almost always provided, and sometimes written, by your professor and either given to every student in class to analyze individually or to a small group of students, or students select a case to analyze from a predetermined list.
- A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined . A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study. The content of a case analysis is determined by your professor and its parameters are well-defined and limited to elucidating insights of practical value applied to practice.
- Case study is fact-based and describes actual events or situations; case analysis can be entirely fictional or adapted from an actual situation . The entire content of a case study must be grounded in reality to be a valid subject of investigation in an empirical research study. A case analysis only needs to set the stage for critically examining a situation in practice and, therefore, can be entirely fictional or adapted, all or in-part, from an actual situation.
- Research using a case study method must adhere to principles of intellectual honesty and academic integrity; a case analysis scenario can include misleading or false information . A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy. A case analysis scenario may include misleading or false information intended to deliberately distract from the central issues of the case. The purpose is to teach students how to sort through conflicting or useless information in order to come up with the preferred solution. Any use of misleading or false information in academic research is considered unethical.
- Case study is linked to a research problem; case analysis is linked to a practical situation or scenario . In the social sciences, the subject of an investigation is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to generate new knowledge leading to a solution. Case analysis narratives are grounded in real life scenarios for the purpose of examining the realities of decision-making behavior and processes within organizational settings. A case analysis assignments include a problem or set of problems to be analyzed. However, the goal is centered around the act of identifying and evaluating courses of action leading to best possible outcomes.
- The purpose of a case study is to create new knowledge through research; the purpose of a case analysis is to teach new understanding . Case studies are a choice of methodological design intended to create new knowledge about resolving a research problem. A case analysis is a mode of teaching and learning intended to create new understanding and an awareness of uncertainty applied to practice through acts of critical thinking and reflection.
- A case study seeks to identify the best possible solution to a research problem; case analysis can have an indeterminate set of solutions or outcomes . Your role in studying a case is to discover the most logical, evidence-based ways to address a research problem. A case analysis assignment rarely has a single correct answer because one of the goals is to force students to confront the real life dynamics of uncertainly, ambiguity, and missing or conflicting information within professional practice. Under these conditions, a perfect outcome or solution almost never exists.
- Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis . The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem. For a case analysis assignment, your professor will often ask you to examine solutions or recommended courses of action based solely on facts and information from the case.
- Case study can be a person, place, object, issue, event, condition, or phenomenon; a case analysis is a carefully constructed synopsis of events, situations, and behaviors . The research problem dictates the type of case being studied and, therefore, the design can encompass almost anything tangible as long as it fulfills the objective of generating new knowledge and understanding. A case analysis is in the form of a narrative containing descriptions of facts, situations, processes, rules, and behaviors within a particular setting and under a specific set of circumstances.
- Case study can represent an open-ended subject of inquiry; a case analysis is a narrative about something that has happened in the past . A case study is not restricted by time and can encompass an event or issue with no temporal limit or end. For example, the current war in Ukraine can be used as a case study of how medical personnel help civilians during a large military conflict, even though circumstances around this event are still evolving. A case analysis can be used to elicit critical thinking about current or future situations in practice, but the case itself is a narrative about something finite and that has taken place in the past.
- Multiple case studies can be used in a research study; case analysis involves examining a single scenario . Case study research can use two or more cases to examine a problem, often for the purpose of conducting a comparative investigation intended to discover hidden relationships, document emerging trends, or determine variations among different examples. A case analysis assignment typically describes a stand-alone, self-contained situation and any comparisons among cases are conducted during in-class discussions and/or student presentations.
The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2017; Crowe, Sarah et al. “The Case Study Approach.” BMC Medical Research Methodology 11 (2011): doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-100; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Works
- Next: Writing a Case Study >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Free Interview Course

CASE STUDY ASSESSMENT PRACTICE SAMPLE CASE STUDY ASSESSMENTS!
(12 Case Studies and Fully-Worked Answers For All Job Roles!)
Trusted by 100,000s worldwide:
Why do I need to take a Case Study Assessment? When applying for a job after the initial application, or sometimes even before, the company you are applying to may ask you to sit a Case Study Assessment. This, in fact, is now a common way of assessing applicants’ logical thinking by creating a scenario based on the role and the industry to which you are applying. This is carried out to ensure that only the very best candidates make it through to the latter stages. This saves the organisation time and money and helps them to find the very best person for the job.
Case study assessments – initially started in the professional services industries – are commonly used by companies such as Deloitte, PWC, and KPMG. However, case study assessments are becoming ever more popular and are expanding into multiple industries, such as retail, manufacturing, healthcare, project management, and logistics.
Many employers now use Case Study Assessments to assess candidates for suitability for the position and the organisation, and we see this only growing further over the next few years.
ABOUT CASE STUDY ASSESSMENT TESTS
Case study assessments are used in a growing number of industries and professions. They are used to assess a candidate’s potential within a given role or industry. It will consist of a fictitious scenario in which the candidate will be required to analyse, answer questions and use logical reasoning skills to ascertain solutions to complex and challenging problems.
A case study assessment will focus on a specific situation and the candidate will take the role of a new employee, tasked with analysing the issues using presented background information, various tables, graphs and charts. The goal of the assessment is to use logic to understand the root cause of the various issues, and provide solutions & recommend a plan of action to prevent the same concerns moving forward.
DOWNLOAD THE CASE STUDY ASSESSMENT GUIDE NOW (CONTAINS 12 COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENTS WITH FULLY-WORKED SUGGESTED ANSWERS)

CASE STUDY ASSESSMENT PRACTICE SCENARIOS!
Case study assessments are designed to assess a candidate’s suitability for various roles. Each assessment will vary in subject and difficulty depending on the role which the candidate has applied for. Our case studies are expertly designed for all roles and industries to give you the edge!
For example, if you are applying for a role in a financial company as an administrator, you are likely to be assessed within a scenario which will focus on your attention to detail, analytical, numerical and assessing information skills.
What are Case Study Assessments?
What is the purpose of a case study assessment.
The purpose of a case study assessment is for a potential employer to simulate a candidate’s handling in a work-related scenario, which will be focussed on the role and the industry. Case study assessments are an accurate tool to ensure that any candidates passed through to the latter stages of the process are highly suitable candidates.
What is the best way to prepare for your Case Study Assessment?
In our experience, and having consulted many previous applicants, the most effective way to prepare is to undertake numerous sample case study assessments under timed conditions. By practising under timed conditions, it enables you to improve your scores dramatically and also simulates the actual test. When preparing for your case study assessment, follow these 3 simple steps:
STEP 1 : Obtain different examples of scenarios which simulate both the job and the industry you are applying to.
STEP 2 : Practice different sample case study assessments regularly before the real assessment.
STEP 3 : The most important step when preparing for your assessment is to make sure you practice case study assessments under strict timed conditions. During the real assessment, you will undoubtedly be nervous. By practising numerous example scenarios under timed conditions, it helps to increase your speed of working and competency levels.
Now INSTANTLY access all 12 Case Study Assessment scenarios including suggested solutions and answers.
Here's What People Are Saying...
(worldwide success stories from our YouTube community!)

1 week ago (edited)

Have an assessment centre tomorrow and praying i'll also get it.
Update: Got the job! Thank you!
2 months ago (edited)

I've got a online assessement with an investment bank coming up and would love to get the right list of questions for it 🙂
3 months ago (edited)

Thank you so much! I went today and got the job on the spot!
2 weeks ago

...they made me take a basic vocabulary and typing test...I fortunately got a call back the next day saying I got the job!
3 months ago

I have my test tomorrow...
UPDATE: I'm Hired♥️♥️ I am so happy 😊😊😊😊

Richard, After getting myself trained from your tutorials , I GOT THE BEST JOB IN AUSTRALIA 🙂 . I have to say that I cracked my assessment for a Big company because of your lessons. A big thanks to you ,God bless you.

...I'm so nervous! Hope these tips will help out :') UPDATE: I got the job!!! These tips were so helpful thank you!
6 days ago (edited)

I am sooooo NERVOUS! ...Fingers crossed 🤞🏾
UPDATE: I GOT THE JOB! 🥂🍾

Thanks to you I got the job. THANK YOU SO MUCH❤️
1 month ago

Thank u very much this helped me in my college entrance tests!

I just want to say thank you. I went to sit my test yesterday and I passed. I practiced ur test questions and it made me feel really confident!
GET INSTANT ACCESS TO 12 PRACTICE CASE STUDY ASSESSMENTS AND SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS!
FOR JUST £7.99
What you’ll get…
12 Case Study Assessments test questions designed to help you effectively prepare for your case study assessment!
Suggested solutions/answers to all of the scenarios to ensure you gain an advantage and pass.
In-depth and challenging scenarios designed to ensure you get the maximum benefit from each assessment.
Instant access to your product via a download link and can be used from any device.
All of the above for just £7.99.
Pass your Case Study Assessment today. Trusted by 10,000s of customers worldwide.

- 30-Day Money Back Guarantee
PLUS… BONUS In addition to the Case Study Assessment Pack, you will also receive the following BONUS:

Online Psychometric Test Training Course – FREE bonus access to our bestselling online psychometric training course, which contains over 30 powerful video modules to quickly get you assessment-ready (and they work for ANY assessment). This online course will instantly be free for you to access via a 30-day trial, thereafter, it is automatically renewed at just £27+vat per month. No minimum terms. Cancel anytime. Limited time offer.

30-DAY MONEYBACK GUARANTEE
We have eliminated all risk for you. All of our products and training resources are protected by our 30-day no questions asked money-back guarantee. Whatever the reason…or no reason at all…you can have a full refund if this resource isn’t right for you. So there is no risk.
Who has created the questions and answers to the test questions?
Richard McMunn is a former Fire Officer turned psychometric assessment coach who has over 20 years experience within the recruitment industry.
He is extremely passionate about helping people pass their assessments, and his success rate is unrivalled within the assessment training sector.
Still not convinced? Here’s why you should buy with How2Become.com…
Firstly, these practice questions and answers are created by us and our team of experts – we have all the most commonly used (and less common) practice questions industry assessors are using and we will help you succeed (like we’ve been doing for the last 17 years) and we update our material frequently.
Secondly, we provide exclusive bonuses with all our products that you won’t find anywhere else. These bonuses include free guides, powerful online training and more!
Thirdly, our testing preparation packages and training just work. Take a look at our customer reviews and feedback where our customers share their positive buying experiences and more importantly the time-saving success our resources have given them (hint: they passed their job assessments).
Finally, we have eliminated all risk for you. All of our products and resources are protected by our 30-day no questions asked money-back guarantee. Whatever the reason…or no reason at all…you can have a full refund if this training isn’t right for you. So there is no risk.
MORE TESTIMONIALS
Having helped 100,000s of candidates over the past 17 years, it is no wonder our community loves us…

*100,000+ relates to all How2Become resources designed to help people like you pass their recruitment processes being used worldwide.
- Free Aptitude Tests

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Campus Maps
- Faculties & Schools
Now searching for:
- Home
- Courses
- Subjects
- Assessment and Artificial Intelligence
- Design standards
- Methods
- Exams
- Online exams
- Interactive oral assessment
- Report
- Case study analysis or scenario-based questions
- Essay
- Newspaper article/editorial
- Literature review
- Student presentations
- Posters/infographics
- Portfolio
- Reflection
- Annotated bibliography
- OSCE/Online Practical Exam
- Viva voce
- Marking criteria and rubrics
- Review checklist
- Alterations
- Moderation
- Feedback
- Teaching
- Learning technology
- Professional learning
- Framework and policy
- Strategic projects
- About and contacts
- Help and resources
Case study analysis or scenario-based questions
Case studies and scenario-based assessments allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge to a real organisational issue.
They're powerful learning tools requiring learners to draw from their own experiences and skills to analyse and respond to a situation.
By using cased studies and scenarios, teachers aim to develop student reasoning, problem-solving and decision-making skills (Tunny, Papinczak & Young, 2010; Bloomfield & Magney, 2009).
They allow students to see how their learning can be applied in a real-world situation, without the real-world pressure and constraints.
When to use case studies or scenarios
Use case studies or scenarios to:
- assess reasoning and decision-making skills
- assess the application of knowledge and skills to a professional practice learning situation.
Case studies and scenarios are particularly useful where situations are complex and solutions are uncertain.
Advantages and limitations
- Limitations
- Requires learners to provide an original response.
- Focuses on the ability to use skills or knowledge to develop solutions to problems.
- Can assess significant content and a number of outcomes.
- Simulates real life situations.
- Can allow for group or individual approaches.
- application
- evaluation.
- Involves problem solving and decision making skills in authentic situations.
- Can require a large amount of instructor time to assess.
- Requires considerable time in developing the scope of the case study or the parameters of the cases that may be looked at.
- Needs to be well written as a task to ensure alignment with content and outcomes.
- May need significant scaffolding if the format is unfamiliar.
Things to keep in mind
When using case studies or scenarios as assessment items, consider the following pointers:
- Assessment by case study or scenario can involve a verbal presentation or a written submission, or both.
- Assessment by case study or scenario could occur in a group situation or individually.
- identification of a problem
- generation of a hypothesis
- construction of an enquiry plan
- research or enquiry
- interpretation of findings
- investigation of results.
- You can base case study teaching and assessment on a number of methods, e.g. the Harvard Business School method . Bear in mind that there are critiques of each method.
- You can use technology to track case discussions and development.
- You can prepare for a case study or scenario assessment by presenting examples of cases in class prior to assessment. This can provide familiarity and understanding of the relevance of cases.
- Why are you choosing a case study or scenario format?
- Which learning outcomes does it align with?
- Do you want to make sure students cover a specific area of knowledge?
- Will students develop knowledge of concepts, ideas, theory or technology?
- How authentic do you want the case study to be? I.e. How will you develop the case?
- What is the specific focus of the content?
- Which area of subject content do you want the student to integrate knowledge from?
- How will you indicate which content areas students need to address?
- What questions/areas do you want learners to focus on?
- How should they structure the case study to maintain this focus and cover the content in a way that is authentic to a case study/scenario?
- Will you provide a structure or template for students to follow?
- How will you direct analysis in terms of presentation to the audience? Is there an approach you can incorporate?
More resources
- Using case studies to teach - Boston University
- Case studies - UNSW
- Case collection - National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science
- What is investigative case-based learning - Science Education Resource Centre
- UQ Assessment Ideas Factory - University of Queensland
Case Studies
Case studies during an assessment.
Different types of case studies are used in assessment centers. Companies may use a case study interview or a written exercise ( In-Tray and E-Tray exercise ). Case studies are used to measure your analytic skills, problem-solving abilities, communication skills and ability to deliver quality and results. These exercises also help to determine how you prioritize and organize your work.
How does a Case Study work?
During a case study interview, individuals or a small group of candidates are presented with a business case and then given time to evaluate the information and brainstorm a solution. These studies rely on real-life or hypothetical scenarios and are likely to involve a quantitative aspect that includes financial understanding, statistics, and other data. Candidate(s) have to give a recommendation or solution that refers to the integration of the presented information. Consultancy and business management companies use these tests as part of their selection process.
How to prepare for a Case Study Interview
These tests usually do not require any prior knowledge. Nevertheless, before taking these tests, it is recommended to check the particular company's website, recruitment literature and the industry's overview and recent news to have an idea of what to expect during the exercises. Furthermore, you can identify some of the competencies the company is likely looking for, and try to work them into your case study.
Tips for a successful Case Study Interview
- Don’t panic and try to relax. We know this is easier said than done, but you will have a better performance if you are relaxed. The interviewers are professionals, and they want you to succeed and perform well.
- Take your time. Do not feel rushed to provide an answer immediately, work through the issues and ask the interviewer(s) for a moment to think or clarify anything you do not understand.
- Apply a structured approach to the problem to prioritize the issues and objectives. Filter the data and focus on the most relevant information.
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions. The case interview is meant to be interactive, going back and forth between you and the interviewer(s). Questions are expected, but make sure to ask your questions in a logical – not random – progression.
Examples of Psychometric test exercises:
- Numerical Reasoning
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Number Sequences
- Antonyms
- E-Tray Exercise
- Verbal Analogies
- Verbal Reasoning
- Mental Arithmetic test
- Spatial Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Error Checking test
- Situational Judgement test (SJT)
All Aptitude Tests Package
- 206 Aptitude Tests
- 3281 Aptitude Test Questions
- One-off Payment
Welcome to Assessment-Training.com
We are here to help you pass your tests and job interviews. Before you start practicing, please complete your full profile for our Personal Progression System (PPS) to run smoothly. Track your progress, and pass your tests easily. Prepare to succeed!
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Undergrad Neurosci Educ
- v.19(2); Spring 2021
Effective Use of Student-Created Case Studies as Assessment in an Undergraduate Neuroscience Course
Dianna m. bindelli.
1 Neuroscience Department, Carthage College, Kenosha, WI 53140
Shannon A.M. Kafura
Alyssa laci, nicole a. losurdo, denise r. cook-snyder.
2 Department of Physiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI 53226
Case studies and student-led learning activities are both effective active learning methods for increasing student engagement, promoting student learning, and improving student performance. Here, we describe combining these instructional methods to use student-created case studies as assessment for an online neurovirology module in a neuroanatomy and physiology course. First, students learned about neurovirology in a flipped classroom format using free, open-access virology resources. Then, students used iterative writing practices to write an interrupted case study incorporating a patient narrative and primary literature data on the neurovirulent virus of their choice, which was graded as a writing assessment. Finally, students exchanged case studies with their peers, and both taught and completed the case studies as low-stakes assessment. Student performance and evaluations support the efficacy of case studies as assessment, where iterative writing improved student performance, and students reported increased knowledge and confidence in the corresponding learning objectives. Overall, we believe that using student-created case studies as assessment is a valuable, student-led extension of effective case study pedagogy, and has wide applicability to a variety of undergraduate courses.
It is well established that active learning increases student engagement, promotes student learning, and improves student performance compared to traditional lecture ( Armbruster et al., 2009 ; Haak et al., 2011 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). Moreover, active learning is a critical component of inclusive pedagogy that is effective for all students, and decreases the achievement gap for persons excluded because of their ethnicity or race (PEERs; Haak et al., 2011 ; Ballen et al., 2017 ; Penner, 2018 ; Theobald et al., 2020 ; Asai, 2020 ). Frequent student-led learning activities are an important component of an active learning classroom, where students engage with course content and work collaboratively with their peers to increase their own and each other’s learning. Student-led learning techniques range from short, cooperative activities like think-pair-share and the jigsaw method ( Faust and Paulson, 1998 ; Lom, 2012 ; Lang, 2016 ), to full collaborative learning courses where students prepare and lead most classes ( Casteel and Bridges, 2007 ; Davidson and Major, 2014 ; Kurczek and Johnson, 2014 ). Case studies are also an effective active learning method that uses narratives to engage students in higher-level learning objectives within Bloom’s Taxonomy ( Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001 ; Handelsman et al., 2004 ; Herreid et al., 2012 ; Wiertelak et al., 2016 ). As one example, case studies have been incorporated into introductory and upper-level neuroscience courses to promote student analysis and evaluation of primary literature ( Cook-Snyder, 2017 ; Sawyer and Frenzel, 2018 ; Rollins, 2020 ). Typically, student-led learning activities and case studies are both used as in-class practice before a separate, larger assessment, like an exam testing similar content ( Freeman et al., 2014 ; Cook-Snyder, 2017 ; Sawyer and Frenzel, 2018 ). Here, we describe using the case study itself as the assessment, where students work collaboratively to write a case study that demonstrates and applies their neurovirology knowledge and requires analysis and evaluation of the primary literature. In turn, students lead their peers in discussion of their case to promote their own and each other’s learning.
As described here, we used student-created case studies as assessment in a four-week, online neurovirology module in an upper-level neuroanatomy and physiology course. Neurovirology is the interdisciplinary study of viruses that affect the central nervous system ( Nath and Berger, 2020 ) and students voted to learn more about neurovirology during the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic in the spring 2020 semester. Accordingly, student-created case studies focused on neurovirulent viruses, or viruses that can cause disease of nervous tissue ( Racaniello, 2020a ). Students used iterative writing practices to write their case studies, which were graded as writing assignments. Then, students exchanged case studies with their peers, and both taught and completed the cases in small groups as low-stakes assessment. Student performance data and self-reported evaluations support the success of the neurovirology module and case study assignment in meeting the content and skills learning objectives listed below. Case studies are highly effective tools in undergraduate education ( Handelsman et al., 2004 ; Herreid et al., 2012 ; Wiertelak et al., 2016 ), and we believe that using student-created case studies as assessment is a valuable extension of established case study pedagogy.
Learning Objectives
Content objectives.
After this module, students should be able to:
- ○ Viral properties and classification
- ○ Viral pathogenesis, including infection and immune response
- ○ CNS barriers, including the blood-brain barrier
- ○ Mechanisms of neurotoxicity and neuronal death
Skills Objectives
Additionally, students will increase their skills in:
- Applying virology and neuroscience principles to neurovirulent viruses and neurologic disorders
- Using resources from the neurovirology module to learn more about virology
- Analyzing and evaluating primary literature
- Collaborating to write original case studies
- Leading peers in analysis and evaluation of case studies
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Neurovirology module.
The neurovirology module was developed for a one-semester, neuroanatomy and physiology lecture and laboratory course for junior and senior neuroscience majors at a small liberal arts college (Neuroscience 4100, Carthage College). Enrollment for the course is typically 25–30 students, with greater than 60% of students reporting clinically focused health care career goals. The most common career goals are physician (M.D. or D.O.), physician assistant, physical or occupational therapist, and clinical psychologist, consistent with the hypothesis that students believe a neuroscience major will better prepare them for health care careers ( Prichard, 2015 ; Ramos et al., 2016a , 2016b ).
The neurovirology module was developed as a substitution for in-person labs when remote instruction was implemented in the spring 2020 semester due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Student survey data was collected using Google Forms at the beginning of remote instruction, and 96% of students voted in favor of using lab time to learn more about virology and infectious disease, with an emphasis on neurovirology ( n = 26 enrolled students; 24/26 students for, 0/26 students against, 2/26 students abstained). Accordingly, the neurovirology module was administered over Zoom ( https://zoom.us/ ) during weekly 3-hour lab periods for a total of four weeks (Week 1 to Week 4; 12 hours total; see Supplementary Material Appendix A , Appendix B ). Students received instruction in using Zoom prior to the neurovirology module, including joining a Zoom class, providing verbal and non-verbal feedback to the instructor, and joining breakout rooms to work with peers.
The neurovirology module followed a flipped classroom format, in which students gained familiarity with neurovirology content before class, and used class time for active learning strategies ( Mazur, 2009 ; Brame, 2013 ). Appendix A provides details on before class readings, videos, and assignments, and in-class activites for the neurovirology module. Briefly, in Week 1, students learned basic principles of virology using recorded lectures and readings from a free, online, open-access virology course ( https://www.virology.ws/course/ ) and blog ( https://www.virology.ws/virology-101/ ) courtesy of Vincent Racaniello at Columbia University ( Racaniello, 2004 ; Racaniello, 2009a , 2009b , 2009c , 2009d , 2009e , 2009f , 2009g ; Racaniello, 2020a , 2020b , 2020c ). These materials were supplemented with textbook readings on the immune system ( Widmaier et al., 2014 ). Week 1 materials were chosen to provide students with enough background on viral properties, classification, and pathogenesis that they could apply their knowledge to neurovirulent viruses and neurologic disorders in Week 2. Accordingly, in Week 2, students read about central nervous system barriers in the course textbook ( Kandel et al., 2013 ), and watched a brief, recorded lecture summarizing major mechanisms of neurotoxicity and neuronal death ( Appendix A ; Fink and Cookson, 2005 ; Jellinger, 2010 ; Fan et al., 2017 ; full lecture available from the corresponding author by request). After completing these additional background readings, students read a neurovirology review article describing mechanisms of invasion and disease for specific neurovirulent viruses ( Swanson and McGavern, 2015 ).
Before class assignments for Week 1 and Week 2 included short, online comprehension quizzes, and collaborative “neurovirology dictionary” assignments, where students were responsible for adding new terms and definitions to create a shared “neurovirology dictionary” from the before class readings and videos ( Appendix A ). Both of these graded assignments incentivized student preparation before class and provided checks of student understanding, which are key elements of a flipped classroom ( Brame, 2013 ).
Week 1 and Week 2 class time used cooperative, student-led learning, where students worked together to complete questions based on the before class content ( Davidson and Major, 2014 ). Specifically, students were randomly assigned to groups of 3–4 using the breakout room function in Zoom. Each group was assigned a different set of instructor-created questions to discuss and complete in a shared Google Slides document, and the instructor circulated between groups to check understanding. Then, each group presented their answers to the full class. This format provided structure for students to create their own study guide summarizing neurovirology content, and provided additional practice in cooperative, student-led learning ( Davidson and Major, 2014 ).
Case Study Assignment
Weeks 3–4 of the neurovirology module were used for the case study assignment. Broadly defined, case studies use narratives to engage students and meet learning objectives ( Herreid, 2007 ). The case study assignment was worth 6% of the final course grade, and Appendix B provides details on assignment requirements and a grading rubric. Briefly, students worked in self-selected groups of 2–3 to write their case study on any neurovirulent virus of their choosing. Case studies were required to follow an interrupted, literature-based format ( Herreid et al., 2012 ; Prud’homme-Généreux, 2016 ; Cook-Snyder, 2017 ), where the first part of the case study used a patient narrative or primary literature data and asked questions on the epidemiology and/or symptoms and diagnosis of the virus. The second part of the case study was required to use primary literature data and ask questions on the pathogenesis and/or treatment of the virus. Students included answers to their own questions, and the answers were required to be clearly supported by the course materials and by their case study. Supplementary Material Appendices C and D provide example student-created case studies on rabies virus and enterovirus 71, respectively.
Students followed an iterative writing practice to create their case studies, which sought to couple goal-directed practice with targeted feedback ( Ambrose et al., 2010 ). Specifically, students submitted the first draft of their co-authored case study in Week 3, which was graded by the instructor using a holistic rubric that included a grading scale, comments, and specific examples from the students’ draft ( Appendix B ; Allen and Tanner, 2006 ). The first draft was worth 10% of the students’ final grade on the assignment, which incentivized student performance on the draft while still serving as a low-stakes assesment and providing formative feedback ( Birol et al., 2013 ; Brownell et al., 2013 ; Cotner and Ballen, 2017 ; Cyr, 2017 ). Then, students revised and submitted the final draft of their case study in Week 4, which was graded by the instructor using the same rubric as the first draft to provide summative feedback, and was worth 90% of the students’ final grade. Students were asked to write new or edited text on the final draft in a different color, so the instructor could more easily identify the students’ improvements from the first draft and incorporation of first draft feedback.
Students also shared their case study final draft with one other student group, and the case study authors led their peers through their case studies following a previously described classroom management strategy ( Cook-Snyder, 2017 ). This classroom management strategy is consistent with effective student-led discussion practices, including students working in teams to create and disseminate discussion questions before leading class discussion ( Casteel and Bridges, 2007 ; Kurczek and Johnson, 2014 ). Briefly, in Week 4, peers completed the student authors’ case study questions as homework before class, and class time was used to discuss their answers. Discussion was facilitated by the student authors, and emphasized that there can be multiple "correct" answers where the best answers are accurate and well-supported. Well-supported answers cited the case study itself, the neurovirology module, previous course content, and/or the primary literature as needed. This approach encourages students to apply course knowledge and conduct targeted literature searches to increase their knowledge. Peers edited their answers based on the discussion, and these edits were factored into a pass/fail grade from the instructor. Each case study was allotted 30 minutes for discussion; at the end of 30 minutes, the peers and students authors switched roles and discussed the peers’ case study. Appendix B provides a table illustrating this format for a three-hour class period. Overall, each student received three grades on the case study assignment: a grade on the first draft and a grade on the final draft of the case study they wrote, and a pass/fail grade on the case study they completed ( Appendix B ). Additionally, each student had the opportunity to teach their case study to their peers as a student-led learning activity. By implementing the case study assignment workflow outlined here, students both created original work and led their peers in analysis and evaluation of their work, consistent with higher-level learning objectives from Bloom’s Taxonomy ( Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001 ).
Assessment of Learning Objectives
Learning objectives for the neurovirology module and case study assignment were assessed directly and indirectly using student performance data and self-reported evaluations, respectively ( Muir, 2015 ). Data and evaluations were collected in accordance with federal guidelines for research in education settings, and with approval from the Institutional Review Board at Carthage College. All statistical analyses were performed in GraphPad Prism 8 for macOS (San Diego, CA) with a significance level of p <0.05.
Analyzed student performance data included student grades on the first draft and final draft of the case study assignment ( Figure 1 ). Comparison of first draft and final draft case study grades was analyzed using a parametric paired t -test.

