Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Ricardo Caballero

Departments
As taught in.
- International Economics
- Macroeconomics
Learning Resource Types
Principles of macroeconomics, assignments.
| assignments | solutions |
|---|---|
| Problem Set 1 ( ) | ( ) |
| Problem Set 2 ( ) | ( ) |
| Problem Set 3 ( ) | ( ) |
| Problem Set 4 ( ) | ( ) |
| Problem Set 5 ( ) | ( ) |
| Problem Set 6 ( ) | ( ) |

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
110 Macroeconomics Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that focuses on the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. It deals with factors such as inflation, unemployment, economic growth, and government policies that affect the overall economy. If you are studying macroeconomics and need some inspiration for essay topics, look no further. Here are 110 macroeconomics essay topic ideas and examples to get you started:
- The impact of fiscal policy on economic growth
- Analyzing the causes of inflation
- The role of central banks in controlling inflation
- The effects of globalization on economic growth
- The relationship between unemployment and inflation
- The effects of government spending on economic growth
- The impact of technological innovation on the economy
- The role of interest rates in the economy
- The effects of exchange rates on international trade
- Analyzing the business cycle
- The effects of income inequality on economic growth
- The impact of government regulation on the economy
- The relationship between government debt and economic growth
- The effects of supply-side economics on the economy
- The role of monetary policy in controlling inflation
- The effects of trade barriers on international trade
- The impact of consumer confidence on economic growth
- Analyzing the causes of economic recessions
- The effects of demographic changes on the economy
- The relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability
- The impact of automation on the labor market
- The effects of government subsidies on the economy
- The role of the Phillips curve in macroeconomics
- The effects of foreign direct investment on economic growth
- The relationship between government spending and inflation
- The impact of population growth on the economy
- Analyzing the effects of a minimum wage increase on unemployment
- The effects of government debt on interest rates
- The role of the multiplier effect in fiscal policy
- The impact of educational attainment on economic growth
- Analyzing the effects of a trade deficit on the economy
- The relationship between economic growth and happiness
- The effects of income taxes on economic growth
- The impact of government subsidies on the housing market
- The role of the labor market in economic growth
- The effects of government regulation on small businesses
- The relationship between government spending and economic growth
- The impact of income inequality on consumer spending
- Analyzing the effects of a recession on the stock market
- The effects of technology on productivity growth
- The role of the IS-LM model in macroeconomics
- The impact of government spending on infrastructure projects
- The relationship between interest rates and investment
- The effects of government debt on future generations
- The impact of globalization on income inequality
- Analyzing the effects of a currency devaluation on the economy
- The effects of government subsidies on the energy sector
- The role of the Laffer curve in supply-side economics
- The impact of government regulation on the financial sector
- The relationship between economic growth and poverty reduction
- The effects of income taxes on consumer spending
- The impact of government spending on healthcare outcomes
- Analyzing the effects of a housing bubble on the economy
- The relationship between inflation and interest rates
- The impact of government subsidies on the agriculture sector
- The role of the AD-AS model in macroeconomics
- The effects of government regulation on the pharmaceutical industry
- The relationship between economic growth and social mobility
- The impact of trade agreements on international trade
- Analyzing the effects of a recession on the manufacturing sector
- The effects of government debt on credit ratings
- The role of the multiplier effect in monetary policy
- The impact of government spending on education outcomes
- The relationship between income inequality and political stability
- The impact of government subsidies on the technology sector
- Analyzing the effects of a trade war on international trade
- The effects of government regulation on the banking sector
- The relationship between economic growth and income distribution
- The impact of globalization on job creation
- The role of the AD-IA model in macroeconomics
- The effects of government debt on economic growth
- The relationship between inflation and unemployment
- The impact of government subsidies on the transportation sector
- Analyzing the effects of a recession on consumer confidence
- The effects of income taxes on household savings