Student performance improved with iterative writing practice and low-stakes assessment. Student group grades for the first draft and final draft of the case study are shown as a percentage of the total possible points for the draft (grey circles). Lines connect the first draft and final draft grades from the same student group ( n = 12 student groups; paired t -test, **** p <0.001).
De-identified student self-reported evaluations were collected using Google Forms after Week 4 of the neurovirology module and case study assignment. Quantitative evaluations used a Likert scale with the following responses: 5-Strongly Agree; 4- Agree; 3- Neutral; 2- Disagree; 1- Strongly Disagree ( Figures 2 2 – 4 ). All questions included a “prefer not to respond” option for student response, although no students chose this option for the questions reported here. Student responses were analyzed using a nonparametric one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test, with a hypothetical median of 3- Neutral. If the responses were significantly different from 3- Neutral, we concluded that the students agreed/strongly agreed (4–5) or disagreed/strongly disagreed (1–2) with the question. This analysis method is consistent with previous research analyzing student-led learning activities ( Stavnezer and Lom, 2019 ).

Students self-reported familiarity with neurovirology ( A ), increased knowledge in content learning objectives ( B ), and activities contributing to knowledge ( C ). Evaluations used a Likert scale: 5-Strongly Agree; 4- Agree; 3- Neutral; 2- Disagree; 1- Strongly Disagree. Scatter plots show individual student responses (grey circles) and the median response (black bar) for each question ( n = 23–24 students; one-sample Wilcoxon signed rank test to a hypothesized median of 3- Neutral (dotted line); ** p <0.01, **** p <0.0001).

Students self-reported increased confidence in skills learning objectives. Evaluations used a Likert scale: 5-Strongly Agree; 4- Agree; 3- Neutral; 2- Disagree; 1- Strongly Disagree. Scatter plots show individual student responses (grey circles) and the median response (black bar) for each question ( n = 23–24 students; one-sample Wilcoxon signed rank test to a hypothesized median of 3- Neutral (dotted line); **** p <0.0001).

Students self-reported satisfaction with the neurovirology module and case study assignment. Evaluations used a Likert scale: 5-Strongly Agree; 4- Agree; 3- Neutral; 2- Disagree; 1- Strongly Disagree. Scatter plots show individual student responses (grey circles) and the median response (black bar) for each question ( n = 24 students; one-sample Wilcoxon signed rank test to a hypothesized median of 3- Neutral (dotted line); *** p <0.001, **** p <0.0001).
De-identified qualitative evaluations included three open-ended questions: (1) What will you take away from the neurovirology module?; (2) What aspects of the neurovirology module were most valuable?; (3) What suggestions do you have for how Dr. Cook-Snyder (i.e., instructor and corresponding author) can improve the neurovirology module? The corresponding author categorized student responses to align with the content and skills learning objectives, or with the neurovirology module materials ( Appendix A ) and case study assignment ( Appendix B ; Figure 5 ). Some student responses contained module/case study assignment category. Additionally, some student responses (31.03% of responses) did not contain a suggestion for improvement, and were omitted from analysis. Accordingly, qualitative evaluation sample sizes vary from course enrollment because one response can contain zero or multiple categories, consistent with analysis methods from previous studies ( Stavnezer and Lom, 2019 ).

Students self-reported content and skills learning objective takeaways, and provided strengths and areas for improvement for the neurovirology module and case study assignment. Qualitative evaluations used open-ended questions to assess takeaways ( A ), strengths ( B ), and areas for improvement ( C ). ( A ) Students responses on takeaways were aligned with content learning objectives (above dotted line) or skills learning objectives (below dotted line), and the percentage of total responses for each learning objective is shown ( n = 38 responses). ( B, C ) Student responses on strengths ( B ) and areas for improvement ( C ) were aligned with neurovirology module materials (above dotted line) or the case study assignment (below dotted line), and the percentage of total responses for each category is shown ( B : n = 39 responses; C : n = 20 responses)
Student Performance
Student learning in the neurovirology module ( Supplementary Material Appendix A ) was primarily assessed with the case study assignment ( Supplementary Material Appendix B ). As examples, two student-created case studies on neurovirulent viruses are included in Supplementary Material Appendices C and D . Student authors (DMB, SAMK, AL, NAL) had substantial familiarity with interrupted, literature-based case studies before writing their own case study in this format. Indeed, almost all students who wrote case studies (25 out of 26 students) had previously completed 13 interrupted, literature-based case studies over two semesters in the corresponding author’s courses ( Cook-Snyder, 2017 ). In Appendix C , the student-created case study on rabies virus applies content from the neurovirology module with detailed analysis of primary literature data on rabies virus, blood-brain barrier permeability, and vaccine efficacy ( Long et al., 2020 ). In Appendix D , the student-created case study on enterovirus 71 also applies neurovirology content to investigate vaccine efficacy ( Li et al., 2008 ; Zhang et al., 2012 ). Additionally, this case study reviews cerebellar and pontine structure and function, which were previously discussed in the course, in relation to viral pathogenesis ( Huang et al., 1999 ; Shen et al., 1999 ; Jain et al., 2014 ). In both case studies, student authors successfully met the skills learning objectives of the neurovirology module and case study assignment by applying their knowledge of neurovirology and analyzing and evaluating primary literature.
The case study assignment used an iterative writing process and low-stakes assessment, where the first draft of the case study was worth 10% of the students’ final grade on the assignment, and the final draft was worth 90%. Iterative writing practices and low-stakes assessment have been shown to improve student performance and confidence within a course ( Freestone, 2009 ; Brownell et al., 2013 ; Cyr, 2017 ). Therefore, we compared student grades on the first draft and final draft of the case study, and consistent with previous literature, our results show that every student group increased their grade from the first draft to the final draft ( Figure 1 ). These results further support that iterative writing practices and low-stakes assessment can improve student performance.
Student Evaluations
For quantitative evaluations, students used a Likert scale to self-report their knowledge of content learning objectives and confidence in skills learning objectives after completion of the neurovirology module and case study assignment. Our results show that the majority of students had not studied neurovirology in a previous college course, and that they reported increased knowledge of content learning objectives after completing the neurovirology module and case study assignment ( Figure 2A, 2B ). Moreover, students reported that writing, teaching, and completing a neurovirology case study all increased their neurovirology knowledge, with writing (median = 5- Strongly Agree) ranking higher than teaching or completing (median = 4- Agree; Figure 2C ). Additionally, students reported increased confidence in skills learning objectives ( Figure 3 ), and agreed that if they took the course again, they would want the neurovirology module included, and to write more case studies ( Figure 4 ). Taken together, these data suggest that the neurovirology module and case study assignment were largely successful in meeting content and skills learning objectives and student satisfaction.
For qualitative evaluations, students answered open-ended questions on takeaways, strengths, and areas for improvement after completion of the neurovirology module and case study assignment. When asked what they will take away from the neurovirology module, student responses spanned the module’s learning objectives but reported more content than skills takeaways ( Figure 5A ; 55.3% of responses for content learning objectives; 44.7% of response for skills learning objectives). Additionally, students emphasized the importance of the module as a foundation for further exploration, as exemplified by the following responses:
“I will take away how much I loved learning about neurovirology. I was always interested in infectious diseases and loved neuroscience so tying them together has been fantastic… I am definitely more confident in reading primary literature on the topic due to this section and that will hopefully carry me through any future education.” “I thought the material was interesting and relevant and I appreciated that I could take the information and neurovirology definitions we were learning about and begin to apply them to literature being published now about COVID-19….”
When asked about the most valuable aspects of the neurovirology module, students identified before class readings and videos, and in-class active learning strategies in Weeks 1–2 of the module ( Appendix A ), and writing and teaching their case studies in Weeks 3–4 of the case study assignment ( Appendix B ; Figure 5B ; 56.4% of responses for the neurovirology module, 43.6% of responses for the case study assignment). Writing the case study was the most commonly identified valuable aspect of the class (33% of responses; Figure 5B ), as exemplified by the following responses:
“I found the case study we created to be most helpful. It pushed me to go through the neurovirology material learned in the lectures, readings, and videos and truly understand the topic I had to eventually write and teach about. I felt that it allowed for more active learning in which I had to think about the topic from multiple angles-researching a virus, creating the prompt, writing questions and answers...” “I really enjoyed having the challenge of writing our case study. It made me think more like a scientist and a physician regarding viruses and how they can affect the nervous system. It is very interesting to apply the theory to what we could see in real life on a patient undergoing a viral infection.” “I think the aspect that was most valuable was the creation of the case study. I thought it was beyond inspiring to have crafted our very own case study that seemed so professional and to teach it to our peers was very meaningful.”
When asked for suggestions for improving the neurovirology module, student feedback spanned the module and the case study assignment ( Figure 5C ; 55% of responses for the neurovirology module, 45% of responses for the case study assignment). The most common areas for improvement were adding more content, especially clinical symptoms and diagnosis (30% of responses) and completing more case studies (30% of responses). Interestingly, adding more content was also the most common area for improvement for students that reported neutral or disagree with knowledge of content learning objectives ( Figure 2B ) or confidence in skills learning objectives ( Figure 3 ; 57% of responses from these students). As two students wrote:
“Discussing more symptoms and how you would classify a disease based on the symptoms presented [is an area of improvement]…learning how to diagnose/differentiate these types of diseases would be helpful.” “…I think it would be interesting if we all got to do or at least listen in on everyone's case study. This would allow us to learn about different neuroviruses.”
Interestingly, some students also identified providing more instruction on teaching the case study as an area for improvement ( Figure 5C ; 15% of responses). As one student wrote:
“While I did think that creating our own case study was very valuable, I did think that some of the expectations on how it was going to be presented were unclear. I wish there was a little more format to that portion of the project. Other than that I really did enjoy this module and I hope that you can find a way to integrate it into the class material in the future.”
Taken together, qualitative student evaluations suggest that student takeaways aligned with content and skills learning objectives, and that students valued the structure of the neurovirology module and case study assignment, although important improvements to content and instruction are needed.
In this article, we describe using student-created case studies as assessment for a neurovirology module. Our results suggest that the neurovirology module and the case study assignment met their intended content and skills learning objectives by improving student performance and increasing students’ self-reported knowledge and confidence. We believe our approach is a valuable extension of case study pedagogy with broad applicability to a variety of undergraduate courses.
As described in this article, students followed iterative writing practices to create their case studies, which have been shown to improve student performance and confidence within a course ( Freestone, 2009 ; Brownell et al., 2013 ; Cyr, 2017 ). Our data was consistent with the previous literature, showing improved student grades from the first draft to the final draft of the case study assignment ( Figure 1 ). Previous studies also suggest that iterative writing practice coupled with calibrated peer review may be particularly effective in improving performance for the lowest-performing students ( Birol et al., 2013 ). Future version of the case study assignment could repeat the iterative writing practices described here and included calibrated peer review for the first draft, then measure improvement from the first draft to the final draft for high- and low-performing students. Moreover, additional studies suggest that iterative writing practices may not improve student writing performance across all domains or in subsequent courses ( Rayner et al., 2014 ; Holstein et al., 2015 ). Further analysis would be necessary to determine if students show longitudinal improvements in writing performance across multiple writing assignments and courses after completion of the case study assignment described here.
Quantitative and qualitative student self-report evaluations support that the neurovirology module and case study assignment promoted content and skills learning objectives in understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating ( Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001 ), and that students valued the structure of the neurovirology module and case study assignment ( Figures 2 2 – 5 ). Importantly, student self-report evaluations of active learning may underestimate the amount of actual student learning ( Deslauriers et al., 2019 ), so the high student evaluations of learning objectives are notable. However, students also offered important areas for improvement, including adding more content on clinical symptoms and diagnosis on neurovirulent disorders ( Figure 5C ). To address this, future iterations of the neurovirology module should include clinical textbook readings and primary literature ( Bookstaver et al., 2017 ; Nath and Berger, 2020 ) coupled with public health resources on symptoms and diagnosis ( Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020 ; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, 2020 ; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2020 ). Encouraging students to read scientific articles written for the general public prior to or concurrent with reading primary literature on the same topic improves student understand of complex or unfamiliar literature ( Gottesman and Hoskins, 2013 ; Bodnar et al., 2016 ; Kararo and McCartney, 2019 ). Additionally, students suggested providing more instruction on teaching case studies and completing more case studies ( Figure 5C ). This area for improvement is consistent with quantitative evaluations, where students reported that writing, teaching, and completing a neurovirology case study all increased their neurovirology knowledge, but writing ranked higher than teaching or completing ( Figure 2C ). To address this, future iterations of the case study assignment will include teaching guidelines in the assignment requirements ( Appendix B ) based on nine facilitator strategies for student-led discussion ( Rees, 1998 ; Soranno, 2010 ). Students will be asked to reflect on these strategies and write a short paragraph at the end of their first draft on how they will work as a team to teach their case study using these strategies. Additionally, students will share their case study final draft with at least two other student groups to increase the number of case studies each student completes. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations should be repeated to determine if these interventions address students’ areas for improvement.
Students had considerable familiarity with interrupted, literature-based case studies before writing their own cases. Indeed, almost all students who wrote case studies (25 out of 26 students) had previously completed 13 interrupted, literature-based case studies over two semesters in the corresponding author’s courses ( Cook-Snyder, 2017 ). This is consistent with active learning pedagogy, which emphasizes students practicing the skills necessary to succeed in assessment before they are assessed ( Armbruster et al., 2009 ; Haak et al., 2011 ; Freeman et al., 2014 ). However, previous research suggests that more limited practice with case studies prior to writing a case study may still be effective. For example, research on collaborative learning courses describe instructor modeling of good discussion practices “several” times before students prepared and led classroom discussions ( Casteel and Bridges, 2007 ; Kurczek and Johnson, 2014 ). Therefore, we suggest that students complete several (two to four) instructor-provided and -taught case studies following the structure and classroom management of the case study assignment before writing and leading their own case.
Active learning is a critical component of inclusive pedagogy that is effective for all students, and decreases the achievement gap for PEERs ( Haak et al., 2011 ; Ballen et al., 2017 ; Penner, 2018 ; Theobald et al., 2020 ; Asai, 2020 ). Studies suggest that active learning may be particularly effective for PEERs because active learning helps students identify as scientists, and science identity is critical for persistence in STEM ( Graham et al., 2013 ; Trujillo and Tanner, 2014 ; Theobald et al., 2020 ). Case studies are important components of active learning ( Handelsman et al., 2004 ; Herreid et al., 2012 ; Wiertelak et al., 2016 ), and some qualitative student evaluations suggest that the case study assignment promoted scientific identity, where students described thinking “more like a scientist and a physician,” and that writing a case study “seemed so professional.” However, direct questions on students’ science identities are needed for future iterations of the case study assignment to determine if the assignment promoted science identity ( Trujillo and Tanner, 2014 ). Likewise, further studies are needed to determine if the case study assignment promoted persistence in STEM. In this article, the case study assignment was used in a spring semester course for junior and senior neuroscience majors at Carthage College, where nearly 100% of junior and senior neuroscience majors graduate from Carthage with a neuroscience degree (data not shown). This is consistent with previous research, which estimates that STEM attrition rates peak in students’ first and second academic year, and plateau in third and fourth year ( Aulck et al., 2017 ; Chen et al., 2018 ). However, if the case study assignment was used in first or second year neuroscience courses, when STEM attrition rates are higher, measuring subsequent retention of students in a STEM major could be particularly valuable metric.
We believe that using student-created case studies as assessment has wide applicability to undergraduate education because case studies themselves have wide applicability. Case studies have been used effectively in introductory and advanced neuroscience courses with small and large student enrollments to address a variety of content and skills learning objectives ( Herreid et al., 2012 ; Brielmaier, 2016 ; Ogilvie and Ribbens, 2016 ; Roesch and Frenzel, 2016 ; Wiertelak et al., 2016 ; Lemons, 2017 ; Nagel and Nicholas, 2017 ; Sawyer and Frenzel, 2018 ; Mitrano, 2019 ; Ogilvie, 2019 ; Watson, 2019 ; Rollins, 2020 ). Case studies are also effective active learning methods for synchronous and asynchronous online and hybrid teaching ( Brooke, 2006 ; Schiano and Anderson, 2014 ). Accordingly, we believe that the case study assignment described here could be adapted to follow any of these existing methods of case study writing and teaching. Additionally, we encourage instructors to adapt our neurovirology module to their students’ needs and interests, taking advantage of the free virology resources available online ( https://www.virology.ws/course/ ; https://www.virology.ws/virology-101/ ). Moreover, we believe the module format and case study assignment described here could be duplicated for other important neuroscience topics that are highly relevant to students but not always discussed in the neuroscience curriculum, like social neuroscience or neuroethics ( Flint and Dorr, 2010 ; Abu-Odeh et al., 2015 ; Wiertelak et al., 2018 ). Overall, we believe that using student-created case studies as assessment is a valuable, student-led extension of effective case study pedagogy, and has wide applicability to a variety of undergraduate courses.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Neuroscience Case Network (NeuroCaseNet; NSF-RCN-UBE Grant #1624104). The authors thank the students in Neuroscience 4100 at Carthage College for their participation and feedback, and Dr. Kristen Frenzel for editing the manuscript.
APPENDIX 1. NEUROVIROLOGY MODULE MATERIALS
Before class readings and videos.
Instructions for students: Please read and watch the following in order. Note that most of these are short readings and videos, but Infection Basics is an hour-long lecture.
- What is a virus?: https://www.virology.ws/2004/07/28/what-is-a-virus/
- How viruses are classified: https://www.virology.ws/2009/08/07/how-viruses-are-classified/
- Simplifying virus classification: The Baltimore system: https://www.virology.ws/2009/08/12/simplifying-virus-classification-the-baltimore-system/
- Recorded lecture: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fBJ0vcOlS7I&feature=youtu.be
- Slides: https://virology2020.s3.amazonaws.com/012_4310_20.pdf
- Please watch the entire lecture
- pg. 652 – 656
- pg. 662- adaptive immune responses overview
- These pages define immune cell types and cytokines, and give overviews of the innate immune response and adaptive immune response
- The rest of the chapter is for your reference
- Innate immune defenses: https://www.virology.ws/2009/06/03/innate-immune-defenses/
- The inflammatory response: https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/01/the-inflammatory-response/
- Adaptive immune defenses: https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/03/adaptive-immune-defenses/
- Adaptive immune defenses: Antibodies: https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/22/adaptive-immune-defenses-antibodies/
- Immunopathology: Too much of a good thing: https://www.virology.ws/2009/01/23/immunopathology-too-much-of-a-good-thing/
- Recorded lecture: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TQkg0mID-w8&feature=youtu.be
- Slides: https://virology2020.s3.amazonaws.com/016_4310_20.pdf
- Please watch until 8:00 (slide 7) of this lecture. The rest of the lecture is posted for your reference.
- Recorded lecture: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oWRynTL8NI4&feature=youtu.be
- Slides: https://virology2020.s3.amazonaws.com/017_4310_20.pdf
- Please watch until 5:30 (slide 6) of this video. The rest of the lecture is posted for your reference
Before Class Assignments
Instructions for students.
- Quiz ( Instructor note: Figure A1 provides sample quiz questions ).
- Neurovirology dictionary ( Instructor note: Figure A2 provides example neurovirology dictionary entries ). Neurovirology has so many terms that we’re going to create our own neurovirology dictionary. You are responsible for adding two new definitions to the dictionary this week. Your two definitions should be unique- they should not have already been defined by your classmates. I’ve included a few definitions to get us started. Your neurovirology dictionary definitions are worth 5 points, and you will receive full credit for being thoughtful, thorough, and on time.
In Class: Zoom lecture
- Study questions will be distributed at the beginning of class. You'll have the first part of class to work on the study questions in groups, and we'll discuss the answers to the study questions during the second part of class.
- At the end the end of class, please submit your study questions to the assignment posted below ( Instructor note: this course uses Schoology as learning management software ). Your study questions are worth 5 points, and you will receive full credit for being thoughtful, thorough, and on time.
Please read and watch the following in order.
- Kandel, Appendix D , The Blood-Brain Barrier, Choroid Plexus, and Cerebrospinal Fluid: pgs. 1565–1575.
- Mechanism of neurotoxicity and neuronal death ( Instructor note: this is a brief, recorded lecture focusing on key definitions, including apoptosis, autophagy, necrosis, inflammation, excitotoxicity, trophic factor withdrawal, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, protein misfolding and aggregation, and axonal transport dysfunction ).
- Swanson and McGavern, 2015 - Viral Diseases of the Central Nervous System ( Instructor note: key concepts from this review include viral spread, CNS entry, viral cytopathology, and immunopathology).
- Quiz ( Instructor note: Figure A3 provides sample quiz questions ).
- At the end of class, please submit your study questions to the assignment posted below ( Instructor note: this course uses Schoology as learning management software ). Your study questions are worth 5 points, and you will receive full credit for being thoughtful, thorough, and on time.

Sample quiz questions for Week 1 neurovirology module.

Example student-created neurovirology dictionary entries for Week 1 and Week 2 neurovirology module. Student names have been redacted.