- The role of the Phillips curve in monetary policy
- The impact of government spending on public infrastructure
- The relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation
- The effects of income inequality on social cohesion
- The impact of government subsidies on the renewable energy sector
- Analyzing the effects of a currency appreciation on the export sector
- The effects of government regulation on the telecommunications industry
- The relationship between government debt and economic stability
- The impact of technological innovation on job displacement
- The role of the IS-LM model in monetary policy
- The effects of government subsidies on the healthcare sector
- The relationship between economic growth and income mobility
- The impact of trade agreements on economic growth
- Analyzing the effects of a recession on government revenue
- The effects of income taxes on consumer behavior
- The role of the multiplier effect in trade policy
- The impact of government spending on public services
- The relationship between inflation and economic growth
- The effects of government debt on fiscal policy
- The impact of government subsidies on the tourism sector
- Analyzing the effects of a housing market crash on the economy
- The effects of income inequality on economic stability
- The relationship between government regulation and business confidence
- The impact of globalization on income distribution
- The role of the AD-IA model in monetary policy
- The relationship between inflation and economic stability
- The impact of government subsidies on the manufacturing sector
- Analyzing the effects of a recession on government spending
- The effects of income taxes on economic development
- The role of the Phillips curve in fiscal policy
- The impact of government spending on social welfare
- The relationship between economic growth and income inequality
These essay topic ideas and examples cover a wide range of macroeconomic issues and concepts. Whether you are writing a research paper, essay, or term paper, these topics provide a great starting point for your macroeconomics assignments. Good luck with your writing!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research
Take a look at our macroeconomics research topics and select the most suitable one. And don’t forget to check out our tips on how to compose a paper.
🔝 Macroeconomic Topics — Best Selection
🤔 what is macroeconomics.
- 🏆 Best Topics & Essay Examples
📚 Topics in Macroeconomics
- 📑 Good Research Topics
- ⭐ Simple Essay Titles
👍 Good Essay Topics on Macroeconomics
🤗 interesting macroeconomic topics.
- 📄 Essay Topics
🗺️ Globalization & Macroeconomics Research Paper Topics
- 🖥️ Presentation Topics
🏛️ Macroeconomic Research Topics on Policy
- 📊 Project Topics
- 📈 Presentation Topics on Economic Growth
- 👩💻 Topics for Research Paper
- ✍️ Topics for Term Paper
- 🔥 20 More Hot Topics
❓ Macroeconomics Essay Questions
- 🔨 Tricks for a Paper
All finance students are required to take the macroeconomics course throughout their studies. Although the subject is crucial and useful, it is pretty challenging. In particular, it can become a problem if you want to nail an original macroeconomics project. Topics to write about can be tricky to find for students regardless of their school level.
But you won’t face any difficulties.
Our team of experts has prepared a comprehensive list of macroeconomic topics. Here you can find fascinating ideas for any type of assignment.
- Macroeconomic and Microeconomic Analysis of Nestle Nutrition
- Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Basics of Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Johnson & Johnson: Macroeconomic Variables Analysis
- New Classical Macroeconomics
- Analysis of Macroeconomic Condition of Argentina
- How Macroeconomics Affects on Remote Industry & Operating Environments
- Mexico Country: Micro and Macroeconomic Environment
- Macroeconomic Policies in Australia
- Macroeconomic Concepts and Models Application
Of course, you could go straight away to the essay ideas search. But are you familiar with essential economic terms? If not, then the topic selection process can turn into huge trouble.
We have good news for you!
For your convenience, we developed a brief study guide on the basics of economics. So, don’t hesitate to use our prompts to make your studying process more pleasurable.
⚖️ Macroeconomics & Microeconomics
In essence, macroeconomics and microeconomics are two fundamental parts of economic science. They perfectly complement each other and provide a wide range of opportunities for economists. Nevertheless, the microeconomic and macroeconomic objectives differ to a great extent.

So, what are they?
Macroeconomics is a field of economics that studies the economic performance of countries. By employing it, governments can analyze the financial situation within a country. Macroeconomic theory’s concepts help to predict and prevent possible economic obstacles. Generally, the field presents the big picture. That is to say, it shows the economic development on a national and international level.