Sample quiz questions for Week 2 neurovirology module.
APPENDIX 2. CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT REQUIREMENTS AND RUBRIC
What is a neurovirology case study.
We’ve used case studies to practice applying our knowledge from lecture to solve biomedically-relevant problems. By now, you all are experts in answering case studies questions- now it’s your turn to work in groups to write your own case study, similar to the case studies we’ve completed in class, and teach it to your peers.
What should you include in your neurovirology case study?
You should work with your lab group to write a neurovirology case study on any neurovirulent virus of your choosing. Your virus can also be neurotropic and/or neuroinvasive, but this is not required. ( Instructor note: neurovirulent viruses cause disease of nervous tissue. Neurotropic viruses infect neural cells; infection may occur by neural or hematogenous spread from a peripheral site. Neuroinvasive viruses enter the CNS after infection of a peripheral site ).
Your neurovirology case study should have two parts:
- Part #1 of your case study should investigate your neurovirulent virus using a patient narrative and/or primary literature data. You are encouraged to refer back to our previous case studies as examples.
- Based on your patient narrative and/or primary literature data, you should write a minimum of two questions, with answers, which address the epidemiology and/or symptoms and diagnosis of your virus.
- Part #2 of your case study should continue to investigate your neurovirulent virus using primary literature data. You are encouraged to refer back to our previous case studies as examples- nearly all of our case studies include questions based on primary literature data.
- Based on your primary literature data, you should write a minimum of three questions, with answers, which address the pathogenesis and/or treatment of your virus.
- Answers to your questions should be clearly supported by previous readings, videos, and lectures from class, and by the case study itself. You are encouraged to use any material from class as needed- you are not limited to just our neurovirology readings, videos and lectures.
- Remember, your peers are going to read your case study and answer your questions. So, your peers should be able to answer your questions based on material from class, plus any additional information you provide for them in the case study. Your peers should have to do minimal additional research to answer your questions correctly.
Your neurovirology case study should also have two versions:
- The answers to your questions
- In-text citations for all parts of your case study, especially your patient narrative/primary literature data and the answers to your questions.
- A list of references on the last page.
- You will write a 1st draft and a final draft of your Answer Key- see the Submission requirements and Grading and Feedback sections below for details
- This is the version you will share with your peers, so they can read your case study and answer your questions. This version should be identical to your Answer Key final draft, but not include the answers to your questions, in-text citations, or your list of references at the end.
How will you teach your neurovirology case study to your peers?
During Week 4, you will be leading your peers in a discussion of your case study, similar to our class discussions of case studies ( Instructor note: see Cook-Snyder, 2017 for a detailed classroom management strategy for case studies ).
- You will share your Neurovirology Case Study- Without Answer with your peers
- Your peers will read your case study, answer the questions, and submit their answers to Schoology before class.
- Then, in class, you will lead your peers in a discussion of your case study, and your peers will submit their original answers plus annotations to Schoology after class
| Timeslot | Case Study Authors | Peers |
|---|---|---|
| 8:00–8:30am | Group A | Group B |
| 8:30–9:00am | Group B | Group A |
| 9:00–9:30am | Group C | Group D |
| 9:30–10:00am | Group D | Group C |
| 10:00–10:30am | Group E | Group F |
| 10:30–11:00am | Group F | Group E |
Submission requirements
- ○ Your 1st draft is due Tuesday, May 5th, before your lab section starts (Instructor note: this is Week 3).
- ○ Your final draft is due Monday, May 11th, 10:30am (Instructor note: this is Week 4).
- ○ Even though you’re writing one case study per lab group, all group members should submit the case study to Schoology. This will ensure that all group members receive their case study grades.
- Your Neurovirology Case Study- Without Answers should be emailed to your peers by Monday, May 11th, 10:30am (Instructor note: this is Week 4).
Grading and Feedback
You will be graded according to the Neurovirology Case Study Grading Rubric posted below. Note that 10% of your case study grade will be earned on your 1st draft, and 90% will be earned on your final draft.
I will provide feedback electronically on all drafts (1st and final). My feedback will summarize the strengths, areas for improvement, and specific actions you can take to improve. IMPORTANT: I will provide a maximum of two comments per rubric section. This doesn’t mean that there aren’t any additional areas for improvement, or that if you only address these comments that you will get a 100%. But, I believe targeting your attention and effort to these top areas will make the most improvement.
Neurovirology Case Study Grading Rubric

APPENDIX 3. STUDENT-CREATED CASE STUDY- RABIES VIRUS
Instructor note: This case was written by Alyssa Laci and Nicole A. Losurdo, undergraduate students in Neuroscience 4100, Spring 2020 semester, Carthage College. In-text citations and references are in blue font. The answer key version of this case is available via request to [email protected] . The corresponding author (DRCS) has edited the case for formatting and clarity and has indicated whether each answer is supported by the case study in the neurovirology module, previous course content, and/or the primary literature in blue font.
Brian was engaging in yard work when he heard his wife yell to him.
“Brian! There is a stray dog in the yard that is acting rather strange. He is staggering and having a hard time standing upright. I think I also saw a foamy discharge coming from his eyes and mouth. I noticed him while I was in the garden because he was making this weird high-pitched noise” ( Taylor and Nel, 2015 ).
Brian walked over to his wife.
She looked concerned and asked him, “What do you think we should do about him?”
Brian replied with a similar concerned tone, “Well we better make sure he is okay and consider calling animal control. In the meantime, I’ll go take a closer look at him.”
Brian slowly moved closer to the dog, trying not to disturb or frighten him. He reached toward the dog, trying to comfort his fear. Instead, the dog lunged at his hand and bit him.
Brian pulled his hand away in pain. He glanced down at his fingers and found blood oozing from them. He stepped away from the dog and went inside to wash his hands off from the bite.
As he was washing his hands, the area around the bite tingled and itched ( CDC, 2019 ). He continued to scrub until the blood was gone, applied a bandaid and grabbed the phone to call animal control.
A week passed, and the area of Brian’s bite began to itch more excessively and he just couldn’t drum up the motivation to leave his bed because he felt so sleepy ( CDC, 2019 ). His wife entered into his bedroom, “Honey, please quit itching. You’re just going to make it worse.” She reached for his forehead, it felt warm.
Extremely irritated by her suggestion, Brian tried to keep his response low, but raised his voice at her ( CDC, 2019 ). “Don’t tell me what to do! I am a grown man! And stop coming in here to turn my light on. It’s so bright and hurts my eyes!” Shocked, his wife turned down the light and left the room, giving him time to rest.
Several more days passed. As he laid in bed, Brian began to lose feeling in his hand. He glanced down at it, noticing that it was twitching ( CDC, 2019 ). He looked up at the bedroom doorway. “Where am I?” He thought. “My mouth is so full of spit and I can hardly swallow because my throat feels so tight. Almost like its spasming.” He got out of bed and walked toward the hallway to splash his face with water. While he walked through the hallway, he noticed a creepy figure standing above him. Thinking that he may be hallucinating, Brian called to his wife. “Sweetie, please call 911.”
Part I Questions
- What are Brian’s signs and symptoms? (Answer based on case study)
- Brian was brought to the hospital after his wife called him an ambulance. Based on his symptoms, what do you think he will be diagnosed with? What diagnostic tests do you think physicians will use to achieve this diagnosis? (Answer based on case study and requires primary literature search)
After being taken to the hospital, Brian was diagnosed with rabies virus. Rabies virus enters peripheral nerves directly, and then can migrate to the central nervous system and up to the brain ( Rupprecht, 1996 ). One mechanism of entry into the peripheral nerves is through the neuromuscular junction ( Rupprecht, 1996 ). Once symptoms begin to appear, both general symptoms of fever or fatigue and neurological symptoms like hydrophobia, the disease cannot be reversed or cured ( Rupprecht, 1996 ). If the rabies vaccine is administered before the onset of symptoms, it can generally prevent or destroy the disease and the inevitable death that follows ( Long et al., 2020 ). Since Brian has already developed neurological symptoms, it is unlikely that the current rabies vaccine will be able to cure him ( Long et al., 2020 ).
The efficacy of the vaccine is reliant upon a permeable blood brain barrier (BBB) to allow immune cells to reach the virus in the brain and destroy it ( Kandel et al., 2013 ; Long et al., 2020 ). A study looked at the role of the phosphoprotein gene of the rabies virus on the permeability of the BBB ( Long et al., 2020 ). The study inoculated mice with either a wild-type (GD-SH-01), an attenuated rabies virus (HEP-Flury), or a chimeric virus that had the phosphoprotein gene of the wild-type inserted into the genome of the attenuated version (rHEP-SH-P). The rHEP-SH-P phosphoprotein gene is silenced by the placement in the attenuated genome. GD-SH-01 generally produced mild inflammation with eventual complete breakdown of the BBB, while the HEP-Flury produces high inflammation, but a more transiently permeable BBB. Figure 1 shows the data on BBB permeability (modified from Figure 1 in Long et al., 2020 ).
Part II Questions
- Is the rabies spread by hematogenous spread or neural spread? (Answer based on neurovirology module)
- Does the phosphoprotein cause a relative increase or decrease in BBB permeability? Use Figure 1 to explain your answer. (Answer based on case study)
- Would the incorporation of a phosphoprotein antagonist improve vaccine efficacy in the attenuated virus? Use Figure 1 to explain your answer. (Answer based on case study and neurovirology module)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Rabies. 2019. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/symptoms/index.html .
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ. Principles of Neural Science. 5th Ed. New York: McGraw Hill Medical; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Long T, Zhang B, Fan R, Wu Y, Mo M, Luo J, Chang Y, Tian Q, Mei M, Jiang H, Luo Y, Guo X. Phosphoprotein Gene of Wild-Type Rabies Virus Plays a Role in Limiting Viral Pathogenicity and Lowering the Enhancement of BBB Permeability. Front Microbiol. 2020; 11 :109. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Racaniello VR. Immunopathology: Too much of a good thing. Virology Blog. 2009a. Jan 23, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/01/23/immunopathology-too-much-of-a-good-thing/
- Racaniello VR. Virology Lectures 2020 #12: Infection Basics Biology 4310: Virology. Columbia University; 2020a. Mar 8, Available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fBJ0vcOlS7I&feature=youtu.be . [ Google Scholar ]
- Rupprecht CE. Chapter 61. Rhabdoviruses: Rabies Virus. In: Baron S, editor. Medical Microbiology. 4th edition. Galveston, TX: University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; 1996. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8618/ [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swanson PA, 2nd, McGavern DB. Viral diseases of the central nervous system. Curr Opin Virol. 2015; 11 :44–54. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor L, Nel L. Global Epidemiology of Canine Rabies: Past, Present, and Future Prospects. Veterinary Medicine: Research and Reports. 2015; 6 :361–371. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang X, Luo M, Zhang S, et al. Pivotal role of dogs in rabies transmission, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005; 11 (12):1970–1972. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
APPENDIX 4. STUDENT-CREATED CASE STUDY- ENTEROVIRUS 71
Instructor note: This case was written by Dianna M. Bindelli and Shannon A.M. Kafura, undergraduate students in Neuroscience 4100, Spring 2020 semester, Carthage College. In-text citation and references are in blue font. The answer key version of this case is available via request to [email protected] . The corresponding author (DRCS) has edited the case for formatting and clarity and has indicated if each answer is supported by the case study the neurovirology module, previous course content, and/or the primary literature in blue font.
It was the summer of 1998 in China when Finley Chang, a 10-year-old boy, went to the orthodontist to get his braces. It was mid-July, so Finley was extremely warm on his way to the orthodontist, also he was nervous. His mom, Mrs. Chang waited for him in the waiting room and was delighted to see her little boy growing up with his new braces.
The orthodontist, Dr. Wung had noticed that Finley was visibly sweating. He asked Finley if he was feeling fine. Finley said, “just nervous”. Dr. Wung had informed Mrs. Chang that the braces were all in place and his mouth had looked good! He warned that he may have pain in his mouth for a few days while adjusting to the braces.
One morning he woke up and he complained of a stomachache. He decided that he must just be hungry and proceeded to go downstairs for breakfast. On his way down the stairs, he began to feel woozy. He felt like the room was spinning, so he hurried down the stairs to sit down.
His mom had made pancakes and had orange juice for him.
“Good morning! What’s the rush? How did you sleep?” asked his mom.
“Fine.” responded Finley.
Mrs. Chang knew something was wrong when Finley did not dive into his sugary pancakes and was sitting there with his eyes closed.
Finley really did not feel like eating. He did not want to tell his mom about his stomachache. So, he decided to stick with the juice for now. After a couple sips of juice, he got a sour face.
“What happened?” asked his mom.
Finley began to feel the inside of his mouth and responded, “I have weird cuts in my mouth”. His mom looked and saw cuts on his gums and mouth and thought it may be from the braces ( Huang et al., 1999 ). However, it has been over a month since he had them, so she decided to call the orthodontist and have the alignment checked out.
While Finley was getting ready to leave for the orthodontist, he began vomiting. Mrs. Chang thought he had the flu bug and canceled the appointment, for now.
The next morning Mrs. Chang thought Finley would be better. However, Finley woke up with sweating and vomiting, and with even more sores in his mouth ( Huang et al., 1999 ). He sat up in bed and felt even more dizzy than yesterday and had to lie down. Mrs. Chang felt his head and thought his fever was even higher ( Huang et al., 1999 ). At this point she decided to take Finley to the pediatrician.
Dr. Hu looked at Finley’s mouth sores and brought him some water. She decided to run a few tests. She set up Finley with some anti-nausea medication and ordered an IV. In the meantime, she was analyzing the tests she ran.
- What are Finley’s signs and symptoms? (Answer based on case study)
- What tests would you run based on Finley’s signs and symptoms? Hypothesize the expected results. (Answer based on neurovirology module and previous course content)
Three days after coming back from the doctor, Finley’s mother went into his room to see if he wanted dinner. “Finley, time to eat.” He was waking up from a nap. “Finley, are you okay?” she asked, concerned. “I don’t feel so good, mom,” mumbled Finley, slurring his words. She helped him sit up and felt his forehead to see if fever had returned.
“Well, you don’t seem to have a fever again. Let’s try and eat some food, maybe that will help.” She then helped him get out of bed and into the kitchen.
When Finley was eating, he kept dropping food because his hands were shaking, and he had extreme difficulty bringing his chopsticks to his mouth. He kept accidently hitting his nose or chin. “Finley, do you want me to help you?” asked his mom. When he answered, she noticed that he also couldn’t focus straight on her and instead his eyes would bounce away ( Huang et al., 1999 ; Bae et al., 2013 ; Kandel et al., 2013 ; Jain et al., 2014 ; Cook-Snyder, 2020c ). Finley’s mother knew something was wrong and brought him to the emergency room.
The ER doctor walked into the room, “Hello, my name is Dr. Chen, and you must be Finley. Can you tell me what is going on?” Finley told her, “My arms don’t seem to be working right and I don’t feel very good,” again slurring his words ( Kandel et al., 2013 ; Cook-Snyder, 2020c ).
“Okay, and according to your chart, you’ve been sick recently?” asked Dr. Chen. “Yes, he was just at the doctor three days ago and the pediatrician diagnosed him with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease,” replied Finley’s mother ( Rhoades et al., 2011 ; Chen, et al., 2020 ).
“I see. His blood work also shows that Finley had viremia, specifically Enterovirus 71 (EV71). Enterovirus 71 is known to cause Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease, so this is making more sense. Finley also has increased amounts of lymphocytes and monocytes in his blood. Well, before I can make a diagnosis, I would like to take an MRI.” Dr. Chen said ( Rhoades et al., 2011 ; Chen et al., 2020 ; Racaniello, 2020a ). Finley’s expected MRI results are shown in Figure 1 (modified from Figure 2A in Shen et al., 1999 ; and Figure 1B in Huang et al., 1999 ).
“Based on the expected MRI results and the viremia, it looks like Finley has rhombencephalitis. This is a pretty serious diagnosis. He’s lucky that you brought him in,” said Dr. Chen. “I’d like to admit him to the hospital for care.” She discussed the treatment plan with Finley’s mom and left the room ( Huang et al., 1999 ; Chen et al., 2007 ; Jubelt et al., 2011 ; Jain et al., 2014 ; Chen et al., 2019 ).
Dr. Chen recommended a treatment called Ribavirin, an antiviral treatment. She presented the data in Figure 2 (modified from Figure 1B in Li et al., 2008 ) and Figure 3 (modified from Figure 3B in Zhang et al., 2012 ).
- What are Finley’s new signs and symptoms? (Answer based on case study and previous course content).
- Looking at Figure 1 , what brain regions are marked by the arrows? Use full neuroanatomical descriptions to explain your answer. (Answer based on previous course content).
- Could damage to these brain areas cause the signs and symptoms seen in Finley? (Answer based on previous course content).
- Hypothesize how Finley may have developed rhombencephalitis. In other words, propose a possible mechanism of pathogenesis for how the virus infected the CNS. (Answer based on neurovirology module).
- Using Figure 2 and and3, 3 , would Ribavirin be an effective treatment? Depending on your answer, either explain a possible mechanism of action for Ribavirin or possible solutions to make the drug effective. (Answer based on case study).
- Bae YJ, Kim JH, Choi BS, Jung C, Kim E. Brainstem pathways for horizontal eye movement: pathologic correlation with MR imaging. Radiographics. 2013; 33 (1):47–59. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen SC, Chang HL, Yan TR, Cheng YT, Chen KT. An eight-year study of epidemiologic features of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007; 77 (1):188–191. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen YF, Hu L, Xu F, Liu CJ, Li J. A case report of a teenager with severe hand, foot, and mouth disease with brainstem encephalitis caused by enterovirus 71. BMC Pediatr. 2019; 19 (1):59. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen BS, Lee HC, Lee KM, Gong YN, Shih SR. Enterovirus and Encephalitis. Front Microbiol. 2020; 11 :261. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook-Snyder DR. Neuroscience 4100: Neuroanatomy and Physiology. Kenosha, WI: Carthage College; 2020a. Feb 10, Structure and function of the human CNS. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook-Snyder DR. Neuroscience 4100: Neuroanatomy and Physiology. Kenosha, WI: Carthage College; 2020b. Mar 25, ANS and hypothalamus. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook-Snyder DR. Cerebellum. Neuroscience 4100: Neuroanatomy and Physiology. Kenosha, WI: Carthage College; 2020c. Apr 8, [ Google Scholar ]
- Dalpiaz RA, Pavan B. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Antiviral Drugs: A Way to Overcome Their Active Efflux? Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10 (2):39. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang CC, Liu CC, Chang YC, Chen CY, Wang ST, Yeh TF. Neurologic complications in children with enterovirus 71 infection. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341 (13):936–942. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jain S, Patel B, Bhatt GC. Enteroviral encephalitis in children: clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment advances. Pathog Glob Health. 2014; 108 (5):216–222. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jeulin H, Venard V, Carapito D, Finance C, Kedzierewicz F. Effective ribavirin concentration in mice brain using cyclodextrin as a drug carrier: evaluation in a measles encephalitis model. Antiviral Res. 2009; 81 (3):261–266. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jubelt B, Mihai C, Li TM, Veerapaneni P. Rhombencephalitis / brainstem encephalitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011; 11 (6):543–552. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ. Principles of Neural Science. 5th edition. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Medical; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li ZH, Li CM, Ling P, et al. Ribavirin reduces mortality in enterovirus 71-infected mice by decreasing viral replication. J Infect Dis. 2008; 197 (6):854–857. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rhoades RE, Tabor-Godwin JM, Tsueng G, Feuer R. Enterovirus infections of the central nervous system. Virology. 2011; 411 (2):288–305. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shen WC, Chiu HH, Chow KC. MR imaging findings of enteroviral encephalomyelitis: an outbreak in Taiwan. Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20 :1889–95. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang G, Zhou F, Gu B, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ribavirin and pleconaril antiviral activity against enterovirus 71 infection. Arch Virol. 2012; 157 (4):669–679. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abu-Odeh D, Dziobek D, Jimenez NT, Barbey C, Dubinsky JM. Active learning in a neuroethics course positively impacts moral judgment development in undergraduates. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2015; 3 (2):A110–A119. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen D, Tanner K. Rubrics: tools for making learning goals and evaluation criteria explicit for both teachers and learners. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2006; 5 :197–203. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ambrose SA, Bridges MW, DiPietro M, Lovett MC, Norman MK. How learning works: seven research-based principles for smart teaching. 1st Edition. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson LW, Krathwohl DR. A taxonomy of learning, teaching, and assessing: a revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. New York, NY: Longman; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Armbruster P, Patel M, Johnson E, Weiss M. Active learning and student-centered pedagogy improve student attitudes and performance in introductory biology. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2009; 8 :203–213. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asai DJ. Race matters. Cell. 2020; 181 (4):754–757. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aulck L, Aras R, Li L, L’Heureux C, Lu P, West JD. STEM-ming the tide: predicting STEM attrition using student transcript data. 2017 arXiv:1708.09344v1. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ballen CJ, Wieman C, Salehi S, Searle JB, Zamudio KR. Enhancing diversity in undergraduate science: self-efficacy drives performance gains with active learning. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2017; 16 (4):ar56. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birol G, Han A, Welsh A, Fox J. Impact of a first-year seminar in science on student writing and argumentation. J Coll Sci Teach. 2013; 43 :82. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bodnar RJ, Rotella FM, Loiacono I, Coke T, Olsson K, Barrientos A, Blachorsky L, Warshaw D, Buras A, Sanchez CM, Azad R, Stellar JR. “C.R.E.A.T.E.”-ing unique primary-source research paper assignments for a pleasure and pain course teaching neuroscientific principles in a large general education undergraduate course. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016; 14 (2):A104–A110. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bookstaver PB, Mohorn PL, Shah A, Tesh LD, Quidley AM, Kothari R, Bland CM, Weissman S. Management of viral central nervous system infections: a primer for clinicians. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2017; 9 :1179573517703342. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brame C. Flipping the classroom Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. Nashville, TN: Vanderbilt University; 2013. Available at http://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/flipping-the-classroom/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Brielmaier J. The woman born without a cerebellum: a real-life case adapted for use in an undergraduate developmental and systems neuroscience course. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016; 15 (1):C1–C3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brooke SL. Using the case method to teach online classes: promoting Socratic dialogue and critical thinking skills. IJTLHE. 2006; 18 (2):142–149. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownell SE, Price JV, Steinman L. A writing-intensive course improves biology undergraduates’ perception and confidence of their abilities to read scientific literature and communicate science. Advan in Physiol Edu. 2013; 37 :70–79. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Casteel M, Bridges K. Goodbye lecture: a student-led seminar approach for teaching upper division courses. Teach Psychol. 2007; 34 :107–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diseases & conditions. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2020. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/DiseasesConditions/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen Y, Johri A, Rangwala H. LAK ’18: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge. New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery; 2018. Running out of STEM: a comparative study across STEM majors of college students at-risk of dropping out early; pp. 270–279. Available at https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3170358.3170410 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook-Snyder DR. Using case studies to promote student engagement in primary literature data analysis and evaluation. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2017; 16 (1):C1–C6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cotner S, Ballen CJ. Can mixed assessment methods make biology classes more equitable? PLoS One. 2017; 12 (12):e0189610. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cyr NE. “Brevity is the soul of wit”: use of a stepwise project to teach concise scientific writing. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2017; 16 (1):A46–A51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson N, Major CH. Boundary crossings: cooperative learning, collaborative learning, and problem-based learning. J Excell Coll Teach. 2014; 25 (3&4):7–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Deslauriers L, McCarty LS, Miller K, Callaghan K, Kestin G. Measuring actual learning versus feeling of learning in response to being actively engaged in the classroom. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019; 116 (39):19251–19257. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fan J, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Cell Death Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration. Adv Neurobiol. 2017; 15 :403–425. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Faust JL, Paulson DR. Active learning in the college classroom. J Excel Coll Teach. 1998; 9 :3–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fink SL, Cookson BT. Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 2005; 73 (4):1907–1916. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flint RW, Jr, Dorr N. Social neuroscience at the College of Saint Rose: the art of team teaching in emerging areas of psychological science. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2010; 8 (2):A122–A127. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman S, Eddy SL, McDonough M, Smith MK, Okoroafor N, Jordt H, Wenderoth MP. Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014; 111 (23):8410–8415. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freestone N. Drafting and acting on feedback supports student learning when writing essay assignments. Adv Physiol Educ. 2009; 33 (2):98–102. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gottesman AJ, Hoskins SG. CREATE cornerstone: introduction to scientific thinking, a new course for STEM-interested freshmen, demystifies scientific thinking through analysis of scientific literature. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2013; 12 (1):59–72. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Graham MJ, Frederick J, Byars-Winston A, Hunter AB, Handelsman J. Science education. Increasing persistence of college students in STEM. Science. 2013; 341 (6153):1455–1456. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haak DC, HilleRisLambers J, Pitre E, Freeman S. Increased structure and active learning reduce the achievement gap in introductory biology. Science. 2011; 332 (6034):1213–1216. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Handelsman J, Ebert-May D, Beichner R, Bruns P, Chang A, DeHaan R, Gentile J, Lauffer S, Stewart J, Tilghman SM, Wood WB. Scientific teaching. Science. 2004; 304 :521–522. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Herreid CF, editor. Start with a story: the case study method of teaching college science. Arlington, VA: NSTA Press; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Herreid CF, Schiller NA, Herreid KF. Science stories: using case studies to teach critical thinking. Arlington, VA: NSTA Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Holstein SE, Mickley Steinmetz KR, Miles JD. Teaching science writing in an introductory lab course. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2015; 13 (2):A101–A109. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jellinger KA. Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: a critical update. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14 (3):457–487. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ. Principles of Neural Science. 5th edition. New York: McGraw Hill Medical; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kararo M, McCartney M. Annotated primary scientific literature: a pedagogical tool for undergraduate courses. PLoS Biol. 2019; 17 (1):e3000103. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurczek J, Johnson J. The student as teacher: reflections on collaborative learning in a senior seminar. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2014; 12 (2):A93–A99. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lang JM. Small teaching: everyday lessons from the science of learning. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemons ML. Locate the lesion: a project-based learning case that stimulates comprehension and application of neuroanatomy. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2017; 15 (2):C7–C10. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li ZH, Li CM, Ling P, Shen FH, Chen CH, Liu CC, Yu CK, Chen SH. Ribavirin reduces mortality in enterovirus 71-infected mice by decreasing viral replication. J Infect Dis. 2008; 197 (6):854–857. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lom B. Classroom activities: simple strategies to incorporate student-centered activities within undergraduate science lectures. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2012; 11 (1):A64–A71. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Long T, Zhang B, Fan R, Wu Y, Mo M, Luo J, Chang Y, Tian Q, Mei M, Jiang H, Luo Y, Guo X. Phosphoprotein gene of wild-type rabies virus plays a role in limiting viral pathogenicity and lowering the enhancement of BBB permeability. Front Microbiol. 2020; 11 :109. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mazur E. Education. Farewell, lecture? Science. 2009; 323 (5910):50–51. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mitrano DA. Two scientists share Nobel Prize for the first time! A case study developed for exploring the history of neuroanatomy. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2019; 17 (2):C1–C5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Muir GM. Mission-driven, manageable, and meaningful assessment of an undergraduate neuroscience program. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2015; 13 (3):A198–A205. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nagel A, Nicholas A. Drugs & the brain: case-based instruction for an undergraduate neuropharmacology course. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2017; 15 (2):C11–C14. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nath A, Berger JR. Clinical neurovirology. 2nd edition. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease [NIAID] Diseases & conditions. Rockville, MD: NIAID; 2020. Available at https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions . [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Disorders. Bethesda, MD: NIH Neurological Institutes; 2020. Available at https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders . [ Google Scholar ]
- Ogilvie JM, Ribbens E. Professor Eric can't see: a project-based learning case for neurobiology students. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016; 15 (1):C4–C6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ogilvie JM. The mysterious case of Patient X: a case study for neuroscience students. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2019; 18 (1):C1–C4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Penner MR. Building an inclusive classroom. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2018; 16 (3):A268–A272. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prichard JR. A changing tide: what the new 'foundations of behavior' section of the 2015 medical college admissions test® might mean for undergraduate neuroscience programs. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2015; 13 (2):E2–E6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prud’homme-Généreux A. Writing a journal case study. J Coll Sci Teach. 2016; 45 (6):65–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos RL, Guerico E, Levitan T, O’Malley S, Smith PT. A quantitative examination of undergraduate neuroscience majors applying and matriculation to osteopathic medical school. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016a; 14 (2):A87–A90. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos RL, Esposito AW, O’Malley S, Smith PT, Grisham W. Undergraduate neuroscience education in the U.S.: quantitative comparisons of programs and graduates in the broader context of undergraduate life sciences education. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016b; 15 (1):A1–A4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Racaniello VR. What is a virus? Virology Blog. 2004. Jul 28, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2004/07/28/what-is-a-virus/
- Racaniello VR. immunopathology: too much of a good thing. Virology Blog. 2009a. Jan 23, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/01/23/immunopathology-too-much-of-a-good-thing/
- Racaniello VR. Innate immune defenses. Virology Blog. 2009b. Jun 3, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/06/03/innate-immune-defenses/
- Racaniello VR. The inflammatory response. Virology Blog. 2009c. Jul 1, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/01/the-inflammatory-response/
- Racaniello VR. Adaptive immune defenses. Virology Blog. 2009d. Jul 3, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/03/adaptive-immune-defenses/
- Racaniello VR. Adaptive immune defenses: Antibodies. Virology Blog. 2009e. Jul 22, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/07/22/adaptive-immunedefenses-antibodies/
- Racaniello VR. How viruses are classified. Virology Blog. 2009f. Aug 7, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/08/07/how-viruses-are-classified .
- Racaniello VR. Simplifying virus classification: The Baltimore system. Virology Blog. 2009g. Aug 12, Available at https://www.virology.ws/2009/08/12/simplifying-virus-classification-the-baltimore-system/
- Racaniello VR. Virology Lectures 2020 #16: Acute infections Biology 4310: Virology. Columbia University; 2020b. Mar 30, Available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TQkg0mID-w8&feature=youtu.be . [ Google Scholar ]
- Racaniello VR. Virology Lectures 2020 #17: Persistent infections Biology 4310: Virology. Columbia University; 2020c. Apr 2, Available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oWRynTL8NI4&feature=youtu.be . [ Google Scholar ]
- Rayner G, Papakonstantinou T, Gleadow R, Abbott K. Iterative writing programs may generate higher student confidence about their ability to write, but not necessarily improved writing ability. J Acad Lang and Learn. 2014; 8 (2):A60–A71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rees F. The facilitator excellence handbook: Helping people work creatively and productively together. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roesch LA, Frenzel K. Nora's medulla: a problem-based learning case for neuroscience fundamentals. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016; 14 (2):C1–C3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rollins L. Meningitis in college students: using a case study to expose introductory neuroscience students to primary scientific literature and applications of neuroscience. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2020; 18 (2):C8–C1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sawyer NT, Frenzel KE. Epilepsy and the action potential: using case based instruction and primary literature in a neurobiology course. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2018; 16 (2):C7–C10. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schiano B, Anderson E. Teaching with cases: a practical guide. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Review Press; 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Soranno PA. Improving student discussions in graduate and undergraduate courses: transforming the discussion leader. J Nat Resour Life Sci Edu. 2010; 39 :84–91. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stavnezer AJ, Lom B. Student-led recaps and retrieval practice: a simple classroom activity emphasizing effective learning strategies. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2019; 18 (1):A1–A14. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Theobald EJ, et al. Active learning narrows achievement gaps for underrepresented students in undergraduate science, technology, engineering, and math. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020; 117 (12):6476–6483. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Trujillo G, Tanner KD. Considering the role of affect in learning: monitoring students' self-efficacy, sense of belonging, and science identity. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2014; 13 (1):6–15. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson TD. 'Without a key': a classroom case study. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2019; 18 (1):C5–C7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Widmaier EP, Raff H, Strang KT. Vander’s Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function. 13th edition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiertelak EP, Frenzel KE, Roesch LA. Case studies and neuroscience education: tools for effective teaching. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2016; 14 (2):E13–E14. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiertelak EP, Hardwick J, Kerchner M, Parfitt K, Ramirez JJ. The new blueprints: undergraduate neuroscience education in the twenty-first century. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2018; 16 (3):A244–A251. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang G, Zhou F, Gu B, Ding C, Feng D, Xie F, Wang J, Zhang C, Cao Q, Deng Y, Hu W, Yao K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ribavirin and pleconaril antiviral activity against enterovirus 71 infection. Arch Virol. 2012; 157 (4):669–679. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Case studies
Case studies allow you to apply what you are learning to a real-world example, or ‘case’. The case could be either an actual or hypothetical situation, person, business or organisation.
Case studies usually ask you to:
- describe the case
- identify key issues of the case
- analyse the case using relevant theory or concepts
- make recommendations for the case.
General tips for case studies
Analyse the task carefully.
Case studies vary between disciplines, so read the assignment instructions and marking rubric carefully to understand what is expected.
Some case study assignments will ask you to answer very specific questions related to the case. For other case studies, you will decide on the content by interpreting the case information and connecting it with what you have been learning.
Read the case information thoroughly
Read the case information multiple times. You can use a range of reading strategies, including:
- skimming to get an idea of the case study scenario
- scanning to find specific information relevant to the assignment
- reading in detail to develop an in-depth understanding of the case.
While reading, keep the task in mind and ask yourself relevant questions, such as:
- How does this case relate to what I have been learning in class?
- What issues are evident in the case?
- What are the causes of these issues?
- What are some possible solutions to these issues?
Highlight any important information and make notes with your answers to these questions.
Connect the case, theory or concepts, and your analysis
Use a mind map or table to help you make connections between the case and theory or concepts. Draw on what you remember from classes and prescribed readings, and then conduct further research to help you analyse the case.
Use a mind map or table to help you plan the structure and content of your writing.
Example mindmap - Nursing