In contrast, microeconomics focuses on specific firms or companies. It analyzes the business owners’ decision-making process. Microeconomics does not interact with national or even international economic problems. It mainly investigates enterprises and their internal issues.
🏆 Best Macroeconomics Topic Ideas & Essay Examples
- The Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Factors in a Startup Café The objectives of this poster are to illustrate the importance of the microeconomics and macroeconomics factors in my project, which is a Startup Cafe.
- Macroeconomic Environment: Oversight and Governance In order for the business to be listed on the exchange, it must first meet all of the listing rules and then pay any expenses associated with being listed.
- Insurance in Europe Profitability and the Macroeconomic Environment The assignment analyses the cost structure of the industry, the economic landscape in Europe, and how it relates to the insurance sector, changing consumer preference, and the impact of Covid-19 on the industry.
- Articles Explaining Macroeconomic Concepts and Events The model interprets the characteristics of the financial markets and investigates the stability of a country’s economy. The LM curve indicates the GDP output levels where the money supply is equal to the demand.
- Macroeconomic Problems Faced by Sweden and Saudi Arabia Macroeconomics studies the behavior of the economy, as well as its major sectors, such as the public and private sectors, and the monetary system, as well as the relationships between the most significant general economic […]
- The Impacts of the Macroeconomic Variables on the Business Environment These are also indicators of the rank of the well-being of the population, exports and imports operations, the overall rate of economic growth, and other economic processes.
- Macroeconomics Principles: International Commerce On the other hand, the higher the productivity gap, the greater the concentration of export businesses and the fewer their links with the rest of the economy.
- Macroeconomics Principles of Demand and Supply The article suggested that the aggregate demand must be boosted to support the monetary policies and decrease the risks faced after the pandemic’s shock for the worldwide economy.
- United States National Debt and Macroeconomics The national debt of the United States is one of the most known economic phenomena in the world. This is the real danger of using the national debt as a solution to the lack of […]
- The United States Macroeconomic Policies During COVID-19 One of the main reasons is the social hardship caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and, consequently, the government’s need to ensure a steady flow of funds to support the budget.
- Macroeconomic Variables Overview According to the data, GDP growth in 2017 was 2. The inflation rate in the same years was 2.
- Economic Principles: Macroeconomics This paper intends to describe the housing industry in the United States as presented in the Census Bureau. The housing industry is one of the most vibrant in the United States and the rest of […]
- Behavioral Finance: Meaning of Macroeconomics Keen disapproves of all the economic theories that support the concept describing their flaws and mishaps. The theories they disapprove of have some flaws that are well stated and displayed.
- Macroeconomics: US Monetary Policies in 1980-1990 The chart shows the rise in inflation that reached peak levels in the late 70’s, causing the Federal Reserve to come up with new policies to solve the issue.
- Food Security and Macroeconomics Discussion This is a bad trend which severely hurts the supply of food in third world countries which are not food sufficient.
- Macroeconomic Overview and Employment Rates in India The occupational structure of India shifted since the 1990s, and the percentage of people employed in the agricultural sector decreased considerable, which also positively affects economic growth. In summary, both the internal and external environment […]
- Macroeconomics in Unemployment Frictional unemployment is described as the unemployment that takes place because of the movement of people from one occupation to another.
- Macroeconomics and Hyperinflation in 1914-1923 The officials of the Central bank of Germany thought the cause of hyperinflation was the depreciation of the mark in foreign exchange currency.
- Interpreting World Macroeconomic Conditions The production of wine is related more to the gross domestic product compared to the rates of interest. In the United States the fast food industry is said to contribute a total of $ 1.
- Gas Prices and Macroeconomic Indicators The paper will investigate the possible effects of the change of gasoline price on changes in GDP, CPI, and unemployment rate.
- Macroeconomic Study of Latin America The economic growth as in the third quarter of 2008 was at 4. 8% and with the economic stimulus plan of $ 4Billion that is intended to quash the current meltdown in the economy, economic […]
- Macroeconomics – Fiscal Policy The stability of the Fiscal Policy is of great significance to any economy because it is one of the prime determinants of the strength of the economy of the country.
- Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Differences The perception of macroeconomics is in terms of a worldly view of resources while microeconomics entails a more individual feature of the economy. This makes the difference from macroeconomics, which appertains to the sum total […]
- Macroeconomic Development of Haiti The political condition in Haiti is in the shambles with a long history of anarchy, insurrection, dictatorship and political infighting the Haitian economy has remained one of the poorest economies of the world. Then the […]
- Evaluating Effectiveness of Supply Side Economics on Macroeconomic Objectives This paper takes the position that supply side economics has had its day and the deregulation aspect of the theory has gone too far with the result that the US economy as well as the […]
- Macroeconomic Impact on UK Hotel Chain’s Marketing Mix Other harbingers of the current economic travails are tight credit and falling home prices The country has not been spared the effects of the global economic slowdown that commenced with a recession across the Atlantic […]
Macroeconomics is a broad field that covers a wide range of issues. The two topics of primary concern in macroeconomics are:
- the behavioral tendencies;
- the decision-making processes of an economy as a whole.
In other words:
Macroeconomics explores human actions and interactions from an economic perspective.
Have you ever noticed any macroeconomic topics in the news? Or maybe in the headings of magazine articles, in the posts on social media? Or have you heard the discussion of high inflation and unemployment rate on the radio or television? These are all examples of the application of macroeconomics in real life.

The spectrum of issues examined by macroeconomics impresses with its diversity. To make your studying more pleasant, our team gathered ideas in one place.
The topics studied in macroeconomics include:
- Price levels
- Inflation rates
- Political economy
- Unemployment rates
- Finance development
- Fiscal and monetary policies
- National and international trade
- Government savings and investments
📑 Good Research Topics about Macroeconomics
- Kenya’s Macroeconomic Activities With the expansion of tourism, transport, and recovery in Agriculture which is in the due process, the gross domestic product per capita is expected to increase with high percentage. On top of that, Kenya’s economy […]
- Reductionist Effect in Macroeconomics Coddington says that limiting the supply of a product or service in the market will pull down the performance of a firm since the firm will lose its market share to competitors.
- Macroeconomics: Aggregate Demand and Supply The overall effect of the drilling in Alaska on the economy is that the economy will be rejuvenated and this cannot be more welcome in the united states at this time of financial crisis.
- Australian Fashion Industries. Macroeconomic Situation. It has been investing heavily in the industry by having designer wear that are readily available in the market and shopping malls and there are many customers who are interested and exposed to the products […]
- Macroeconomics: Increasing Firm’s Income The assumption of the equilibrium state within national income will hold and that the supply in national income is equal to the demand for the same income.
- Macroeconomics: South Africa’s Fiscal Space Reforms The purpose of this paper is to review the article and express the author’s opinion on the subject matter. The budget of South Africa should implement the government’s commitments to reduce the budget deficit and […]
- Fiscal Policy and Macroeconomics Moreover, the peculiarities and current state of the fiscal policy can be discussed by the Council of Economic Advisers, which means that this body is another aspect that might include macro.
- Macroeconomics: Unemployment Rate in North America Such indicators of economic development as the labor force rate and the unemployment rate are the significant aspects of state development and its policies regarding the labor market.
- France: Applying Macroeconomic Concepts Its continental borders are the North Sea, the English Channel, the Atlantic Ocean, the Bay of Biscay, Spain, Monaco, and Andorra, the Mediterranean Sea, and Italy, Switzerland and Germany, and Belgium and Luxemburg.
- “The Trouble with Macroeconomics” by Paul Romer In his article, Paul Romer addresses the challenges that the global economy has been experiencing due to the rise in the influence of the factors such as scientific research on the development of macroeconomics and […]
- Macroeconomics: McDonald’s Challenges in 2012 Therefore, this hurts McDonald’s reputation as a global fast-food business. The price demand elasticity strategy was a tactic to increase McDonald’s market share.