Example table for note-taking - Cybersecurity
This table shows how the student has analysed case evidence to identify problems in the case. The student has then researched relevant theory and made recommendations to solve the problems.
| Evidence | Problem (Analysis) | Theory or concepts | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP front end for employees with password-only protection | Relies on strong passwords Vulnerable to attack Potential to add fake data to database | Attack vector: guessing password repeatedly (Kapersky 2019) Windows XP has account lockout after multiple incorrect guesses (Microsoft 2017), but this can be bypassed (CVE 2014). | Two-factor authentication |
| Windows Server 2012 with password-only protection | Vulnerable to attack as account lockout can be bypassed Potential for attackers to manipulate log files | Server admin accounts have access to sensitive information (Solarwinds 2019) Database breach and potential for data manipulation leads to integrity breach = data no longer legitimate or trusted (Henderson 2017) Manipulation of logs means attacker can’t be held accountable = breach of non-repudiation (IBM 2019). | Two-factor authentication |
Writing a case study
Case studies are commonly written in a report or essay format. Regardless of the format, all case studies should include three elements:
- facts from the case
- theory or concepts from literature (e.g. books, journals)
- your analysis.
This paragraph includes:
- case evidence (about Darren's drinking and smoking)
- theory (about the effect of alcohol and smoking and pain) and in-text citations (Chiang et al., 2016; Miyoshi, 2007)
- analysis (the implications for Darren's nursing care after the operation)
Darren’s potential for pain is also influenced by lifestyle factors including excessive drinking and long-term smoking. [Case evidence] Darren identifies as a social drinker and consumes two beers each day after work and up to ten beers per day on weekends. [Theory] Frequent consumption of alcohol at high levels can increase a postoperative patient’s need for pain-relieving opioid medications, due to stimulating neuropathic pain delivered through both peripheral nervous system and central nervous system (CNS) pathways (Miyoshi, 2007, p. 208). [Case evidence] In addition to his high alcohol consumption, Darren is a current smoker and has smoked 30 cigarettes per day for the past 20 years. [Theory] Chiang et al. (2016) found that patients who smoke metabolise analgesic medications faster than non-smokers, as nicotine stimulates the CNS and produces analgesia in low quantities, resulting in smokers having a lower pain tolerance or hyperalgesia. [Analysis] Therefore, Darren’s alcohol use and smoking status mean that he is likely to experience higher levels of pain and require higher amounts of analgesia following his operation.
Paragraph adapted and used with student permission
- case evidence (about access to Green Coin Company's network)
- theory (about attacks on passwords and Windows XP) and in-text citations (CVE 2014; Kapersky 2007; Windows 2017)
- analysis (the consequences of an attack on the company)
A major ICT weakness in Green Coin Company is that [Case evidence] employees access the network through a Windows XP frontend with a password authentication system. Passwords can be an effective way to authenticate into the system, provided that the password is strong and that the user keeps it secret. [Theory] However, a common attack vector on passwords is a trial-and-error approach where the attacker tries passwords repeatedly until they guess correctly and gain access to the network (Kapersky 2019). On a system with good security controls, the account will be locked out for a specified period after several wrong guesses, and an admin will be alerted that the account has been locked out (Windows 2017). However, Windows XP has a vulnerability that can bypass the lockout system, giving an attacker the ability to guess the password as many times as needed without being detected by the system (CVE 2014). [Analysis] If the attacker compromises an account that has access to the database, they will be able to add fake sales records, shipping requests and bullion transactions, thus compromising the integrity of the overall database.
For more complete example case studies with further annotations, see the Word and PDF documents below.
Example case studies
- Example case study - Nursing [Word - 68KB]
- Example case study - Nursing [PDF - 170KB]
- Example case study - Cybersecurity [Word - 61KB]
- Example case study - Cybersecurity [PDF - 168KB]
Pathfinder link
Still have questions? Do you want to talk to an expert? Peer Learning Advisors or Academic Skills and Language Advisors are available.
- << Previous: Reports
- Next: Reflective writing >>
Case Studies
Case studies (also called "case histories") are descriptions of real situations that provide a context for engineers and others to explore decision-making in the face of socio-technical issues, such as environmental, political, and ethical issues. case studies typically involve complex issues where there is no single correct answer--a student analyzing a case study may be asked to select the "best" answer given the situation 1 . a case study is not a demonstration of a valid or "best" decision or solution. on the contrary, unsuccessful or incomplete attempts at a solution are often included in the written account. 2.
The process of analyzing a case study encourages several learning tasks:
Exploring the nature of a problem and circumstances that affect a decision or solution
Learning about others' viewpoints and how they may be taken into account
Learning about one's own viewpoint
Defining one's own priorities
Making one's own decisions to solve a problem
Predicting outcomes and consequences 1
Student Learning Outcomes in Ethics
Most engineering case studies available pertain to engineering ethics. After a two year study of education in ethics sponsored by the Hastings Center, an interdisciplinary group agreed on five main outcomes for student learning in ethics:
Sensitivity to ethical issues, sometimes called "developing a moral imagination," or the awareness of the needs of others and that there is an ethical point of view;
Recognition of ethical issues or the ability to see the ethical implications of specific situations and choices;
Ability to analyze and critically evaluate ethical dilemmas, including an understanding of competing values, and the ability to scrutinize options for resolution;
Ethical responsibility, or the ability to make a decision and take action;
Tolerance for ambiguity, or the recognition that there may be no single ideal solution to ethically problematic situations 2 .
These outcomes would make an excellent list of attributes for designing a rubric for a case analysis.
Ideas for Case Study Assignments
To assign a case analysis, an instructor needs
skill in analyzing a case (and the ability to model that process for students)
skill in managing classroom discussion of a case
a case study
a specific assignment that will guide students' case analyses, and
a rubric for scoring students' case analyses.
Below are ideas for each of these five aspects of teaching with case studies. Another viewpoint is to consider how not to teach a case study .
1. Skill in analyzing a case
For many engineering instructors, analyzing cases is unfamiliar. Examining completed case analyses could help develop case analysis skills. As an exercise for building skill in analyzing cases, use the generic guidelines for case analysis assignments (#4 below) to carefully review some completed case analyses. A few completed case analyses are available:
Five example analyses of an engineering case study
Case study part 1 [Unger, S. The BART case: ethics and the employed engineer. IEEE CSIT Newsletter. September 1973 Issue 4, p 6.]
Case study part 2 [Friedlander, G. The case of the three engineers vs. BART. IEEE Spectrum. October 1974, p. 69-76.]
Case study part 3 [Friedlander, G. Bigger Bugs in BART? IEEE Spectrum . March 1973. p32,35,37.]
Case study with an example analysis
2. Skill in managing classroom discussion of a case
Managing classroom discussion of a case study requires planning.
Suggestions for using engineering cases in the classroom
Guidelines for leading classroom discussion of case studies
3. Case studies
Case studies should be complex enough and realistic enough to be challenging, yet be manageable within the time frame. It is time-consuming to create case studies, but there are a large number of engineering case studies online.
Online Case Libraries
Case Studies in Technology, Ethics, Environment, and Public Policy
Teaching Engineering Ethics: A Case Study Approach
The Online Ethics Center for Engineering and Science
Ethics Cases
The Engineering Case Library
Cases and Teaching Tips
4. A specific assignment that will guide students' case analyses
There are several types of case study assignment:
Nine approaches to using case studies for teaching
Written Case Analysis
Case Discussions
Case analyses typically include answering questions such as:
What kinds of problems are inherent in the situation?
Describe the socio-technical situation sufficiently to enable listeners (or readers) to understand the situation faced by the central character in the case.
Identify and characterize the issue or conflict central to the situation. Identify the parties involved in the situation. Describe the origins, structure, and trajectory of the conflict.
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the arguments made by each party.
How would these problems affect the outcomes of the situation?
Describe the possible actions that could have been taken by the central character in the case.
Describe, for each possible action, what the potential outcomes might be for each party involved.
Describe what action was actually taken and the outcomes for each party involved.
How would you solve these problems? Why?
Describe the action you would take if you were the central character in the case. Explain why.
What should the central character in the situation do? Why?
Describe the action you think that the central character in the case should take. Explain why.
What can be learned from this case?
Delineate the lessons about ethical (or other) issues in engineering that are illuminated by this case.
This list is adapted from two online case analysis assignments by McGinn from 3 & 4 ):
5. A rubric for scoring students' case analyses
Case studies help students explore decision-making in the face of issues. Thus, for an engineering ethics case study, the outcomes that can be assessed by scoring case analyses are a) sensitivity to ethical issues, b) recognition of ethical issues, c) the ability to analyze and critically evaluate ethical dilemmas, d) the ability to make an ethical decision and take action, and e) tolerance for ambiguity. Scoring rubrics for ethics case analyses should address these outcomes, not basic knowledge of the ethical standards of the profession. Professional standards can best be assessed by a traditional graded exam in which students must demonstrate, for example, which practices are ethically acceptable versus which are in violation of ethical standards given a hypothetical scenario 5 .
Making Scoring/Grading Useful for Assessment
General principles for making scoring/grading useful for assessment ( rubrics )
Example rubrics
For a written analysis of a case study in engineering
For a written analysis of a case study in general #1
For a written analysis of a case study in general #2
For a written and oral analysis of a case study by a group
For an oral analysis of a case study by a group
For a written analysis of a case study on ethics
For a self-assessment of learning from a case study
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Writing A Case Study
Case Study Examples
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
15 min read
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
It’s no surprise that writing a case study is one of the most challenging academic tasks for students. You’re definitely not alone here!
Most people don't realize that there are specific guidelines to follow when writing a case study. If you don't know where to start, it's easy to get overwhelmed and give up before you even begin.
Don't worry! Let us help you out!
We've collected over 25 free case study examples with solutions just for you. These samples with solutions will help you win over your panel and score high marks on your case studies.
So, what are you waiting for? Let's dive in and learn the secrets to writing a successful case study.
- 1. An Overview of Case Studies
- 2. Case Study Examples for Students
- 3. Business Case Study Examples
- 4. Medical Case Study Examples
- 5. Psychology Case Study Examples
- 6. Sales Case Study Examples
- 7. Interview Case Study Examples
- 8. Marketing Case Study Examples
- 9. Tips to Write a Good Case Study
An Overview of Case Studies
A case study is a research method used to study a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves analyzing and interpreting data from a variety of sources to gain insight into the subject being studied.
Case studies are often used in psychology, business, and education to explore complicated problems and find solutions. They usually have detailed descriptions of the subject, background info, and an analysis of the main issues.
The goal of a case study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Typically, case studies can be divided into three parts, challenges, solutions, and results.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is:
Case Study Sample PDF
How to Write a Case Study Examples
Learn how to write a case study with the help of our comprehensive case study guide.
Case Study Examples for Students
Quite often, students are asked to present case studies in their academic journeys. The reason instructors assign case studies is for students to sharpen their critical analysis skills, understand how companies make profits, etc.
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students:
|
Case Study Example in Software Engineering
Qualitative Research Case Study Sample
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
Social Work Case Study Example
Ethical Case Study
Case Study Example PDF
These examples can guide you on how to structure and format your own case studies.
Struggling with formatting your case study? Check this case study format guide and perfect your document’s structure today.

Business Case Study Examples
A business case study examines a business’s specific challenge or goal and how it should be solved. Business case studies usually focus on several details related to the initial challenge and proposed solution.
To help you out, here are some samples so you can create case studies that are related to businesses:
|
|
Here are some more business case study examples:
Business Case Studies PDF
Business Case Studies Example
Typically, a business case study discovers one of your customer's stories and how you solved a problem for them. It allows your prospects to see how your solutions address their needs.
Medical Case Study Examples
Medical case studies are an essential part of medical education. They help students to understand how to diagnose and treat patients.
Here are some medical case study examples to help you.
Medical Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Example
Want to understand the various types of case studies? Check out our types of case study blog to select the perfect type.
Psychology Case Study Examples
Case studies are a great way of investigating individuals with psychological abnormalities. This is why it is a very common assignment in psychology courses.
By examining all the aspects of your subject’s life, you discover the possible causes of exhibiting such behavior.
For your help, here are some interesting psychology case study examples:
Psychology Case Study Example
Mental Health Case Study Example
Sales Case Study Examples
Case studies are important tools for sales teams’ performance improvement. By examining sales successes, teams can gain insights into effective strategies and create action plans to employ similar tactics.
By researching case studies of successful sales campaigns, sales teams can more accurately identify challenges and develop solutions.
Sales Case Study Example
Interview Case Study Examples
Interview case studies provide businesses with invaluable information. This data allows them to make informed decisions related to certain markets or subjects.
Interview Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Examples
Marketing case studies are real-life stories that showcase how a business solves a problem. They typically discuss how a business achieves a goal using a specific marketing strategy or tactic.
They typically describe a challenge faced by a business, the solution implemented, and the results achieved.
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like.
: ABC Solutions, a leading provider of tech products and services.
Engaging and informative content highlighting products and services. Incorporating real-world examples to showcase the impact of ABC Solutions. Utilizing analytics to refine content strategies. Aligning content with customer needs and pain points. Content marketing efforts led to a significant boost in brand visibility. Compelling narratives highlighting how products and services transformed businesses.
|
Here are some more popular marketing studies that show how companies use case studies as a means of marketing and promotion:
“Chevrolet Discover the Unexpected” by Carol H. Williams
This case study explores Chevrolet's “ DTU Journalism Fellows ” program. The case study uses the initials “DTU” to generate interest and encourage readers to learn more.
Multiple types of media, such as images and videos, are used to explain the challenges faced. The case study concludes with an overview of the achievements that were met.
Key points from the case study include:
- Using a well-known brand name in the title can create interest.
- Combining different media types, such as headings, images, and videos, can help engage readers and make the content more memorable.
- Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
“The Met” by Fantasy
“ The Met ” by Fantasy is a fictional redesign of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, created by the design studio Fantasy. The case study clearly and simply showcases the museum's website redesign.
The Met emphasizes the website’s features and interface by showcasing each section of the interface individually, allowing the readers to concentrate on the significant elements.
For those who prefer text, each feature includes an objective description. The case study also includes a “Contact Us” call-to-action at the bottom of the page, inviting visitors to contact the company.
Key points from this “The Met” include:
- Keeping the case study simple and clean can help readers focus on the most important aspects.
- Presenting the features and solutions with a visual showcase can be more effective than writing a lot of text.
- Including a clear call-to-action at the end of the case study can encourage visitors to contact the company for more information.
“Better Experiences for All” by Herman Miller
Herman Miller's minimalist approach to furniture design translates to their case study, “ Better Experiences for All ”, for a Dubai hospital. The page features a captivating video with closed-captioning and expandable text for accessibility.
The case study presents a wealth of information in a concise format, enabling users to grasp the complexities of the strategy with ease. It concludes with a client testimonial and a list of furniture items purchased from the brand.
Key points from the “Better Experiences” include:
- Make sure your case study is user-friendly by including accessibility features like closed captioning and expandable text.
- Include a list of products that were used in the project to guide potential customers.
“NetApp” by Evisort
Evisort's case study on “ NetApp ” stands out for its informative and compelling approach. The study begins with a client-centric overview of NetApp, strategically directing attention to the client rather than the company or team involved.
The case study incorporates client quotes and explores NetApp’s challenges during COVID-19. Evisort showcases its value as a client partner by showing how its services supported NetApp through difficult times.
- Provide an overview of the company in the client’s words, and put focus on the customer.
- Highlight how your services can help clients during challenging times.
- Make your case study accessible by providing it in various formats.
“Red Sox Season Campaign,” by CTP Boston
The “ Red Sox Season Campaign ” showcases a perfect blend of different media, such as video, text, and images. Upon visiting the page, the video plays automatically, there are videos of Red Sox players, their images, and print ads that can be enlarged with a click.
The page features an intuitive design and invites viewers to appreciate CTP's well-rounded campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team. There’s also a CTA that prompts viewers to learn how CTP can create a similar campaign for their brand.
Some key points to take away from the “Red Sox Season Campaign”:
- Including a variety of media such as video, images, and text can make your case study more engaging and compelling.
- Include a call-to-action at the end of your study that encourages viewers to take the next step towards becoming a customer or prospect.
“Airbnb + Zendesk” by Zendesk
The case study by Zendesk, titled “ Airbnb + Zendesk : Building a powerful solution together,” showcases a true partnership between Airbnb and Zendesk.
The article begins with an intriguing opening statement, “Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend,” and uses stunning images of beautiful Airbnb locations to captivate readers.
Instead of solely highlighting Zendesk's product, the case study is crafted to tell a good story and highlight Airbnb's service in detail. This strategy makes the case study more authentic and relatable.
Some key points to take away from this case study are:
- Use client's offerings' images rather than just screenshots of your own product or service.
- To begin the case study, it is recommended to include a distinct CTA. For instance, Zendesk presents two alternatives, namely to initiate a trial or seek a solution.
“Influencer Marketing” by Trend and WarbyParker
The case study "Influencer Marketing" by Trend and Warby Parker highlights the potential of influencer content marketing, even when working with a limited budget.
The “Wearing Warby” campaign involved influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses during their daily activities, providing a glimpse of the brand's products in use.
This strategy enhanced the brand's relatability with influencers' followers. While not detailing specific tactics, the case study effectively illustrates the impact of third-person case studies in showcasing campaign results.
Key points to take away from this case study are:
- Influencer marketing can be effective even with a limited budget.
- Showcasing products being used in everyday life can make a brand more approachable and relatable.
- Third-person case studies can be useful in highlighting the success of a campaign.
Marketing Case Study Template
Marketing Case Study Example
Now that you have read multiple case study examples, hop on to our tips.
Tips to Write a Good Case Study
Here are some note-worthy tips to craft a winning case study
- Define the purpose of the case study This will help you to focus on the most important aspects of the case. The case study objective helps to ensure that your finished product is concise and to the point.
- Choose a real-life example. One of the best ways to write a successful case study is to choose a real-life example. This will give your readers a chance to see how the concepts apply in a real-world setting.
- Keep it brief. This means that you should only include information that is directly relevant to your topic and avoid adding unnecessary details.
- Use strong evidence. To make your case study convincing, you will need to use strong evidence. This can include statistics, data from research studies, or quotes from experts in the field.
- Edit and proofread your work. Before you submit your case study, be sure to edit and proofread your work carefully. This will help to ensure that there are no errors and that your paper is clear and concise.
There you go!
We’re sure that now you have secrets to writing a great case study at your fingertips! This blog teaches the key guidelines of various case studies with samples. So grab your pen and start crafting a winning case study right away!
Having said that, we do understand that some of you might be having a hard time writing compelling case studies.
But worry not! Our expert case study writing service is here to take all your case-writing blues away!
With 100% thorough research guaranteed, we can craft an amazing case study within 24 hours!
Besides, if you're pressed for time, simply uttering the words just do my essay for me will get your essay done quickly and flawlessly!
So why delay? Let us help you shine in the eyes of your instructor!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
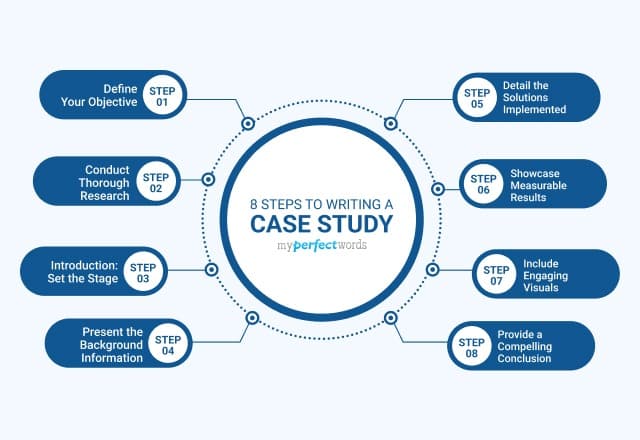
- TemplateLab
Case Study Templates
49 free case study examples & templates.
A case study is a report of an event, problem or activity. A case study format usually contains a hypothetical or real situation. It would also include any intricacies you might come across in the workplace.
You can use a case study to help you see how these intricacies might affect decisions.
Table of Contents
- 1 Case Study Templates
- 2 Common types of case study templates
- 3 Case Study Examples
- 4 Benefits of using case study templates in businesses
- 5 Case Study Formats
- 6 Tips for writing a case study template
- 7.1 Decide on the type of case study you will perform
- 7.2 Reach out to potential participants for your case study
- 7.3 Prepare your questions
- 7.4 Lay out the case study
When you make a case analysis format, you would have to analyze the situation at hand. You have to apply your own thinking skills and knowledge when performing the case study.
Also, doing this will hone your reasoning skills and your ability to draw conclusions. An effective case study example should:
- Have their basis from real-life situations but you may conceal identities.
- Consist of a number of parts which would end with points for discussion.
- Include enough information the reader can use to deal with issues and problems.
- Be very believable for anyone who reads it.