- American Macroeconomic Situation in 2011 It should be known that various insolvencies that had been experienced are falling and this is good as far as the economy is concerned. The Federal Reserve has maintained low-interest rates and this has been […]
- Australia’s Macroeconomic Policies The unemployment rate had been above 3% once since the the1940s went above 4% in the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s recessions. The inflation rate was above 10% in the early 1990s.
- Macroeconomic Issues and Funding Adjustments When ADF and ASF are equal, the amount of group 3 funds has for lending would be equal to the total amount group 2iwould be willing to borrow.
- Macroeconomics: Origins, Development and Current State In the event that there are these changes to these variables, the graphs presented in appendix 1 are a show of what is anticipated to happen to the core macroeconomic elements of the economy.
- Macroeconomics Course: Japanese Yen and US Dollar March 1: 1 USD = 81. 8425 JPY March 12: 1 USD = 81.
- 2008 Macroeconomic Collapse and Prevention Efforts The rise in the subprime mortgage rates led to the crash of the stock prices in the US. Therefore, in a volatile market, the aim is to reduce portfolio risk and not maximize trading profits.
- Macroeconomic Determinants of Savings in the UK The neoclassical model examines whether the development between steady states, positive changes in the savings ratio may stimulate the growth rate in the economy.
- Macroeconomic Factors of Website Content and Services Since internet usage is advancing significantly, the long-run prices offered in internet marketing would significantly decline as a result of high competition.
- “Lectures in Macroeconomics” by Arnold Kling Both increased productivity and trade are regarded as beneficial for the economy due to the potential ability to move labor resources from one sector that experiences productivity exceeding demand to those that encounters prevalence of […]
- Classical Macroeconomic Analysis and Its Principles The repercussion of the ASF line being horizontal is seen given a scenario where the APE line shifts to the right; implying an increase in expenditure with no funding to compliment it.
- Macroeconomics: Aggregate Planned Expenditures The major role of any economy is to ensure that it coordinates the changes in the level of goods produced and the changes in the demand for the goods.
- Macroeconomic Factors and Hong Kong Stock Returns This chapter covers the background of the study, problem statement, research objectives and hypotheses and the significance of the study. He argues that the inverse relationship between inflation and real stock returns is as a […]
- Macroeconomic Coordination and Demand Shocks Based on their needs, the most appropriate options are for the consumers, especially group two to borrow money in the form of loans, spend the money, and pay back the loan with interest. However, the […]
- Britain’s Economic Issues and Macroeconomic Concepts The spending power of the population has been eroded and the growth of wages is half the level of inflation. This is because there is little excess to be affected than in the first occurrence […]
- Russian Federation’s Macroeconomics in 2011 This resulted in a major decline of the economy with the GDP and the industrial output dropping by up to 50%.
⭐ Simple & Easy Macroeconomics Essay Titles
- Macroeconomics Performance and Policies of Mexico That is why it is possible to claim that inflation is one of the important macroeconomic issues that are to be solved in the future.
- Brexit Macroeconomic Impact on the United Kingdom One of the most important aspects of the referendum that appealed to pro-Brexit voters was the perception of how immigration can affect the labour market.
- Greece and Ireland: Macroeconomic and Financial Comparison However, the growth in Ireland was more than that in Greece. For Greece, it was engaged in fighting a runaway debt since the 1990s.
- US Macroeconomic Indicators in 2005-2012 The decline in economic growth reported in the first quarter of the year 2012 is a reflection of a lower growth rate in fixed investments and inventory by businesses.
- Scarcity, Decision-Making, and Macroeconomics The inability to concentrate on a particular task due to distractive thoughts about an ill parent/child or the need to make provision for a family usually plays a huge disservice in the matters of general […]
- Azerbaijan Macroeconomic Risk Analysis When entering the gas and oil sector of Azerbaijan, the CEO of the company should determine whether the risk factors outweigh the positive aspects of the industry.
- Japan Macroeconomics: Problems and Possible Solutions Based on this, the problems that need to be addressed as a result of this crisis are threefold: the first is the need to implement some form of reconstruction, the second is to address the […]
- Macroeconomic Environment: Self Correction of the Economy However, if the demand of shares in the stock market drops, it means that there will be a drop in income payments and many firms will be affected.