A case study is a type of research methodology. It’s typically utilized in social sciences. When you do this, you’d have to study a phenomenon or issue from a real-life perspective.
Such studies are usually based on in-depth analysis of a person, a group or even an event. You perform them to investigate the underlying causes of specific principles.
Common types of case study templates
Anyone who wants to perform a collective study may use a case study format. You can create a case analysis format on your own or download a template from here.
When you use such templates, you won’t have to think about what you need to include in your document. You can focus more on the individual, group, or event that you’re studying.
You can use different types of templates you can use for your case study. These include:
- Student case study template
- Nursing case study template
- Clinical case study template
- Memorial hospital case study template
- Basic psychology case study template
- Treatment injury case study template
Create or find a template which would suit your own needs. There aren’t any strict formats for these documents. The process is more important. In fact, some people see a case study as a type of research strategy. You can use it to investigate a phenomenon and see its influence over time. When do the process, you’d need a template to input all the information from your study.
Case Study Examples

Benefits of using case study templates in businesses
Before we discuss how to write a case study, let’s go through its benefits. The document you create while conducting your study is very relevant. When decision-makers do research on a new product, they would use this document as a reference.
They can help you identify possible solutions to their problems. This is why it’s important to keep the documents along with other important files. Serving as a reference is only one of the benefits of creating and using such templates. Here are the other benefits:
- To help influence customers more effectively In businesses, customer testimonials are extremely important. You can use them to see what you need to do to keep your business going. A case study example can be a form of support from a satisfied customer given directly to the business. You can use the template to bulk up your marketing campaign. It can serve the same purpose as product reviews on online shops like Amazon. These reviews can sway the buyers in a positive way. So you can use the case study to raise awareness on how to serve your customers more effectively. This will help encourage your customers and increase sales .
- To help encourage empathy The information contained within the document may help encourage empathy in its readers. In businesses, it may help the customers see how the product will help or work for them. To make it more effective, the document should focus on the readers and not the product you’re selling. You can describe real-life issues and explain how your product helped solve them. This would make the customers see why they need your product. It may also help your customers see why they need to patronize your business over others.
- To show that you understand and care for the customers When it comes to businesses, case studies are usually focused on their products and sales. However, this isn’t advisable as customers aren’t really fooled by such strategies. Instead, your document should address questions and issues which your customers frequently encounter. When you create such a document through your study, it will show that you care about the customers. It will help them see that you put in an effort to understand them and cater to their needs.
- To strengthen the brand When you create a case study, you can use it to strengthen your brand. Since it’s typically based on real-life situations, it becomes relatable. Through this document, you can create an emotional connection with your customers. If you can execute the study and the document well, it will be very beneficial for your business . You can show the customers that you have what they need. This will help make your brand stronger and more established.
- To repurpose content Finally, you can also use the document’s content for other things. This serves as a benefit because repurposing the content will save you a lot of time and money. You can use the document as a reference to create other written works for your business. You can also use the document as a basis to create another case study in the future. Create a similar template which focuses on other types of customers. These customers are the ones who patronize your business.
Case Study Formats
Tips for writing a case study template
You can use case studies for different purposes. In social science, it can help you understand the situations and problems of other people. In education, it can help you see how certain factors affect student academics.
In businesses, it can help earn the trust of potential customers. But do you know how to write a case study?
For some people, writing a case analysis format comes easy. For some, they need to look at some case study examples before they start making their own document. You can also download a template from here if you want to make things easier for you.
Case Analysis Formats

If you want to prove something you believe in, you need to create a compelling case study template. When you’ve done so, this will have a powerfully positive impact on what you made it for. Here are some tips, steps, and guidelines to help you out:
Decide on the type of case study you will perform
First and foremost, you need to determine which type of case study you will perform. You need to plan your case study well. You don’t just pick a topic then write about it. You need to find a cause you really believe in or a problem you want to solve.
In business, you need to focus on your customers. If you want to sell your products and services, think about your customers. Here are some things you can consider when making a case study for your business:
- When you make your study, be sure you have an extensive knowledge of your products. Without this knowledge, you won’t be able to create an effective document. One which will connect with your readers or your customers.
- If you want to show the best side of your business, be smart when creating your document. Find customers who have wonderful things to say about your product. Use their testimonials in your document. Do this to encourage your readers to support your business.
- Remember that the case study can help strengthen your brand. That’s why it’s important to create a study which will really make your business stand out. Think about how you’d like to present your information.
Reach out to potential participants for your case study
Without participants, you won’t have a case study. Prepare everything you need to before reaching out to your potential participants. Ensure them that there will always be open communication throughout the process.
This means that you’d have to prepare your timeline and expectations right away. This will help avoid any delays in the process.
Before talking to participants, you should already know what you’ll ask of them. For instance, you may want to ask permission to share the information you gather publicly.
You can send a letter or an email to your participants asking them to be part of your study. In the letter, include what you expect from them and what they can expect from you.
This will give them a good idea of what they need to do and prepare. Your introductory letter should contain:
- A clear and concise explanation of your purpose for creating the case study. Also, indicate how you will use the information you collect.
- A statement which would define the information which you’re planning to include. This is especially important if you will add trademarked information about a company.
- A clear explanation of your expectations from the participants. If you have any expectations which extend beyond your case study, explain them too.
- A note about any compensation you’re offering to the participants.
You may also add other information as needed. After you’ve sent out your letter, there’s a whole process which would follow. From acceptance of your offer to the final approval, you need to know all the steps:
- First off, your participants need to accept your offer/proposal. Once they’ve done that, you can include them in your list of participants for the case study.
- Then, you can give your participants a questionnaire to complete. This would help you out as the information would come directly from them. A questionnaire is a very effective way to collect data from your participants.
- After this, you can interview your participants too. Schedule an interview with each of your participants. Before this though, you should have already prepared all your questions.
- Then you can start making a draft of your case study template. If you’re working with a team, have them review your draft before finalizing it. Otherwise, you can ask your superior or manager to review your document.
- After this, you can finalize your case study. Just make sure that you’ve checked and verified all the information on it.
If your participants ask for it, you can give them a copy of your finalized study. Either that or you can tell them where they can access the document. Do this if you’ve posted it online like on your company’s website .
Case study format may vary depending on different factors. These include the nature of the situation, how you intend to use the information, and more.

Prepare your questions
Let’s go back to the interview process. Before you give the questionnaires to your participants, prepare your questions. The same thing goes for your interviews. If you want to make a strong case study, you should have strong questions too.
Here are some examples to start you off. These are great questions to ask if you’re conducting a study for your business:
- What are you looking for in a product?
- Have you experienced any challenges before purchasing our product?
- What makes our product stand out?
- Why did you make the decision to choose our product?
- What benefits have you gained from using our product?
These are some excellent questions which will give you very useful information. The best part is, you’ll gather the data straight from your participants.
Lay out the case study
Finally, when you have all the information you need, you can start laying out your case study. There aren’t any standard rules for structuring this document. However, it’s important to include certain elements to make the document effective.
These include:
- The title which should be brief but compelling.
- The executive summary . This would describe the document in a brief but interesting way.
- The introduction which would contain information about you and your organization.
- The challenges which would describe the problem or issues. Those which pushed you to create the study.
- The description which states how you helped solve the problem.
- The results of your case study.
More Templates

Law School Letters Of Recommendation
Community Service Forms
Genogram Templates

Permission Slip Templates

Story Map Templates

Essay Outline Templates
- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Situational Judgement
- Deductive reasoning
- Critical thinking
- Spatial reasoning
- Error checking
- Verbal comprehension
- Reading comprehension
- Psychometric tests
- Personality test
- In-Tray exercise
- E-Tray exercise
- Group exercise
- Roleplay exercise
- Presentation exercise
- Analysis exercise
- Case study exercise
- Game based assessments
- Competency based assessment
- Strengths based assessment
- Strengths based interview
- Video interview
- Saville Assessment
- Talent Q / Korn Ferry
- Watson Glaser
- Test Partnership
- Clevry (Criterion)
- Criteria Corp
- Aon / Cut-e
- Sova Assessment
- Case Study Exercise
Case Study Exercises are commonly used in assessment centres, and often are unique to each company.
- Buy Full Practice Tests
- What is a Case Study exercise
Page contents:
How do case study exercises work.
Updated: 08 September 2022
Assessment Centre Exercises:
- Analysis Exercise
- Role Play Exercise
- Group Exercise
- Presentation Exercise
During an assessment day, it is common that you need to undertake a case study exercise. These exercises place candidates in real-life situations where they are tasked with solving problems faced by professionals in the real world. A case study typically involves being given various documents containing different information, either detailing a problem or situation that needs dealing with and requiring the candidate to resolve the issue at hand by formulating a plan. The problems or situation in the case study will be similar if not identical to problems encountered in the role itself. Candidates are also provided with background information to the elements of the case study, whether these be details of fictitious companies or sales figures, or other. The resolutions or solutions provided by the candidate regarding the problems are part of the assessment centre performance rating.
Why are case study exercises used?
Case study exercises are proficient predictors of role performance as they will resemble the work being done on the job. Therefore, case study exercises typically tilt highly on an assessment centre rating for candidates. Likewise, if a presentation exercise is required after the case study, based on details brought up during the case study, then your case study rating will likely impact your presentation exercise rating. Equally, this may manifest into the role play exercise which will do a similar thing to the presentation exercise – carrying on the case study situation. It is also entirely possible for the case study to be continued in a group exercise – which evaluate a candidate’s ability to work in a team. Given all this, you will need to perform well in the case study exercise to ensure a high rating.
What will the case study exercise be like?
As mentioned, the case study exercise you will be asked to perform will be similar to the type of work you will have to do in the role you are applying for.
The case study exercise may be purchased off the self from a test provider who specialize in the test style. This will mean that it won't be fully specific to the company you are applying to, but will be related to the role. Likewise, it can be designed bespoke if the organization requires specific role assessment. It's likely the larger and harder to get into the company is, the more tailored their exercises will be.
How can I prepare for the case study exercise?
Analysing technical documents and company reports may be helpful practice in preparation for a case study exercise. This will give a chance to familiarize yourself with the types of information typically found in these documents, and thus the case study exercise. Practicing case study exercises will also act as great preparation and they will provide a great insight into how they work and how they are to be handled. This will also prevent any unnecessary unknowns you could have before taking a case study exercise, as you will have already experienced how they work in practice.
We have an assessment centre pack which contains an example of the exercises you could face.
Browser does not support script.
- Departments and Institutes
- Research centres and groups
- Chair's Blog: Summer Term 2022
- Staff wellbeing
Case studies

Case studies usually involve real-life situations and often take the form of a problem-based inquiry approach; in other words students are presented with a complex real life situation that they are asked to find a solution to. “The benefits of utilizing case studies in instruction include the way that cases model how to think professionally about real problems and situations, helping candidates to think productively about concrete experiences” (Kleinfeld, 1990 in Ulanoff, Fingon and Beltran, 2009). The case study method involves placing students in the role of decision-makers and asking them to address a challenge that may confront a company, non-profit organisation or government department. In the absence of a single straightforward answer students are expected to exchange ideas, consider possible theoretical explanations and data, and weigh up possible solutions. Based on this exchange and evaluation of mixed data they are expected to come up with a decision, and choose a solution to the particular challenge. Though case study learning and assessment may take many forms the common thread is that the case study involves a real-life situation and finding solutions is the focus of the assessment.
Advantages of case studies
- Enables students to apply their knowledge and skills to real life situations.
- Can be undertaken individually or as a group assessment.
- Generally designed to assess the higher levels of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives (application, analysis and evaluation).
- Well adapted to multi- or inter-disciplinary learning.
- Calls on students to demonstrate a range of different skills such as the selection on information, analysis, decision-making problem-solving and presentation.
- In the case of a group-based approach students are given the opportunity to demonstrate their ability to collaborate and communicate effectively.
- Supports the development of a range of valuable employability skills which are likely to be attractive to employers and students alike.
Challenges of case studies
- Case studies can be used in time-constrained examinations but this method of assessment really lends itself better to a coursework approach.
- Can be a complex activity that involves negotiating a range of media that may be hard to contain in a controlled environment.
- It is important to have realistic expectations of what actually can be achieved.
- Planning and preparing for case study work can be time-consuming for teachers.
How students might experience case studies
There is some evidence to suggest that case studies increase students’ motivation. Students are often very interested in working on real life situations. It brings their learning alive and enables them not only to develop solutions to actual situations/problems but also to understand in new ways the valuable role that theory and relevant concepts can play as part of this process. In addition as part of their work on the case study they are clearly developing valuable transferable skills that they can take forward into the workplace and society at large. Students may not be used to this form of assessment so they will need clear guidance as to what is expected (length, format, main elements), a clear explanation of marking criteria as well as development in the different skills they will need to acquire in order to successfully complete the case study. These will in part depend on the nature of the case study - is data analysis involved?; where and how will students find relevant qualitative and quantitative data?; what is the appropriate way of citing and referencing?
Reliability, validity, fairness and inclusivity of case studies
Teaching and learning activities should be carefully designed to support the work on the case study or the development of the relevant skills and knowledge bases. From an inclusive design perspective case studies are an attractive form of learning and assessment. Depending on the nature of the inquiry students may be given a degree of choice over their case study and thus be in a position to bring their different backgrounds and experience to bear. In any case, it is important to ensure that the chosen case studies are accessible to all students taking the course. In the case of first year students the teacher may want to provide all the relevant materials to the students. For more advanced students, they may be expected to do some research and to identify relevant supporting materials for the case study inquiry. Where group work is involved a number of options may be considered to ensure fairness. The students may complete some elements of both formative and summative work as a group as well as others individually. For example, students may complete various tasks or give a presentation on the case study as a group but write up part of the final case study individually. In addition, it is relatively common practice to ask students engaged in groupwork to write a short reflective piece discussing their experience of group work. Students can also be asked to rate their contribution and the contribution of other members of the group using one of a number of online group assessment tools such as WebPA and Teammates.
How to maintain and ensure rigour in case studies
Critical to ensuring rigour is having clarity about the different parts of the case study or, in the case of a single assessment task, the criteria against which the assessment will be marked; the weight that will be attached to different parts of the assignment, and the marking scheme. Marking and moderation should follow departmental practice.
How to limit possible misconduct in case studies
Whether the students are working in groups or individually teachers can check that the work is the work of particular students by designing in opportunities to assess (formatively or summatively) work at several points in the assessment process. This can be done by asking students to present work in written or oral form – either by submitting assignment tasks via Moodle or making short presentations in class. In addition to serving as a check for misconduct this also provides an opportunity for teachers and peers to give constructive feedback on the development of the case study and as such constitutes good practice.
LSE examples
Daniel Ferreira discussed his use of case studies in teaching Master’s level Finance students for many years, and, starting in 2016/17 undergraduates with the introduction of the Finance department’s new BSc programme
http://lti.lse.ac.uk/lse-innovators/irene-papanicolas-healthy-collaboration/
Further resources
University of New South Wales, Sydney: Assessment by Case Studies and Scenarios https://teaching.unsw.edu.au/assessment-case-studies-and-scenarios
Assessment Resources at Hong Kong University: Types of Assessment Methods: Case Study http://ar.cetl.hku.hk/am_case_study.htm
Bonney, K.M. (2015) Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains. Journal of Microbiological Education , 16(1): 21–28
Ulanoff, S.H., Fingon, J.C. and Beltrán, D. (2009) Using Case Studies To Assess Candidates’ Knowledge and Skills in a Graduate Reading Program, Teacher Education Quarterly, 6(2): 125-142
Fry, H., Ketteridge, S. and Marshall, S. (1999) A Handbook for Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, Routledge, UK
Back to Assessment methods

Back to Toolkit Main page

Contact your Eden Centre departmental adviser

If you have any suggestions for future Toolkit development, get in touch using our email below!
Email: [email protected].
- Monash Online
Student Academic Success
- 1:1 Consultation 1:1 Consultation
- Study better Study better
- Build digital capabilities Build digital capabilities
- Understand assessments Understand assessments
- Excel at writing Excel at writing
- Enhance your thinking Enhance your thinking
- Present confidently Present confidently
- Collaborate with others Collaborate with others
- Improve your academic English Improve your academic English
- Maintain academic integrity Maintain academic integrity
- Advance your graduate studies Advance your graduate studies
- O-week workshops O-week workshops
- Let's Talk Assessments Let's Talk Assessments
- Set up for academic success Set up for academic success
- Writing classes Writing classes
- End of semester End of semester
- PhD writing workshops and courses PhD writing workshops and courses
- First Year Undergraduate Success First Year Undergraduate Success
- Graduate coursework success Graduate coursework success
- Academic Language Skills Analysis Academic Language Skills Analysis
- Mathematics skills analysis Mathematics skills analysis
- Orientation Orientation
- SAS cafe SAS cafe
- SAS pop up SAS pop up
- Written Feedback Written Feedback
- About us About us
- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation
Case study example
Atlanta public schools case study.
In 2011, an external investigation of the performance evaluation strategies of the Atlanta Public Schools System revealed that schools had been cheating to obtain high results. For this example case analysis, the student has identified the problems faced by the organisation, outlined factors that contributed to the problem, and proposed solutions and recommendations.
The following case analysis is annotated with tips and explanations in each section. Click the icons to display the annotations. Note that for your actual assignment you may not be required to include all sections in the example case analysis here – check your assignment instructions carefully.
This resource has demonstrated the main steps in producing a case study assignment.
These steps will help you to identify what has happened in a case situation, why it happened, and apply relevant theory. Remember that some case studies require you to evaluate and recommend solutions.
You will need to:
- identify the problems in a case, and
- analyse the problems.
You may also need to:
- develop and evaluate alternative solutions, and
- make recommendations for action.
Remember to check your assignment instructions carefully to determine the type of case study you are required to write. Some units may require you to follow a particular style or structure. Check unit information for templates or guides to ensure that you meet these expectations.
Kimberley, N. (2016). StudentQ Manual (6th ed.) . Faculty of Business and Economics, Monash University.
Van Weelden, S. J. & Busuttil, L. (2018). Student guide to the case method . Ivey Publishing.
Navigating this resource
You can navigate the pages in this resource by either clicking on the page links here or by clicking the navigation buttons below.
What is a case study
Six steps to approaching a case study, how to write up a case study, your feedback matters.
We want to hear from you! Let us know what you found most useful or share your suggestions for improving this resource.

National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment
- Mission & Vision
- National Advisory Panel
- NILOA Staff
- Partner & Collaborating Organizations
- Occasional Papers
- Assessment in Practice
- Case Studies
- Assignment Library
- Featured Assignments
- Assignment Charrette
- Equity Responses
- Transparency Framework
- Excellence in Assessment
- Evidence-Based Storytelling
- Featured Websites Archive
- Curriculum Mapping
- Learning Recognition Collaborative
- Degree Qualifications Profile
- Assessment Resources
- Newsletters
- NILOA Surveys Archive
- Resources for Newcomers
- LARC Assessment Modules
- Questions at Hand
- Audience Type
Case studies provide short, instructive examples of good assessment practice, along with lessons learned that are widely applicable.

Alverno College is a case study site due to innovative and long-standing assessment practices as well as a commitment to student-centered teaching. Although Alverno is well established in its assessment practices, other institutions can learn from and adapt many aspects of Alverno’s assessment model to improve and sustain their own meaningful assessment work.

American Public University System (APUS) is a case study site for its unique mission and significant headway made in working with the Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP), leading to institution-wide implementation and adoption, the thoughtful process for working through DQP use, the development of signature assignments, and the incorporation of the DQP framework into the university system’s program review process.

Augustana College is a case study site due to its approach to faculty involvement and a long-standing commitment to assessing and communicating student learning. Augustana’s focus on teaching and learning, the dynamic role of the Assessment Review Committee, and communication strategies has allowed them to make several improvements on campus based on their assessment activities.
Capella University is a case study site for its systematic, embedded student learning outcomes assessment process; its administrative support and vision of what assessment can do for individual learners; its transparency efforts such as Capella Results, which publicizes assessment results; and its use of assessment results to enhance learner success.

Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) was selected as a case study for the approach to student learning outcomes assessment that reflects the institution’s commitment to interdisciplinarity and innovative teaching and learning. Three elements have been instrumental in CMU’s advances in program-level student learning outcomes assessment: 1) an institutionalized research-oriented and data-informed university decision-making process driven by deans and departments; 2) an organizational culture with established processes promoting continuous improvement; and 3) the elevation of a cross-campus faculty resource–the Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence–as the hub of assessment support. The original case study took place in 2012 with a follow-up study published in 2021 .

Colorado State University publicized its commitment to ensuring transparency and accountability to students, parents, and the public; expanded its continuous improvement system for managing information sharing to serve the decision-making and reporting needs of various audiences through the CSU Plan for Researching Improvement and Supporting Mission, or PRISM; uses a peer review system for feedback, and serves as a model for bridging the work of academic affairs and student affairs together through student learning outcomes assessment.

Daemen College is a case study site due to their involvement in the Council of Independent Colleges (CIC) consortium on the Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP). As part of this project, Daemen College engaged with the DQP to further their preexisting curricular mapping projects, as well as advance their newly instituted assessment program and assignment design initiative, including a co-curricular inventory.

Georgia State University (GSU) and Georgia Perimeter College (GPC) were selected as case study sites for its work in testing the Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) to facilitate transfer. The University of Georgia System project was a partnership between GSU and GPC to explore the application of the DQP to improve the success of transfer students in biology, psychology, and criminal justice programs that involve high numbers of transfer students between the two institutions.

Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI) was invited to write a case study because of its strong and rich history of using numerous forms of applied and experiential learning to promote student engagement along with its ongoing Comprehensive Learner Record (CLR) work.

Juniata College was identified as a case study site for the faculty-led Center for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (SoTL Center) that champions and supports evidence-based teaching; an administration-supported accountability website that provides data and information about outcomes to multiple audiences; and the use of evidence of student learning to make improvements at the institution and individual course levels.

Kansas City Kansas Community College (KCKCC) is a case study site due to its creation of an alternative system for documenting student achievement of Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) proficiencies. Based on an interactive curriculum mapping database where faculty enter information about individual student performance on each learning outcome and competency in their courses, reports are generated for students and programs to review and direct future action.

LaGuardia Community College is a case study site due to its reputation as a leader in learning outcomes assessment, particularly through the use of electronic portfolios (ePortfolios), commitment to assessment, collaboration across units at the college, and the institution’s robust program review system which includes assessment.

McKendree University is a case study site for its crosswalk of various learning frameworks (such as the Degree Qualifications Profile, LEAP Essential Learning Outcomes, National Collegiate Athletic Association’s (NCAA) Division II Life and Balance key attributes) to McKendree’s student learning outcomes, as well as the deliberate process of gaining campus awareness and support through their committee structure and learning outcome timeline. The original case study took place in 2016 with a follow-up study published in 2020 .

National Louis University is a Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) case study institution due to the intentional use of the DQP in the design of its Pathways Program including competency development, curricular focus, and assessment alignment. NLU’s use of the DQP provides an example for other institutions interested in using the DQP to develop new programs as well as curricular pathways that include a focus upon differentiated levels of learning.

North Carolina A&T State University is a case study site due to the commitment to improving the institution by developing a culture of inquiry through administrative leadership that encourages discussions and collaboration around student learning outcomes assessment activities; the use of professional development opportunities to help foster the involvement and commitment of faculty members; and the systematic and intentional use of student feedback.

Palo Alto College was selected as a NILOA case study based on its successful efforts in adapting NILOA’s assignment design toolkit to engage faculty, staff and students in assessment. Offering intimate workshops frequently throughout the academic calendar year has created a ground swell of faculty reinvesting themselves in the curriculum.

Point Loma Nazarene University is a case study site for its involvement of faculty and staff across a range of academic fields to move beyond conversations about outcomes and curriculum alignment to significant assessment activity that is comparable across programs, as well as their efforts in transparency of process and practice.

St. Olaf College is a case study institution due to the framing of assessment as inquiry in support of student learning that is meaningful, manageable, and mission-driven; the utilization-focus/backward-design approach employed in assessment; the integration of student learning outcomes assessment processes into faculty governance structures; along with the collaborative involvement of multiple stakeholders and diverse ways in which evidence of student learning is utilized throughout the institution. The original case took place in 2012 and the update occurred in 2020 .

Texas A&M International University (TAMIU) is a case study site for its commitment to choosing assessment measures and tools appropriate for its students; its long history with and innovative approach to assessment; and the influential role of professional development at the institution to help prepare “Assessment Champions and expand the number of pockets of excellence in terms of assessment practices throughout the campus.

University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign’s case study provides insight into how the Department of African American Studies at UIUC utilizes assessment in course design, being mindful of aligning diversity and inclusion outcomes within the course and program goals, and ensuring students attain these Case Study outcomes in both in-person and online courses utilizing equitable assessments and student involvement in the assessment process

Utah State University is a case study site for the faculty-led involvement in the state of Utah Tuning projects; integration of the Degree Qualifications Profile (DQP) with various programs and colleges on campus; and bridging the work of national initiatives such as Utah’s status as a LEAP state, participation in AAC&U’s Quality Collaboratives project, involvement with the Multi-State Collaborative and WICHE Passports Initiative, general education revision; and its integration of High-Impact Practices to make connections across the entire institution to better serve students.

Washington State University (WSU) is a case study site because of its promising approach to student learning outcomes assessment in the often-challenging context of a large, highly decentralized research university, characterized by a deliberately incremental and iterative process, moving the institution step-by-step toward habits, practices, and policies that support ongoing educational improvement.
Privacy Overview

- be_ixf; php_sdk; php_sdk_1.4.9
- iy_2024; im_09; id_25; ih_18; imh_24; i_epoch:1.72731387699E+12
- ixf-compiler; ixf-compiler_1.0.0.0
- py_2023; pm_11; pd_23; ph_04; pmh_15; p_epoch:1.7007417099E+12
- link-block; link-block_link-block; bodystr
- pn_tstr:Thu Nov 23 04:15:09 PST 2023; pn_epoch:1.7007417099E+12
Popular Searches
- Academic Calendar
- Course Schedule
- Admitted Students
- Current Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Faculty and Staff
- Event Planning
Home » Blog » Unlocking Development: A Case Study in Occupational Therapy for Infants
Unlocking Development: A Case Study in Occupational Therapy for Infants
BY Elizabeth Wanka | 4 MIN READ

Premature birth presents unique challenges for infants and their families, often leading to developmental delays due to the insufficient time spent in the womb. Michael’s story provides a compelling example of how targeted occupational therapy (OT) can significantly impact the developmental trajectory of a preterm infant. Here’s a closer look at how OT can make a difference.
Understanding Michael’s Journey
Michael entered the world 10 weeks earlier than expected, arriving at just 30 weeks of gestation. Premature birth can disrupt the typical developmental timeline, leading to delays in milestones such as head control, which is critical for further motor development. At four months old, Michael’s mother observed that he wasn’t yet holding his head up, a crucial skill typically emerging in the first few months of life. Recognizing this as a red flag, she sought early intervention through OT.
Assessment and Intervention
Assessment:.
The first step in Michael’s OT journey was a comprehensive assessment. The Occupational Therapist Practitioner (OTP) evaluated his fine motor skills and sensory processing abilities. For a baby his age, key developmental milestones include:
- Bringing hands to the mouth
- Pushing up onto elbows and forearms while in a prone position
These actions are essential for developing core strength, which is foundational for sitting, crawling, and eventually walking. The assessment aimed to pinpoint Michael’s developmental delays and to establish a baseline for his therapy goals.
Intervention:
With a clear understanding of Michael’s needs, the OTP designed an intervention plan tailored to his specific challenges. The focus was on integrating Michael’s favorite toys into therapy sessions to make the exercises engaging and motivating. For instance, the therapist placed Michael in a prone position and used toys to encourage him to lift his head and push up with his arms. This approach not only targeted his core strength but also helped him build coordination in a way that was enjoyable and stimulating.
The intervention strategy was grounded in the principle that therapy should be meaningful to the child. By incorporating toys that Michael enjoyed, the OTP increased his motivation to participate in the exercises, leading to more effective and enjoyable therapy sessions.
The Results
Michael’s journey through occupational therapy yielded impressive results. With consistent and targeted intervention, he reached significant developmental milestones: he was able to sit independently by six months and began walking by 13 months. These achievements underscore the effectiveness of the therapy in addressing his initial delays and supporting his overall development.
Key Takeaways for Occupational Therapy Practice
Michael’s case provides valuable insights into effective OT practice, particularly for premature infants:
- Assessment is Crucial: Accurate and thorough assessment of developmental milestones is essential in identifying delays and setting realistic goals. This process ensures that therapy is targeted and effective.
- Meaningful Interventions: Integrating a child’s interests into therapeutic activities can enhance engagement and motivation. In Michael’s case, using his favorite toys made the exercises more enjoyable and effective.
- Family Involvement: Understanding the family’s daily routines and values helps in designing interventions that fit seamlessly into the child’s natural environment. This collaboration ensures that therapy is practical and supportive of the family’s lifestyle.
- Monitoring Progress: Regularly tracking the child’s progress allows for adjustments to therapy goals and methods as needed. This dynamic approach ensures that the therapy remains relevant and responsive to the child’s evolving needs.
- Holistic Approach: Addressing both fine motor skills and sensory processing within the context of play promotes overall development. This comprehensive approach helps children achieve meaningful outcomes and supports their growth across various domains.
Michael’s case exemplifies the profound impact that individualized and targeted occupational therapy can have on the development of premature infants. By focusing on meaningful interventions, involving the family, and maintaining a holistic approach, OT practitioners can facilitate significant progress and help children like Michael reach their developmental potential.
Premature birth can set the stage for a range of developmental challenges, but with the right support and intervention, many children can overcome these obstacles and thrive. Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in this process, offering tailored strategies that address each child’s unique needs and capabilities. Michael’s story is a testament to the power of personalized therapy and the difference it can make in the lives of children and their families.
Elmhurst University’s Master of Occupational Therapy is one of many graduate programs within the health care family of programs in the School of Graduate Studies. To learn more, please fill out the form below.
About the Author

Dr. Elizabeth Wanka joined Elmhurst University after teaching at a master of occupational therapy and post-professional occupational therapy doctoral degree program. She is a registered and licensed occupational therapist.
Posted September 24, 2024

Unlocking the Meaning of Occupation: A Journey into Occupational Therapy
July 2, 2024 | 3 Minute Read

Should I Get a Master’s Degree in Occupational Therapy
August 1, 2023 | 5 Minute Read

Top 5 Questions and Answers About a Master’s in Occupational Therapy
May 17, 2022 | 4 Minute Read
Connect with #elmhurstu
Redirect Notice
Inclusion across the lifespan in human subjects research.
Learn about the Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy and how to comply with this policy in applications and progress reports. All human subjects research supported by NIH must include participants of all ages, including children and older adults, unless there are scientific or ethical reasons not to include them.
The purpose of the Inclusion Across the Lifespan Policy is to ensure individuals are included in clinical research in a manner appropriate to the scientific question under study so that the knowledge gained from NIH-funded research is applicable to all those affected by the researched diseases/conditions. The policy expands the Inclusion of Children in Clinical Research Policy to include individuals of all ages, including children and older adults . The policy also requires that the age at enrollment of each participant be collected in progress reports.
Implementation
The Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy is now in effect, and applies to all grant applications submitted for due dates on or after January 25, 2019 . The policy also applies to solicitations for Research & Development contracts issued January 25, 2019 or later, and intramural studies submitted on/after this date. Ongoing, non-competing awards will be expected to comply with the policy at the submission of a competing renewal application. Research that was submitted before January 25, 2019 continues to be subject to the Inclusion of Children in Clinical Research Policy .
Applications & Proposals
Applications and proposals involving human subjects research must address plans for including individuals across the lifespan in the PHS Human Subjects and Clinical Trial Information Form. Any age-related exclusions must include a rationale and justification based on a scientific or ethical basis. Refer to the PHS Human Subjects and Clinical Trial Information Form Instructions for complete guidance on what to address.
Peer Review
Scientific Review Groups will assess each application/proposal as being "acceptable" or "unacceptable" with regard to the age-appropriate inclusion or exclusion of individuals in the research project. For additional information on review considerations, refer to the Guidelines for the Review of Inclusion in Clinical Research . For information regarding the coding used to rate inclusion during peer review, see the list of NIH Peer Review Inclusion Codes .
Progress Reports
NIH recipients/offerors must submit individual-level data on participant age at enrollment in progress reports. Age at enrollment must be provided along with information on sex or gender, race, and ethnicity in the Inclusion Enrollment Report. Units for reporting age at enrollment range from minutes to years.
Policy Notices
| : NIH Policy and Guidelines on the Inclusion of Individuals Across the Lifespan as Participants in Research Involving Human Subjects | This policy revises previous policy and guidelines regarding the inclusion of children in research. Changes to the policy include (1) the applicability of the policy to individuals of all ages, (2) clarification of potentially acceptable reasons for excluding participants on age, and (3) a requirement to provide data on participant age at enrollment in progress reports. | December 19, 2017 |
| : Inclusion of Children in Clinical Research: Change in NIH Definition | For the purposes of inclusion policy, a child is defined as individuals under 18 years old. Applicants/offerors for NIH funding are still expected to justify the age range of the proposed participants in their clinical research. | October 13, 2015 |
| NIH Policy and Guidelines on The Inclusion of Children as Participants in Research Involving Human Subjects | The goal of this policy is to increase the participation of children in research so that adequate data will be developed to support the treatment modalities for disorders and conditions that affect adults and may also affect children. | March 6, 1998 |
| Infographic that walks through the elements of the existing dataset or resource definition to help users understand whether how it applies to their research. | August 2, 2024 | |
| Report on the representation of participants in human subjects studies from fiscal years 2018-2021 for FY2018 projects associated with the listed Research, Condition, and Disease Categorization (RCDC) categories. | October 31, 2023 | |
| This document describes several mock studies as examples of how to consider the Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy in study design and eligibility criteria. Examples include commentary on scientific and ethical reasons that may be acceptable or unacceptable for age-based exclusion. | September 09, 2023 | |
| This one-page resource highlights allowable costs for NIH grants that can be utilized to enhance inclusion through recruitment and retention activities. Allowable costs listed in the NIH Grants Policy Statement are provided with examples of inclusion-related activities. | August 10, 2023 | |
| April 20, 2022 | ||
| NIH’s Inclusion Policy Officer Dawn Corbett covers inclusion plans during peer review and post-award in Part 2 of this NIH All About Grants podcast miniseries. | April 20, 2022 | |
| Using the Participant-level Data Template | For research that falls under the Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy, submission of individual-level data is required in progress reports. This tip sheet serves as a quick guide for using the participant-level data template in the Human Subjects System to populate data in the cumulative (actual) enrollment table. | January 20, 2022 |
| : Recruitment and Retention | Document listing resources on recruitment and retention of women, racial and ethnic minorities, and individuals across the lifespan. Resources include toolkits, articles, and more. | May 9, 2022 |
| : Including Diverse Populations in NIH-funded Clinical Research | Video presentation by the NIH Inclusion Policy Officer for the NIH Grants Conference PreCon event, Human Subjects Research: Policies, Clinical Trials, & Inclusion, in December 2022. The presentation explains NIH inclusion policies and requirements for applicants and recipients. | January 27, 2023 |
| - (PDF - 1.1 MB) | Report summarizing the presentations and discussions that took place during the Inclusion Across the Lifespan II Workshop on September 2, 2020. | December 10, 2020 |
| : Some Thoughts Following the NIH Inclusion Across the Lifespan II Workshop | Blog post by NIH's Deputy Director of Extramural Research, Dr. Mike Lauer, highlighting the Inclusion Across the Lifespan II Workshop. | December 10, 2020 |
| Entering Inclusion Data Using the Participant Level Data Template | This video tutorial demonstrates how to enter inclusion data using the Participant Level Data Template in the Human Subjects System (HSS). | February 26, 2020 |
| Guidance for Applying the Inclusion Across the Lifespan Policy | At-a-glance guidance for complying with the policy in applications and progress reports. | May 3, 2019 |
| The Inclusion Across the Lifespan Policy | The "All About Grants" podcast featuring an interview with the NIH Inclusion Policy Officer about the Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy. | August 27, 2018 |
| HSS overview and training information | As of June 9, 2018, the Human Subjects System (HSS) replaced the Inclusion Management System (IMS). Similar to IMS, HSS is used by NIH staff, grant applicants, and recipients to manage human subjects information, including inclusion information. | May 25, 2018 |
| The Inclusion Across the Lifespan Policy | Blog post by Dr. Mike Lauer, Deputy Director of Extramural Research, and Dawn Corbett, NIH Inclusion Policy Officer, titled Understanding Age in the NIH Portfolio: Implementation of the NIH Inclusion Across the Lifespan Policy | November 13, 2018 |
| Inclusion Across the Lifespan | Summary report from the Inclusion Across the Lifespan workshop held June 1-2, 2017 | July, 2017 |
Upcoming Events
DHSR One pager of resources for external users
- Human Subjects Research
- National Institute on Aging
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- For NIH Staff
Have additional questions? Contact your program officer or the Inclusion policy team: [email protected]
- Cette page n'est pas disponible en Français
Case Study on the Use of Integrated Approaches for Testing and Assessment (IATA) for Chronic Toxicity and Carcinogenicity of Agrichemicals with Exemplar Case Studies - Ninth Review Cycle (2023)
- Environment
- Chemical safety and biosafety
- Assessment of chemicals
- Testing of chemicals

Cite this content as:
The objective of the Integrated Approaches for Testing and Assessment (IATA) Case Studies Project is to increase experience with the use of IATA by developing case studies which constitute examples of predictions that are fit for regulatory use. The aim of this project is to create common understanding of using novel methodologies and the generation of considerations/guidance stemming from these case studies. This case study was developed by the International Council on Animal Protection in OECD Programmes (ICAPO) to illustrate practical uses of IATA, and was submitted to the 2023 review cycle of the IATA Case Studies Project. The case study provides a framework to fulfil an IATA for chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity assessment through a weight of evidence (WoE)-based approach, in the absence of rodent cancer bioassays. The purpose of this IATA is to illustrate the use of the Rethinking Carcinogenicity Assessment for Agrichemicals Project (ReCAAP) framework, which is a scientific, WoE-based approach that allows the estimation of a Point of Departure (POD) for use in agrochemical risk assessment. To illustrate the use of the ReCAAP framework, two examples are presented in this IATA.
In the same series

Related publications
- Search Close search
- Find a journal
- Search calls for papers
- Journal Suggester
- Open access publishing
We’re here to help
Find guidance on Author Services
Open access
Investigating organised human trafficking crimes: case studies of police investigations in England
- Cite this article
- https://doi.org/10.1080/15614263.2024.2406841
Introduction
Sense-making and decision-making during criminal investigations, balancing investigative goals during human trafficking investigations, methodology, disclosure statement, additional information.
- Full Article
- Figures & data
- Reprints & Permissions
- View PDF PDF
Investigating organised human trafficking criminality is neither easy nor straightforward. Among the complexity is the need to balance and secure multiple, and often competing, investigative goals. Using case studies of actual human trafficking investigations in England, the present exploratory study provides insights into the tensions between safeguarding victims while also (at the same time) building up evidence against those who exploit them in order to secure a successful prosecution. Findings reveal that factors associated with the assessed level of risk of victims, the intelligence available at the start of the investigation and police resources (balanced with opportunities and risk to secure the investigative goals) influence the investigative approach followed and strategies implemented, particularly those aiming to engage with victims. The exploratory findings illustrate the importance of intelligence in risk assessment and decision-making processes during police operations, but also the need to conduct yet further research on risk assessment within the context of human trafficking investigations to inform policy and decision-making policing practices.
- Organised crime
- human trafficking
- decision-making
- risk assessment
- criminal investigation
The UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA Footnote 1 Citation 2021 ) estimates that around 70,000 individuals are involved in organised crime in the UK, many of whom are predicted to be involved in the exploitation and trafficking of vulnerable people (Europol, Citation 2021 ; NCA, Citation 2021 ). In 2023, the number of people referred to the UK’s National Referral Mechanism (NRM Footnote 2 ) was the highest ever. Of the 17,004 individuals referred to the NRM, 49% of the cases concerned individuals exploited within the UK (HM Government, Citation 2024 ). Contrary to common stereotypes of sex trafficking being the predominant form of exploitation and victims being predominantly female (Rodríguez-López, Citation 2018 ), UK statistics reveal a predominance of male victims and identify criminal and labour as the most prevalent forms of exploitation (HM Government, Citation 2024 ). Despite increased UK policing efforts to respond to the crimes and the rise of Human Trafficking (HT) police investigations (from 188 police operations in December 2016 to 3,335 in August 2021), this has only led to 1,175 prosecutions and 819 convictions between 2017–2020 (HM Government, Citation 2021 ). The involvement of victims as commodities (rather than ‘traditional’ commodities associated with organised crime, such as drugs or weapons) presents particular challenges that investigations into other organised criminality may not face. Throughout the course of HT investigations, detectives are faced with various dilemmas, particularly those tensions between preventing further suffering for victims while also (at the same time) having to build up evidence against those who exploit them to secure successful prosecution for their crimes (UNODC, Citation 2014 ). Hence, the decision on what action to take and what investigative route to follow is not always clear or straightforward (Verhoeven & Van Gestel, Citation 2011 ).
While victim safeguarding must be ensured throughout the course of the investigation with a view to promoting their recovery (Council Directive Citation 2011/36/EU ; UNODC, Citation 2009 ), research on HT police investigations has found that the goals of arrest and prosecution very often overweigh meeting victims’ needs (Farrell et al., Citation 2019 ). Despite policy and research recommendations to use victim-centred approaches in HT police operations (David, Citation 2007 ; Farrell et al., Citation 2012 ; Matos et al., Citation 2019 ; Pajon & Walsh, Citation 2020 , Citation 2022 ), the recent report on UK police response to trafficking and exploitation (HM Government, Citation 2022 ) points out the limitations on securing victim safeguarding and the inconsistent approaches when implementing victim-centred and trauma-informed policing practices. In particular, the report found a lack of clear priorities among officers on how to balance victims’ safeguarding needs, mainly when victims have engaged in criminal activities as a result of their exploitation or when they have entered the country illegally (HM Government, Citation 2022 ). Farrell et al. ( Citation 2019 ), when examining HT cases in the United States, also found that police responses need to transition to a more victim-centred approach, highlighting the need to move away from viewing the conviction of offenders as the main strategy to safeguard victims and ‘secure’ justice, and to focus more on the individuals’ needs and concerns through the criminal justice process.
This study set out to identify policing practices and examine investigative choices during HT investigations by examining case studies of actual investigations in England. Using sense-making and decision-making as a theoretical framework, the study will examine the factors influencing investigators’ decision-making on the investigative goals to pursue and the investigative actions to undertake. The purpose of the present study is not to generalise the results but to provide insight into the complexities of balancing investigative goals in HT investigations through the data-driven understanding of investigators’ justifications for the decisions taken.
Referring broadly to the investigation of crime, many authors consider it an information-driven practice (Innes, Citation 2003 ; O’Neill, Citation 2018 ; Stelfox, Citation 2009 ). That is, a criminal investigation is a complex form of sense-making involving a process composed of a series of actions that aim to produce knowledge to establish if, how, where, when, why and by whom a crime has been or will be committed (Ask, Citation 2006 ; Cook & Tattersall, Citation 2014 ; Innes, Citation 2003 ; O’Neill, Citation 2018 ). To this end, investigators will need to gather information, interpret and infer the meaning of such information, and decide what actions to take (Barrett, Citation 2009 ; Canter, Citation 2000 ; Fahsing & Ask, Citation 2013 ; Innes, Citation 2003 ; Stelfox, Citation 2009 ).
Barrett ( Citation 2009 ) argues that the investigation process can be viewed and studied from a problem-solving perspective. That is, the investigation of crime is a cyclical process of sense-making and action-taking. According to Barrett ( Citation 2009 ), the investigation process would start with (i) the recognition of the problem; continuing with (ii) the mental representation and definition of such problem, according to and in the context of the investigative goals; followed by (iii) the development and implementation of strategies or sequences of actions to target the different investigative subgoals; and, finally, (iv) the evaluation of those actions and its outcomes in relation to the end goal (Barrett, Citation 2009 ). Other authors have also found a similar cognitive pattern when examining investigative decision-making. Wright ( Citation 2013 ), for example, qualitatively analysed 40 detectives’ ‘think aloud’ accounts for homicide crime scenes, identifying a cognitive sequence composed of the following phases: (i) assessment of the crime scene; (ii) hypothesis generation of the nature of the event; (iii) inferences about the type of homicide; and (iv) decision-making on the next actions to take. Overall, research findings suggest the investigation process is formed of repetitive cycles of action, evaluation and decision, involving gathering information, then interpreting and evaluating the information available to generate explanations of what may have happened, followed by deciding on the lines of enquiry and the next course of actions to either confirm or falsify the hypothesis (Canter, Citation 2000 ; Stelfox, Citation 2009 ).
Investigators may obtain information from a wide variety of sources, such as the crime scene, witnesses, victims, or databases (Innes, Citation 2003 ; O’Neill, Citation 2018 ). Yet, it is less of a matter of quantity of information and more of relevance, accuracy and detail of the information obtained (Dando & Ormerod, Citation 2017 ; Fahsing & Ask, Citation 2017 ). Innes ( Citation 2021 ) introduced the concept of ‘mosaicking’ to refer to detectives articulating and blending together different types of information, intelligence and evidence to construct a case narrative. However, in most criminal investigations, and indeed in trafficking investigations, the information available and obtained is complex, incomplete, ambiguous, and even contradictory or irrelevant (Barrett, Citation 2009 ; Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Fahsing & Ask, Citation 2013 ; Wallace, Citation 2015 ). In such complex and uncertain situations, individuals tend to rely on heuristics and inferences to fill the gaps and form a coherent story of what has happened, combining both the specific information available for the case as well as their general knowledge/expertise of detective work (Barrett, Citation 2009 ; Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Wright, Citation 2013 ). Investigative sense-making is, therefore, understood as a pragmatic and abductive process, aiming to generate and evaluate different hypotheses to identify the most likely explanation (Fahsing & Ask, Citation 2017 ).
Abductive reasoning involves constructing the best possible account of complex and ambiguous events from limited information and intelligence (Innes, Citation 2003 ). During the sense-making process, cognitive frames are used to compare and order confusing situations (Maitlis & Christianson, Citation 2014 ). That is, cognitive frames help detectives contextualise the information and relate it to previous experiences and future expectations (Hallgren et al., Citation 2021 ). Research has found that detectives often use legal frames to make sense of the situation, looking for cues related to legally determined scripts (Ormerod et al., Citation 2008 ). However, relying on abductive reasoning and heuristics does not come without risks. Inadequate sense-making could lead to missed opportunities, wasting resources and time (Barrett, Citation 2009 ), and in complex crimes such as HT, it could even lead to further offences in addition to an increased number of victims being exploited. Besides, from an evidential perspective, the use of heuristics comes with risks, widely discussed in the criminal investigation literature, such as confirmation bias and tunnel vision (Ask & Alison, Citation 2010 ; Rossmo, Citation 2009 ), where investigators become narrowly focused (say on a suspect or a hypothesis) selecting evidence that confirms a hypothesis and ignoring other information which might undermine it (Findley & Scott, Citation 2006 ).
To avoid such risk, investigators should generate as many hypotheses as possible, gather as much relevant information and evidence as possible before deciding upon which lines of enquiry or courses of action to pursue, and exhaustively test as many hypotheses as possible (ACPO, Citation 2005 ; Innes, Citation 2003 ). However, in practice, research has often found that criminal investigations are defined by (i) uncertain, complex and dynamic environments; (ii) shifting and competing goals that investigation teams need to balance with time (and other resources) constraints; (iii) the interactions of multiple actors (including criminal justice professionals, media, members of the public); and (iv) dynamic risks (Dror & Fraser-Mackenzie, Citation 2009 ; Innes, Citation 2003 ). Hence, while decision-making upon which lines of enquiry to pursue and action to undertake is critical for the investigation process, investigative decision-making is undertaken in a context that is far from ideal (Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Innes, Citation 2003 ; Tong & Bowling, Citation 2006 ).
Previous research on decision-making and sense-making has identified a series of factors that prevent investigators from making decisions in optimal circumstances (Alison et al., Citation 2013 ; Ask, Citation 2006 ; Ask & Granhag, Citation 2005 , Citation 2007 , Fahsing & Ask Citation 2016 ; Kim et al., Citation 2020 ; Wallace, Citation 2015 ). Among the most commonly cited ones are time pressure and resources. Time pressure has been found to (i) affect the flexibility and creativity of the decision-maker, hence impacting the number of alternative hypotheses generated and strategies to test the hypotheses (Alison et al., Citation 2013 ; Kim et al., Citation 2020 ); (ii) lead to a more selective and biased search and assessment of information based on previous beliefs and expectations (Ask & Granhag, Citation 2005 ); and (iii) reduce investigators’ ability to keep an open mind, them becoming more reluctant to change their hypothesis in front of contradictory evidence (Ask & Granhag, Citation 2007 ). The negative effect of time pressure in decision-making is aggravated whenever there are ongoing risks (e.g., to people) involved, as critical decisions will need to be made in a very reduced time frame (Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ). For instance, in trafficking investigations, the unexpected identification of a minor under an exploitative situation while conducting surveillance will likely prompt a quick police response to remove the child from the risky situation. Yet, such a response could potentially blow up the police operation and put other victims in further danger/risk.
Those types of decisions, in which there is no easy or ideal course of action, are referred to as least-worst decisions; decisions in which any course of action will involve high risk and could potentially have significant and negative consequences for the investigation or actors involved in it (Power & Alison, Citation 2017 ). In this type of situation, the decision-maker would mentally represent the potential consequences and implications of different actions that could be undertaken (Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ). To this end, investigators will also use heuristics in the decision-making process by relying on their previous knowledge and experience, and so deciding which course of action to take (Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ; Wright, Citation 2013 ). For example, by reflecting on the actions taken in previous and similar situations that resulted in favourable outcomes (Ask, Citation 2006 ). Such cognitive strategies allow investigators to minimise the complexity and make pragmatic decisions based on the information available rather than on the information that could be obtained (Fahsing, Citation 2016 ). In such contexts, heuristics can become effective strategies for making sense of limited, complex or ambiguous information. Yet, they may also lead to decisions being made more efficiently but not always more effectively (Snook & Cullen, Citation 2009 ). Limited resources have also been found to influence the decision not to gather specific evidence that may be perceived as costly and time-consuming when investigators believe there is already enough evidence to prove the offence (Findley & Scott, Citation 2006 ). Moreover, limited resources and information may result in over-reliance on heuristics and cognitive shortcuts (Barrett, Citation 2009 ). Linked to limited resources, organisational pressures to close the case, or organisational and peer perception of indecisiveness as costly and resource-consuming may also promote a biased search and interpretation of evidence (Fahsing & Ask, Citation 2013 ; Wallace, Citation 2015 ).
During HT criminal operations, investigators are faced with a number of challenges, complexities and uncertainties, from the very early identification of cases to the conviction of offenders and safeguarding of victims, which, together, will likely influence investigators’ decisions and promote their reliance on heuristics when assessing intelligence available and deciding on what goals to pursue and what course of action to take to secure the investigative goals.
HT victims are unlikely to report their experiences to the police (Farrell et al., Citation 2019 ). Reasons include the lack of awareness of their own victimisation and legal rights (Meshkovska et al., Citation 2016 ), fear of retaliation (Newton et al., Citation 2008 ) or fear of being prosecuted or deported due to their involvement in illegal activities as a result of their exploitation (Farrell et al., Citation 2008 ). Additionally, victims might be reluctant to engage with the police due to previous negative experiences or the belief that they will not be believed or helped (Farrell et al., Citation 2008 , Citation 2012 ). The unwillingness of victims to cooperate and actively engage with the police, combined with the lack of training and police awareness on HT, could lead to an overreliance on heuristics and errors in sense-making, leading to the misidentification of victims as illegal immigrants or sex workers, mainly if they do not fit the stereotype of victims (Farrell & Pfeffer, Citation 2014 ; Raphael et al., Citation 2010 ).
Helfferich et al. ( Citation 2011 ), after interviewing 51 victims of exploitation, found that victims’ willingness to make a statement depends, among other factors, on how the police interact with them in the initial encounters and throughout the criminal investigation process. The authors found that factors related to building trust, having empathy, and recognising them as victims promoted victim engagement. Yet, getting the account from HT victims takes time and can become challenging and demanding due to incomplete and conflicting accounts, victims failing to remember specific details and other inaccuracies in the recollection of events due to trauma and/or fear (Clawson et al., Citation 2006 ; Cockbain & Brayley-Morris, Citation 2018 ). Furthermore, if undertaken incorrectly, victim interviewing could re-traumatise them, increase their anxiety and, ultimately, impede the recalling of information and long-term engagement (Farrell et al., Citation 2012 ; Meshkovska et al., Citation 2016 ). Such difficulties in gathering victims’ testimony, alongside resource constraints and time and organisational pressures to minimise risks and threats to victims and wider society (Brunovskis & Skilbrei, Citation 2016 ; David, Citation 2008 ; Farrell et al., Citation 2008 , Citation 2014 , Citation 2019 ), could explain why studies such as the one from De Vries and Farrell’s ( Citation 2023 ) examining police tactics in cases of exploitation found that the most predominant actions used in HT investigations were reactive tactics such as arrests and shutdowns of venues, despite police officers emphasising the need and relevance of victim-centred and trauma-informed approaches. The authors found that organisational priorities and structures, the need to coordinate a response with other agencies (and the time and effort that this implies), and time pressures to manage risk and prevent future victimisation were common justifications that explained the use of reactive practices.
According to sense-making and decision-making research (Barrett, Citation 2009 ; Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Wright, Citation 2013 ), the complexity and uncertainty that investigators face during HT investigations (alongside time and organisational pressures to close the case and safeguard victims at risk) will likely influence their decisions and promote reliance on heuristics to assess the intelligence available and decide what goals to pursue and what course of action to take to secure the investigative goals. This study will explore those factors that influence investigative choices to balance and secure (often competing) investigative goals during HT operations.
The present exploratory study uses data from actual HT investigations, using case study methodology (Baxter & Jack, Citation 2008 ) to examine the investigative practice through the analysis of three HT police operations conducted by an English police force. After obtaining ethical approval from the second author’s Faculty Research Committee and police vetting from the participating police force, the Detective Chief Inspector of the Serious Organised Crime Unit (SOCU) was asked to identify investigations conducted after the implementation of the UK’s Modern Slavery Act 2015 that met the following criteria: (i) that there was a trial date set up by the time data was collected (for those cases yet to involve a conviction); (ii) the case involved adult exploitation and organised criminality; and (iii) the researcher would be able to interview the investigators of the case and have access to police records considered as relevant for the study. Three HT operations met the selection criteria, namely operations Seine, Nile and Thames. Footnote 3 Operation Seine consisted of the investigation of an Organised Criminal Group (OCG) involved in the suspected labour exploitation of Czech Republic nationals; Operation Nile consisted of a joint investigation conducted by English and Romanian police teams investigating an OCG involved in the sex trafficking of Romanian nationals to the UK; while Operation Thames consisted of a large Chinese OCG operating across the UK that was suspected of the sexual exploitation of Chinese women.
Table 1. Participants’ details.
The qualitative analysis of the data reveals two main and interlinked types of decisions detectives made throughout the investigations; they are decisions on what investigative goal(s) to pursue and what investigative approach and action(s) to take to secure such goals. The primary investigative goals identified in all police operations were (i) gathering evidence to secure the prosecution of offenders; and (ii) engaging with victims to safeguard them and involve them in the criminal justice process. Nonetheless, despite victim safeguarding being referred by all interviewees (from all three operations), the main differences found between the police operations analysed related to the planning and implementation of strategies and actions to secure victims’ engagement and safeguarding, which resulted in the engagement and referral to the NRM of 11 victims (out of 15 identified) in Operation Seine and the complete non-engagement of victims in either operations Thames and Nile.
Before the main day [i.e. day of action, aiming to arrest offenders and safeguard victims], we already knew who they [victims] were. I sent an over team to stand by, stop the van they used to transport victims and do a stop routine check with all the body cameras on. And that is how we took all the images of the members inside the van. This was a strategy purely to identify people in the van, so then, when we go to the door on the day, you know the names, and it is a little bit of a break-up: ‘we know you are such and such, come, please, and talk to us’. So you got a little bit more knowledge about it. (Interviewee 4, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
Guys [members of charities] were going out for a smoke and joining them [victims]; they kind of ended up with this kind of commonality. And just let them do the rapport building on our behalf, so then when they say right, let’s start doing the screening process, people were much more relaxed and more willing to speak freely about what happened. (Interviewee 2, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
We would arrest them first because at least we can take them to the police station, which is a place of safety. And just because we arrest someone doesn’t mean we have to charge them with an offence […]. What do we need to do with these girls? […] So, make sure they have someone or somewhere to go; if they need to get a train, we’ll drop them to the train station, or take them home, or whatever it might be, and we’ll make sure before they leave that they know where they go. (Interviewee 1, Detective Inspector, Operation Thames)
Our examination of the data found that the decision to take such different approaches to secure investigative goals was based on (i) the assessment of risk for the victims; and (ii) the intelligence available at the start of the police operation. Furthermore, our data also revealed that the implementation of strategies and actions was influenced (and constrained) by resources, uncertainty, and available opportunities.
Assessment of victims’ risk
It is difficult because, with other trafficking jobs we’ve run, it is how long do we leave these victims in this situation? We had it with some sexual exploitation. We were given a day because you can’t leave an 18-year-old girl being sexually exploited for 3 months; we could not sign for that. (Interviewee 4, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
So from the beginning of the investigation, the biggest issue we had was, how long do we leave it running? What happens if we see something while doing surveillance? Assaults? […]so I had to write a decision policy on what to do […], kind of establish the criteria, how, when do I intervene? At what point do I blow a complete operation for an assault? […], is it worth it? and I know this is, it is always a horrible decision for us, but is worth it to blow a complete operation for somebody being slapped? [.] If, with a small assault, we intervene, but we have no power to do anything else, we could also be causing major risks. And then, it could get worse, and we wouldn’t be able to see it, and I am looking at the risks, and any high assault level […] and there will always be decisions on the moment/day, cause you cannot legislate for every single possible scenario. (Interviewee 4, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
Intelligence available
they discovered more links that tie them all together, which is when they went like this is getting too big […], and this is how we [i.e. SOCU] got involved. (Interviewee 2, Detective Sergeant, Operation Thames)
A victim came forward […], he gave the disclosure […]. Essentially, he told the police everything that matched the intelligence picture. So, we put all the intelligence together and did a form of briefing and, as a partnership [multi-agency operation leading the disruption strategy], we were asked to stop any disruptive plan and wait till the police investigation was completed before taking any further action. (Interviewee 3, Inspector, Operation Seine)
There was more time invested, in terms of the investigation, on what was recovered previously. So most of our time was, literally, collecting everything that has been gathered in terms of the statement, whom they spoke to, the adverts. (Interviewee 5, Detective Inspector, Operation Nile)
The investigation was more reactive from the information that we’ve got, rather than the proactive side of it. (Interviewee 1, Detective Inspector, Operation Thames)
Consequently, actions in operations Thames and Nile were more ‘reactive’ and ‘responsive’ to the evidence and intelligence found from reviewing intelligence and financial information available on the police system. For instance, whenever criminality was suspected of taking place in properties and locations, search warrants were conducted in these addresses to find further evidence and identify victims. Together, the little available information on victims and the risk of sexual exploitation being perceived as high might explain the lack of a proactive and robust strategy to engage with victims even when planning search warrants.
Resources, opportunities and uncertainty
We found throughout the interviews that resources were considered critical factors in the decision to take investigative actions and secure investigative goals. Officers’ accounts reveal that to allocate resources, there is a need to consider (i) the level of threat and risk; (ii) the opportunities different actions generate to achieve the investigative goals; and (iii) the level of uncertainty in securing the intended outcomes.
We could have translated, but at that time, because it was a different department dealing with it and, at that time, they did not realise the extent of the investigation and that it would take as far as this European investigation. At that time, for them, there were single brothels that were popping up, and they were not thinking they were potentially linked, so it would have been a lot of investment for just one single brothel in terms of getting an interpreter, pay them to translate one single phone. (Interviewee 5, Detective Inspector, Operation Nile)
What you are talking about here is about a huge OCG in China, an organised network in the UK, and being honest, the Chinese have been trafficking girls, but this is just one of their forms of criminality, […]. It is huge, […], imagine you try to run an organisation such as Amazon, which operates across the UK, and you are talking about thousands of people to be logistically managed […]. We are taking out six key players, but still, we are missing two of the key players, and this is just for the [police region], that is not including people that we don’t know about or that haven’t been found. (Interviewee 2, Detective Sergeant, Operation Thames)
And we weren’t expecting to find any more victims, and we didn’t, thankfully. Because it was always in the back of my mind we may go through these doors and find other 5 or 6 victims, because I pulled down the surveillance as I couldn’t justify keeping people on surveillance on, because we got so much evidence. (Interviewee 4, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
And a lot of the time, we don’t know what you are going to find till you get there, which can be strange, but we’ve been to a couple of addresses that were empty; you can see that people have been there, you find paperwork, etc., but there is nothing we can use really. (Interviewee 1, Detective Inspector, Operation Thames)
Much volume of work sits behind the scene, all the paperwork. Every time you search a house, and you end up there, you find bags and bags of evidence, and I mean thousands of documents to review. (Interviewee 2, Detective Sergeant, Operation Seine)
It takes a long time, one of the phones we had. It had nearly a million pages of data […]. And [the translator] has constantly been working three days a week just doing the phones, and then there is the analysis. (Interviewee 1, Detective Inspector, Operation Thames)
Similar to search warrants, when reflecting on undercover strategies, interviewees recognised the opportunities these strategies offer to obtain intelligence on offenders, their modus operandi and the victims. Nonetheless, undercover tactics were also identified as highly resource-intensive, with no complete reassurance that they would produce the intelligence and evidence expected. Furthermore, such strategies had the major risk of offenders finding out police were investigating them (by, for instance, police officers having to intervene if a victim was at high risk) and, therefore, jeopardising other strategies such as parallel financial investigations.
Sometimes we would close the house […]. But then, you got a female that has been trafficked, or we believe so, and don’t want to tell us anything, who is now homeless in a strange country, where she can’t speak the language, and this is the problem. So you can end up, if you are not careful, adding vulnerabilities to these individuals. (Interviewee 1, Detective Inspector, Operation Thames)
In the present study, we aimed to provide insight into those elements and factors influencing investigative goals and strategies followed during HT investigations. In all three police operations, we found two clear goals: gathering evidence to secure a conviction and engaging with victims to promote safeguarding. Yet, factors associated with the assessed level of risk of victims, the intelligence available at the start of the investigation and police resources (balanced with opportunities and risk to secure the investigative goals) were found to influence the investigative approach followed and strategies implemented, particularly those aiming to engage with victims.
Previous research on HT investigation has found that the characteristics of the offence and the intelligence available have a cornerstone role in the decision to take (and even change) the investigative direction, approach and action (Pajon & Walsh, Citation 2020 ; Verhoeven & Van Gestel, Citation 2011 ). That is, intelligence and information are constantly gathered and evaluated, considering the specific context, investigative goals, risks and threats (Pajon & Walsh, Citation 2020 ). Nonetheless, according to the literature on sense-making and decision-making (Barrett, Citation 2009 ; Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Power & Alison, Citation 2017 ; Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ; Wright, Citation 2013 ), examination of the intelligence and decisions made are also influenced by previous investigators’ experiences and knowledge. Prior research has found that the analysis and interpretation of intelligence and information, and consequently, the lines of enquiry pursued, are influenced by legal frameworks (Ormerod et al., Citation 2008 ). Officers would use internalised cognitive frames (including stereotypes and misconceptions about who victims of trafficking are and how they behave) and externally imposed legal scripts to make sense of the information, looking for cues that relate to legally determined scripts, to then decide on lines of inquiry (Ormerod et al., Citation 2008 ).
The use of legal frameworks might explain the misidentification of cases of exploitation in Operation Thames and Nile by isolated events/incidents but also the lack of a robust victim strategy and the limited focus on securing evidence from victims in these two operations. Officers need to gather enough evidence to prove to the jury that a crime has been committed and that the defendants are involved. Therefore, it is likely that sense-making was guided by legal scripts to prove HT, and also by officers’ judgments of the quality of the trace to prove and evidence the offence (Bitzer et al., Citation 2016 ). We found in the present study that decision-making was influenced by the assessment of ‘how worthy’ it was to dedicate resources to certain police actions/interventions, considering the opportunities these police actions would offer to secure evidence and the uncertainties and risks they had for the police investigation and the actors involved. Previous research has found that police officers tend to find eyewitness memory significantly less reliable compared to physical traces when it comes to presenting it to the jury (Jang et al., Citation 2020 ). Moreover, in HT cases, difficulties in engaging with trafficked victims (and keeping them involved in the criminal justice procedure) and gathering accurate victims’ accounts are well recognised (Cockbain & Brayley-Morris, Citation 2018 ; Farrell et al., Citation 2008 , Citation 2012 ; Meshkovska et al., Citation 2016 ). Cockbain and Brayley-Morris ( Citation 2018 ), examining labour exploitation investigations in the UK, found that not only is it complex to engage with victims, but it is also challenging to secure and maintain their cooperation throughout the investigation process, resulting in great difficulties in securing their attendance in court. According to Meshkovska et al. ( Citation 2016 ) findings, the length of the criminal process, the limited possibilities for financial compensation, the possibilities for secondary victimisation and the fear of retribution are some of the key reasons for the lack of engagement noted by professionals and victims of trafficking. Besides, changing accounts, inaccuracies, or victims failing to remember specific details about their victimisation experience (Clawson et al., Citation 2006 ) might make them appear as unreliable witnesses. Consequently, detectives´ perceptions of physical and financial evidence being more conclusive to prove exploitation, potential previous failures and known difficulties in securing victims’ testimony, alongside proactive and victim-centred approaches being seen as more time and resource-consuming than reactive approaches, might well explain why, in Operations Thames and Nile, the focus was mainly on gathering financial and physical evidence, while considerably fewer lines of enquiry were taken to identify and engage with potential victims. That is, implementing a proactive strategy to engage with victims and, ultimately, gather their testimony, might have been seen as too costly, time-consuming and with little chance of success when compared to the evidence that could be generated through the analysis of the intelligence available in the police system, and the strategies resulted from this analysis (Findley & Scott, Citation 2006 ).
Different authors have previously identified the challenges and difficulties when dedicating and justifying resources in HT operations (Cockbain & Brayley-Morris, Citation 2018 ; Farrell et al., Citation 2012 ; Gallagher & Holmes, Citation 2008 ; Van der Watt & Van der Westhuizen, Citation 2017 ), either due to a lack of prioritisation of HT criminality at a force level (Farrell et al., Citation 2012 ) or the intrinsic characteristics of the offence which can involve large number of victims/offenders and be committed through extended periods of time (Cockbain & Brayley-Morris, Citation 2018 ). This study found officers relying on heuristics to assess the opportunities for evidence gathering and, in turn, deciding the investigative course of action. In line with previous research (Fahsing, Citation 2016 ; Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ; Wright, Citation 2013 ), we found that investigators from all three operations reflected on past experiences when conducting certain actions and strategies (and their positive and negative outcomes) to justify their implementation (or lack of it).
Nevertheless, despite the importance of balancing resources vs opportunities to prove exploitation, a particularly novel finding was that the assessment of victims´ risk was a more determinant factor in the decision-making process and, in turn, the implementation of a victim-centred approach. According to police guidance, officers and detectives need to assess the victims’ risk and do whatever is possible to eliminate or minimise it (UNODC, Citation 2009 ). Data reveals that such assessment was critical in the implementation (or not) of victim-centred approaches. The risk assessment of victims in Operation Seine was considered low, which allowed investigators more time to gather evidence to prove exploitation and time to build a victim-centred strategy that was informed by intelligence and acknowledged the potential victims’ needs (and involved partner agencies according to such needs). On the contrary, in Operations Thames and Nile, the assessment of victims’ risk was rated as high and immediate, leading to time pressures to quickly intervene to both reduce the immediate risk to victims and preserve evidence; such pressures impacted the actions taken around victims safeguarding and their effectiveness.
Previous decision-making research has demonstrated that time pressure reduces the number of potential strategies generated and promotes the overreliance on heuristics when choosing investigative strategies (Alison et al., Citation 2013 ; Ask & Granhag, Citation 2005 ; Kim et al., Citation 2020 ). This could explain why, in Operations Thames and Nile, when victims were identified during search warrants to different addresses, they were taken to the police station. Such an approach might have worked in the past with other crime-type victims. Nonetheless, with trafficked victims, such practice, however well-intentioned, may well reinforce victims’ fears toward the police (e.g., authoritarian force, fear of deportation) (Nickerson, Citation 1998 ), reducing the likelihood of any later rapport building that would be required to gain information from them (Farrell et al., Citation 2012 ). Instead, what empirical evidence has found is that other strategies, including officers showing empathy and acceptance or police engaging with partners to meet victims’ basic needs (Hemmings et al. Citation 2016 ; Meshkovska et al., Citation 2016 ; Pajon & Walsh, Citation 2022 ) are more effective in promoting victims’ engagement. Consequently, and paradoxically, the study found that the higher the risk for the victims, the less effective the investigative strategies in engaging with victims and safeguarding them are likely to be.
As our findings in the present study highlight, the uncertainty and dynamic characteristics of trafficking offences make the assessment and management of victims´ risks a highly complex task, as it can change throughout the course of the investigation. Thus, any action taken throughout the investigation will likely impact the reaction of the victims and the suspects. When assessing the risk and the best line of action, officers need to anticipate and predict the likely reaction of the actors involved and the consequences and wider implications of these actions (Ormerod et al., Citation 2008 ; Shortland et al., Citation 2020 ). For instance, in Operation Seine the decision on whether to intervene during a covert police operation in the event the level of risk changes (e.g., if the victim is seen being physically assaulted) is based on the predicted impact it would have on the victim(s) (and their level of risk) and the police operation. Likewise, the planning of the victim strategy in Operation Seine for the day of action also considered the risk and the situation as dynamic. Thus, strategies and resources were planned and dedicated in anticipation of the actor´s reaction (e.g., anticipating possible reluctance from victims to engage with the police). Overall, as with previous research findings both on HT investigations (Pajon & Walsh, Citation 2020 ) and on decision-making (Innes, Citation 2021 ), intelligence becomes critical for investigative decision-making and, in turn, in securing (or otherwise) investigative outcomes.
Implications for policy, practice and research
Our findings in the present study illustrate the complexities of safeguarding victims of trafficking while maximising the opportunities for the prosecution of those suspected of criminality. The examination of the three police operations involving organised human trafficking crimes has highlighted the importance of intelligence for effective sense-making and decision-making processes, specifically when assessing the risk and threat and when considering (and planning) opportunities for interventions. Yet, the study also reveals the lack of clear criteria to risk-assess a case of exploitation, identifying differences in how the level of risk is assessed (and treated) at the start of the investigation, as opposed to during the investigations, once a decision has been made on a course of action to take. Our findings highlight that such risk assessment has important implications for the approach and actions taken to safeguard victims. Paradoxically, we found that the higher the risk for the victims, the less likely they will be effectively safeguarded (in part due to the need for a quick response by the police). To minimise investigators’ reliance on heuristics when assessing the risk of the victims and deciding upon a course of action, under such time pressures, while maximising opportunities to secure victim safeguarding and evidence gathering, further research is needed. Another area requiring more study concerns that of developing improved risk assessments within the context of HT investigations, while recognising the complexities and particularities of this form of criminality and its victims’ profiles, in order to help inform both policies and decision-making policing practices.
Limitations and future research
Despite the value of using case study methodology to contextualise and provide insight into investigative decision-making during HT investigations, the data collected can be argued to present some limitations. Interviews provide a rich amount of data for analysis and interpretation (Mason, Citation 2002 ; Walsham, Citation 1995 ). However, interviewees gave their views on decisions taken during the investigation after the case outputs; therefore, they could have responded with what was believed appropriate, logical or expected according to the final outcomes rather than their honest views on why certain decisions were taken (Björklund, Citation 2008 ; Rogers & Ryals, Citation 2007 ). Similarly, aspects including memory fallibility when retrospectively recalling information about an event (see Fisher & Geiselman, Citation 1992 ; Gabbert et al., Citation 2018 ) can ultimately have an impact on the data collected. To minimise such limitations, we complemented the interviewees’ narratives with a review of police files. Yet, because of the nature of some of the police files and the nature of the information that they contain, we could only access those permitted under our level of police vetting. Moreover, during the interviews that were conducted for the present study, police officers were encouraged to look at their investigative notes to help recall information. The data presented does not include descriptive information from the participants, including years of service and experience investigating HT crimes, as gathering such data from a single police force might well lead to the identification of the participants. Nevertheless, it is reasonable to assume that their officer rank would suggest that each participant has significant policing investigative experience and, for some, their leadership of HT investigation teams would indicate that their professional experience is relevant to investigating of these particular crimes. Moreover, we know by police force data record that the force in the study identified more than 100 HT victims per year, which indicates the police force’s experience and activity responding to this form of crime. To complement and strengthen the present study’s findings, future research should use other methodologies, including ‘think aloud’ and ethnographic research methods, to capture ‘real-time’ decision-making to overcome the limitation attributed to the retrospective recalling of information.
The present study provides insights into the complexity of investigating organised human trafficking crimes in which, other than bringing offenders to justice, safeguarding victims and managing risks are also fundamental goals (Stelfox, Citation 2009 ). The examination of HT cases demonstrates the complexities of deciding which lines of enquiry to pursue and what actions to undertake to safeguard vulnerable individuals while maximising successful outputs for prosecution. The findings identify the assessment of risks, intelligence, and resources as crucial factors when defining the investigative purposes and approach. Such findings illustrate the importance of intelligence in risk assessment and decision-making processes, but also the need to conduct yet further research.
Ethical approval
Approval to conduct the study was obtained from the ethics committee of De Montfort University. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Notes on contributors
Laura pajon.
Laura Pajon , PhD, is a Senior Lecturer in the School of Justice Studies at Liverpool John Moores University, UK. Her research focuses on law enforcement and multi-agency responses to serious and organised criminality, in particular, human trafficking and modern slavery crimes.
Dave Walsh , Ph.D., is Professor of Criminal Investigation in the School of Law at De Montfort University, Leicester, UK. He works with many academics and law enforcement agencies around the world, advising on their investigation and interview methods. He has published over 80 peer-reviewed journal articles, books and book chapters on the subject of criminal investigation, particularly in the area of investigative interviewing of victims, witnesses and suspects. He is currently leading an international project called ImpleMendez of 100+ scholars and practitioner from over 40 countries in efforts to strengthen research networks, further develop academic and practitioner collaborations and help implement the Mendez Principles around the world.
1. NCA: The UK agency responsible for developing national intelligence on criminal activity such as human trafficking.
2. NRM: the UK’s national framework for identifying victims of trafficking and ensuring that, once identified, victims are provided with adequate support.
3. The names of the operations have been changed, and identifying details removed to ensure anonymity.
4. Day of action: police operation aiming to enter properties to arrest offenders, gather evidence and safeguard victims.
5. Alpha victims: victims with a higher-status role that can involve supervising, manipulating, and even threatening and assaulting their peers (Cockbain & Brayley-Morris, Citation 2018 ).
- ACPO. (2005). Practice advice on the core investigative doctrine. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from http://library.college.police.uk/docs/acpo/Core-Investigative-Doctrine.pdf Google Scholar
- Alison, L., Doran, B., Long, M., Power, N., & Humphrey, A. (2013). The effects of subjective time pressure and individual differences on hypotheses generation and action prioritization in police investigations. Journal of Experimental Psychology , 19 ( 1 ), 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032148 Google Scholar
- Ask, K. (2006). Criminal investigation: Motivation, emotion and cognition in the processing of evidence [ Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation]. Göteborg University. Google Scholar
- Ask, K., & Alison, L. (2010). Investigators’ decision-making. In P. Granhag (Ed.), Forensic psychology in context: Nordic and international perspectives (pp. 35–55). Willan Publishing. Google Scholar
- Ask, K., & Granhag, P. A. (2005). Motivational sources of confirmation bias in criminal investigations: The need for cognitive closure. The Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling , 2 ( 1 ), 43–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/jip.19 Google Scholar
- Ask, K., & Granhag, P. A. (2007). Motivational bias in criminal investigators’ judgments of witness reliability 1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 37 ( 3 ), 561–591. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2007.00175.x Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Barrett EC. (2009). The interpretation and exploitation of information in criminal investigations [ Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation]. University of Birmingham. Google Scholar
- Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report , 13 , 544–559. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2008.1573 Google Scholar
- Bitzer, S., Ribaux, O., Albertini, N., & Delemont, O. (2016). To analyse a trace or not? Evaluating the decision-making process in the criminal investigation. Forensic Science International , 262 , 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.02.022 PubMed Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Björklund, L. (2008). The repertory grid technique: Making tacit knowledge explicit: Assessing creative work and problem-solving skills. In H. Middleton (Ed.), Researching technology education: Methods and techniques (pp. 46–69). Sense. Google Scholar
- Brunovskis, A., & Skilbrei, M. (2016). Two birds with one stone? Implications of conditional assistance in victim protection and prosecution of traffickers. Anti-Trafficking Review , 6 ( 6 ), 13–30. https://doi.org/10.14197/atr.20121662 Google Scholar
- Canter, D. (2000). Investigative psychology. In J. Siegel, P. Saukko, & G. Knupfer (Eds.), Encyclopaedia of forensic sciences (pp. 1091–1097). Academic Press. Google Scholar
- Clawson, H., Dutch, N., & Cummings, M. (2006). Law enforcement response to human trafficking and the implications for victims: Current practices and lessons learned. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/216547.pdf Google Scholar
- Cockbain, E., & Brayley-Morris, H. (2018). Human trafficking and labour exploitation in the casual construction industry: An analysis of three major investigations in the UK involving Irish traveller offending groups. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice , 12 ( 2 ), 129–149. https://doi.org/10.1093/police/pax032 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Cook, T., & Tattersall, A. (2014). Blackstone’s senior investigating officers’ handbook . University Press. Google Scholar
- Council Directive 2011/36/EU of 5 April 2011 on preventing and combating trafficking in human beings and protecting its victims, and replacing Council Framework Decision 2002/629/JHA. (2011). Official Journal of the European Union, L101/1 . Google Scholar
- Dando, C., & Ormerod, T. (2017). Analysing decision logs to understand decision-making in serious crime investigations. Human Factors: The Journal of Human Factors and Ergonomics Society , 59 ( 8 ), 1188–1203. https://doi.org/10.1177/001872081772789 PubMed Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- David, F. (2007). Law enforcement responses to trafficking in persons: Challenges and emerging good practice. Trends and issues in crime and criminal justice, 347. Australian institute of criminology. Law enforcement responses to trafficking in persons: Challenges and emerging good practice - CORE reader. Retrieved December 27, 2022. Google Scholar
- David, F. (2008). Trafficking of women for sexual purposes. Research and Public policy series, 95. Australian institute of criminology. Retrieved December 27, 2022, from https://www.dss.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/05_2012/rrp95_trafficking_of_women.pdf Google Scholar
- De Vries, I., & Farrell, A. (2023). Explaining the use of traditional law enforcement responses to human trafficking concerns in illicit massage business. Justice Quarterly , 40 ( 3 ), 337–362. https://doi.org/10.1080/07418825.2022.2051587 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Dror, I. E., & Fraser-Mackenzie, P. A. (2009). Cognitive bias in human perception, judgement and decision-making: Bridging theory and the real world. In K. Rossmo (Ed.), Criminal investigative failures (pp. 53–67). CRC Press. Google Scholar
- Europol. (2021). European Union serious and organised crime threat assessment (EU SOCTA). A corrupting influence: The inflation and undermining of Europe’s economy and society by organised crime. socta2021_1.pdf (europa.eu). Retrieved May 17, 2024. Google Scholar
- Fahsing, I. (2016). The making of an expert detective. Thinking and deciding in criminal investigations [ Unpublished Doctoral dissertation]. Göteborg University. Google Scholar
- Fahsing, I., & Ask, K. (2013). Decision making and decisional tipping points in homicide investigations: An interview study of British and Norwegian detectives. The Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling , 10 ( 2 ), 155–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/jip.1384 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Fahsing, I., & Ask, K. (2016). The making of an expert detective: The role of experience in English and Norwegian police officers’ investigative decision- making. Psychology Crime & Law , 22 ( 3 ), 203–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/1068316X.2015.1077249 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Fahsing, I., & Ask, K. (2017). In search of indicators of detective aptitude: Police recruits’ logical reasoning and ability to generate investigative hypotheses. Journal of Police and Criminal Psychology , 33 ( 1 ), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11896-017-9231-3 Google Scholar
- Farrell, A., Dank, M., De Vries, I., Kafafian, M., Hughes, A., & Lockwood, S. (2019). Falling victims? Challenges of the police response to human trafficking. Criminology & Public Policy , 18 ( 3 ), 649–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-9133.12456 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Farrell, A., McDevitt, J., & Fahy, S. (2008). Understanding and improving law enforcement responses to human trafficking. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/222752.pdf Google Scholar
- Farrell, A., McDevitt, J., Pfeffer, R., Fahy, S., Owens, C., Dank, M., & Adams, W. (2012). Identifying challenges to improve the investigation and prosecution of state and local human trafficking cases. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.ojp.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/238795.pdf Google Scholar
- Farrell, A., Owens, C., & J, M. (2014). New laws but few cases: Understanding the challenges to the investigation and prosecution of human trafficking cases. Crime, Law, & Social Change , 61 ( 2 ), 139–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10611-013-9442-1 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Farrell, A., & Pfeffer, R. (2014). Policing human trafficking: Cultural blinders and organizational barriers. The ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 653 , 46–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716213515835 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Findley, K. A., & Scott, M. S. (2006). The multiple dimensions of tunnel vision in criminal cases. Wisconsin Law Review , 2, 291–397. Google Scholar
- Fisher, R. P., & Geiselman, R. E. (1992). The complexity of eyewitness memory. In F. Fisher & R. Geiselman (Eds.), Memory enhancing techniques for investigative interviewing. The cognitive interview (pp. 11–16). Thomas publisher. Google Scholar
- Gabbert, F., Hope, L., & Confrey, M. (2018). Witness testimony. In A. Griffiths & R. Milne (Eds.), The psychology of criminal investigation: From theory to practice (pp. 113–129). Routledge. Google Scholar
- Gallagher, A., & Holmes, P. (2008). Developing an effective criminal justice response to human trafficking: Lessons from the front line. International Criminal Justice Review , 18 ( 3 ), 318–343. https://doi.org/10.1177/1057567708320746 Google Scholar
- Hallgren, M., Lindberg, O., & Rantatalo, O. (2021). Sensemaking in detective work: The social nature of crime investigation. International Journal of Police Science & Management , 23 ( 2 ), 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461355720980759 Google Scholar
- Helfferich, C., Kavemann, B., Rabe, H., Toll, C., & Flach, G. (2011). Determinants of the willingness to make a statement of victims of human trafficking for the purpose of sexual exploitation in the triangle offender–police–victim. Trends in Organised Crime , 14 ( 2–3 ), 125–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12117-011-9125-1 Google Scholar
- Hemmings, S., Jakobowitz, S., Abas, M., Bick, D., Howard, L. M., Stanley, N., Zimmerman, C., & Oram, S. (2016). Responding to the health needs of survivors of human trafficking: A systematic review. BMC Health Service Research , 16 , 320–329. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-016-1538-8 PubMed Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- HM Government. (2021). 2021 UK annual report on modern slavery. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/2021-uk-annual-report-on-modern-slavery Google Scholar
- HM Government. (2022). The hidden victims: Report on Hestia’s super-complaint on the police response to victims of modern slavery. Access 6 May. 2024. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/police-response-to-victims-of-modern-slavery/the-hidden-victims-report-on-hestias-super-complaint-on-the-police-response-to-victims-of-modern-slavery–2 Google Scholar
- HM Government. (2024). Modern slavery: National referral mechanism and duty to notify statistics UK, end of year summary 2023. Access 6 May. 2024. https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/modern-slavery-nrm-and-dtn-statistics-end-of-year-summary-2023/modern-slavery-national-referral-mechanism-and-duty-to-notify-statistics-uk-end-of-year-summary-2023#national-referral-mechanism-referrals Google Scholar
- Innes, M. (2003). Investigating murder: Detective work and the police response to criminal homicide . Oxford University Press. Google Scholar
- Innes, M. (2021). “Mosaicking”: Cross construction, sense-making and methods of police investigation. Policing an International Journal , 44 ( 4 ), 708–721. https://doi.org/10.1108/PIJPSM-02-2021-0028 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Jang, M., Luke, T., Granhag, P., & Vrij, A. (2020). The impact of evidence type on police investigators’ perceptions of suspect culpability and evidence reliability. Zeitschrift für Psychologie , 228 ( 3 ), 188–198. https://doi.org/10.1027/2151-2604/a000411 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Kim, S., Alison, L., & Christiansen, P. (2020). The impact of individual differences on investigative hypothesis generation under time pressure. International Journal of Police Science & Management , 22 ( 2 ), 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461355720905716 Google Scholar
- Maitlis, S., & Christianson, M. (2014). Sensemaking in organizations: Taking stock and moving forward. The Academy of Management Annals , 8 ( 1 ), 57–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/19416520.2014.873177 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Mason, J. (2002). Qualitative researching ( 2nd ed.). Sage, Thousand Oaks. Google Scholar
- Matos, M., Gonçalvez, M., & Maia, A. (2019). Understanding the criminal justice process in human trafficking cases in Portugal: Factors associated with successful prosecutions. Crime, Law & Social Change , 72 ( 5 ), 501–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10611-019-09834-9 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Meshkovska, B., Mickovski, N., Bos, A., & Siegel, M. (2016). Trafficking of women for sexual exploitation in Europe: Prosecution, trials and their impact. Anti-Trafficking Review , 6 ( 6 ), 71–90. https://doi.org/10.14197/atr.20121665 Google Scholar
- National Crime Agency (NCA). (2021). National strategic assessment of serious and organised crime. file (nationalcrimeagency.Gov.uk). Retrieved December 27, 2022. Google Scholar
- Newton, P. J., Mulcahy, T. M., & Martin, S. E. (2008). Finding victims of human trafficking. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/224393.pdf Google Scholar
- Nickerson, R. S. (1998). Confirmation bias: A ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Review of General Psychology , 2 ( 2 ), 175–220. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.2.175 Google Scholar
- O’Neill, M. (2018). Key challenges in criminal investigation . Policy Press. Google Scholar
- Ormerod, T. C., Barrett, E., & Taylor, P. J. (2008). Investigative sense-making in criminal contexts. In J. Schraagen, L. Militello, T. Ormerod, & R. Lipshitz (Eds.), Naturalistic decision making and macrocognition (pp. 81–98). Ashgate Publishing. Google Scholar
- Pajon, L., & Walsh, D. (2020). Proposing a theoretical framework for the criminal investigation of human trafficking crimes. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice , 14 ( 2 ), 493–511. https://doi.org/10.1093/police/pay031 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Pajon, L., & Walsh, D. (2022). The importance of multi-agency collaborations during human trafficking criminal investigations. Policing & Society . https://doi.org/10.1080/10439463.2022.2106984 PubMed Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Power, N., & Alison, L. (2017). Redundant deliberation about negative consequences: Decision inertia in emergency responders. Psychology, Public Policy, & Law , 23 ( 2 ), 243–258. https://doi.org/10.1037/law0000114 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Raphael, J., Reichert, J. A., & Powers, M. (2010). Pimp control and violence: Domestic sex trafficking of Chicago women and girls. Women & Criminal Justice , 20 ( 1–2 ), 89–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/08974451003641065 Google Scholar
- Rodríguez-López, S. (2018). (De)constructing Stereotypes: Media representations, social perceptions, and legal responses to human trafficking. Journal of Human Trafficking , 4 ( 1 ), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322705.2018.1423447 Google Scholar
- Rogers, B., & Ryals, L. (2007). Using repertory grid technique to access the underlying realities in key account relationships. International Journal of Market Research , 49 ( 5 ), 595–612. https://doi.org/10.1177/147078530704900506 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Rossmo, K. (2009). Criminal investigative failures . CRC Press. Google Scholar
- Schoch, K. (2020). Case study research. In G. J. Burkholder, K. A. Cox, L. M. Crawford, & J. H. Hitchcock (Eds.), Research design and methods. An applied guide for the scholar-practitioner (pp. 245–258). Sage. Google Scholar
- Shortland, N., Thompson, L., & Alison, L. (2020). Police perfection: Examining the effect of trait maximisation on police decision-making. Frontiers in Psychology , 11 , 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01817 PubMed Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Snook, B., & Cullen, R. M. (2009). Bounded rationality and criminal investigations: Has tunnel vision been wrongfully convicted? In K. Rossmo (Ed.), Criminal investigative failures (pp. 71–98). CRC Press. Google Scholar
- Stelfox, P. (2009). Criminal investigation: An introduction to principles and practice . William Publishing. Google Scholar
- Tong, S., & Bowling, B. (2006). Art, craft and science of detective work. The Police Journal , 79 ( 4 ), 323–329. https://doi.org/10.1350/pojo.2006.79.4.323 Google Scholar
- United Nations Office of Drugs and Crime (UNODC). (2009). Module 5: Risk assessment in trafficking in persons investigations. Retrieved May 17, 2024, from https://www.unodc.org/documents/human-trafficking/TIP_module5_Ebook.pdf Google Scholar
- United Nations Office of Drugs and Crime (UNODC). (2014). Global report on trafficking in persons 2014. Retrieved December 27, 2022, from https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/glotip/GLOTIP_2014_full_report.pdf Google Scholar
- Van der Watt, M., & Van der Westhuizen, A. (2017). Re)configuring the criminal justice response to human trafficking: A complex-systems perspective an international journal. Police Practice & Research , 18 ( 3 ), 218–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/15614263.2017.1291560 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Verhoeven, M., & Van Gestel, B. (2011). Human trafficking and criminal investigation strategies in the Amsterdam red light district. Trends in Organized Crimes , 14 ( 2–3 ), 148–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12117-011-9126-0 Google Scholar
- Wallace, W. A. (2015). The effect of confirmation bias on criminal investigative decision making [ Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation]. Walden University. Google Scholar
- Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case study in is research: Nature and method. European Journal of Information Systems , 4 ( 2 ), 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1057/ejis.1995.9 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Wright, M. (2013). Homicide detectives’ intuition. The Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling , 10 , 182–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/jip.1383 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Back to Top
Related research
People also read lists articles that other readers of this article have read.
Recommended articles lists articles that we recommend and is powered by our AI driven recommendation engine.
Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations. Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab.
- People also read
- Recommended articles
To cite this article:
Download citation, your download is now in progress and you may close this window.
- Choose new content alerts to be informed about new research of interest to you
- Easy remote access to your institution's subscriptions on any device, from any location
- Save your searches and schedule alerts to send you new results
- Export your search results into a .csv file to support your research
Login or register to access this feature
Register now or learn more

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assess the process of analysis. Case studies allow you to assess a student's demonstration of deeper understanding and cognitive skills as they address the case. These skills include, for example: identification of a problem. hypotheses generation. construction of an enquiry plan. interpretation of findings.
A case study exercise is a type of assessment where candidates are presented with a hypothetical business scenario and asked to provide solutions or recommendations. These exercises assess a range of competencies such as problem-solving, analytical thinking, decision-making, communication, teamwork, and time management.
Step 1. Do the Research. There is a whole range of research you can look into to prepare yourself for the case study exercise: Any of the above should provide you with a better understanding of the job you have applied for, the industry you will work within, and the culture and values of the employer.
A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined. A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study.
STEP 1: Obtain different examples of scenarios which simulate both the job and the industry you are applying to. STEP 2: Practice different sample case study assessments regularly before the real assessment. STEP 3: The most important step when preparing for your assessment is to make sure you practice case study assessments under strict timed ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction. In recent years, ... (iv) ethical considerations, (v) interpretation process, and (vi) criteria for assessment. Application of these protocols is mentioned in Section II. Field Phase. a ...
NCMHCE Sample Case Study. You are a licensed mental health counselor working in a community agency. Your client self-referred for services because "my mother won't stop bugging me for staying in bed all day. I can't help it. I am in a rut and cannot find a way out.".
You can base case study teaching and assessment on a number of methods, e.g. the Harvard Business School method. Bear in mind that there are critiques of each method. You can use technology to track case discussions and development. You can prepare for a case study or scenario assessment by presenting examples of cases in class prior to assessment.
Case studies during an assessment. Different types of case studies are used in assessment centers. Companies may use a case study interview or a written exercise (In-Tray and E-Tray exercise). Case studies are used to measure your analytic skills, problem-solving abilities, communication skills and ability to deliver quality and results.
Case studies are highly effective tools in undergraduate education (Handelsman et al., 2004; Herreid et al., 2012; Wiertelak et al., 2016), and we believe that using student-created case studies as assessment is a valuable extension of established case study pedagogy.
Case studies. Case studies allow you to apply what you are learning to a real-world example, or 'case'. The case could be either an actual or hypothetical situation, person, business or organisation. Case studies usually ask you to: describe the case. identify key issues of the case. analyse the case using relevant theory or concepts.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom). Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30-50 percent of the overall course ...
A case study requires you to analyse a specific situation and discuss how its different elements relate to theory. The case can refer to a real-life or hypothetical event, organisation, individual or group of people and/or issue. Depending upon your assignment, you will be asked to develop solutions to problems or recommendations for future action.
Case Studies. Case studies (also called "case histories") are descriptions of real situations that provide a context for engineers and others to explore decision-making in the face of socio-technical issues, such as environmental, political, and ethical issues. Case studies typically involve complex issues where there is no single correct ...
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students: Example of Case Study Suitable for Students. Title: Energy Efficiency Upgrade: A Case Study of GreenTech Office. Introduction: GreenTech Office embarked on an energy efficiency upgrade to reduce its environmental impact.
Table of Contents. 1 Case Study Templates; 2 Common types of case study templates; 3 Case Study Examples; 4 Benefits of using case study templates in businesses; 5 Case Study Formats; 6 Tips for writing a case study template; 7 Case Analysis Formats. 7.1 Decide on the type of case study you will perform; 7.2 Reach out to potential participants for your case study; 7.3 Prepare your questions
in case study design. The purpose of this paper is to describe the process of designing a progressive version of the standard case study: that is, the continuous case study. Continuous case studies are effective as assignments, in-class activities, or as data collection tools to assess student learning. This paper begins with an evidence-based
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Case study exercises are proficient predictors of role performance as they will resemble the work being done on the job. Therefore, case study exercises typically tilt highly on an assessment centre rating for candidates. Likewise, if a presentation exercise is required after the case study, based on details brought up during the case study ...
Though case study learning and assessment may take many forms the common thread is that the case study involves a real-life situation and finding solutions is the focus of the assessment. Advantages of case studies . ... For example, students may complete various tasks or give a presentation on the case study as a group but write up part of the ...
Atlanta public schools case study. In 2011, an external investigation of the performance evaluation strategies of the Atlanta Public Schools System revealed that schools had been cheating to obtain high results. For this example case analysis, the student has identified the problems faced by the organisation, outlined factors that contributed ...
Case studies provide short, instructive examples of good assessment practice, along with lessons learned that are widely applicable. Alverno College is a case study site due to innovative and long-standing assessment practices as well as a commitment to student-centered teaching. Although Alverno is well established in its assessment practices ...
Michael's case provides valuable insights into effective OT practice, particularly for premature infants: Assessment is Crucial: Accurate and thorough assessment of developmental milestones is essential in identifying delays and setting realistic goals. This process ensures that therapy is targeted and effective.
Inclusion Across the Lifespan Case Studies: This document describes several mock studies as examples of how to consider the Inclusion Across the Lifespan policy in study design and eligibility criteria. Examples include commentary on scientific and ethical reasons that may be acceptable or unacceptable for age-based exclusion.
The objective of the Integrated Approaches for Testing and Assessment (IATA) Case Studies Project is to increase experience with the use of IATA by developing case studies which constitute examples of predictions that are fit for regulatory use. The aim of this project is to create common understanding of using novel methodologies and the generation of considerations/guidance stemming from ...
The present exploratory study uses data from actual HT investigations, using case study methodology (Baxter & Jack, Citation 2008) to examine the investigative practice through the analysis of three HT police operations conducted by an English police force. After obtaining ethical approval from the second author's Faculty Research Committee ...