- Belgium Macroeconomic Data Analysis In Belgium, expenditure by the central government and the regional governments is separate. In 2012, central government expenditure was 23% of the total government expenditure.
- Equilibrium Supply and Demand – Macroeconomic Demand is the quantity of goods desired by consumers while supply is the amount of goods the producers can offer to the market.
- Germany and Its Macroeconomics At the same time, the growing share of private consumer spending in the German GDP is a wonderful opportunity to expand employment prospects and use its positive results to improve the standards of living in […]
- Macroeconomic Factors within the EU Recession in the EU has pushed some of the international companies out of the market because of the increased production costs in the region and low profits.
- Public Debt in Managing Macroeconomics The rates compound, and finally the government’s ability to repay the debt is doubted. The solution to the US’ debt crisis is to reduce government spending.
- Current macroeconomic situation in the USA In order to deal with the problem of inflation, the federal government could sell treasuries of the United States such as bonds in the international market.
- Economic Data Comparison of Australia, China, and Greece The budgetary position for Australia and Greece has been increasing from 1999 up to 2009 when the GFC occurred making the governments of these countries to reduce national expenditure and increase taxation to curb the […]
- Setting Macroeconomic Policies Initially, the government sets the inflation target and the Monetary Policy Committee forecasts the expected future inflation through economic statistics and imposes measures to curb it so as to meet the target.
- Project Macroeconomics Forecast Component Compare and contrast differences for the respective statistics prepared by the forecasters From the projection carried out by the CBO forecasters, the economic indicators seem to be at the highest between 2007 and 2010.
- European Macroeconomic Policies and Risks New entrepreneurs need to consider key macroeconomic factors such as aggregate demand polices, aggregate supply policies, fiscal policies, and the policies for the integration of the macroeconomic factors with the European social model.
- United States of America’s Macroeconomic Analysis The political system in the U.S.has been relatively stable over the years, making it the leading democracy in the world. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, the United States of America had experienced a […]
- Macroeconomic Situation of the US The United States boasts of being a leading economic power in the world, and as a result, the recent economic recession in the country led to the repercussions being felt in almost all the parts […]
- The Impact and Link of Macroeconomic Variables on the Share Prices in UK The reason of the difference of stock market behavior in the two countries is explained to be the result of slump of Japan after 1990 and liquidity trap of the late 1990 and start of […]
- Interpreting Macroeconomic Conditions: interest rate Low income levels means that the industry will spend a lot in an effort to increase sales and this will be reflected in high operating costs.
- Nominal and Real GDP Growth Rates When the real GDP is constant, the inflation rate follows the same trend and the natural rate of unemployment is not necessarily constant. When the Real GDP is high, the unemployment rate is low and […]
- Introduction to Macroeconomics: Sequestration and Its Impacts on an Economy According to Choi and Devereux, an increase in the permanent spending results in an increase in the released money, thus, an increase in the circulating currency.
- Macroeconomic Issues Related to the Federal Deficit and the National Debt What is affected by the federal budget deficit, which is equivalent to government debt level, is the change in the rate of interest.
- GDP Evaluation and Comparison: China, Greece, and Australia China GDP Annual Growth Rate In the year 2000 the annual growth rate of the GDP was 6% while the highest attained was 13% in the year 2009.
- Macroeconomic Policy About Population Growth Below is a list of twenty developing countries whose population growth was high in the 1960’s and 1970’s and declined at the beginning of the 21st century; Population growth rate GDP per capita Argentina 1 […]
- Macroeconomic Policy under Floating Exchange Rate This means that the exchange rate is flexible and can change from time to time in response to the dynamics of the foreign exchange markets.
- Macroeconomics: Socialism, Totalitarism and US Economics Compare and contrast the approach to economics of the U.S.system of government to Socialism Capitalism, which is the economic system in the U.
- Macroeconomic Analysis Using an Article The prize that a commodity or service is worth in the market is accumulated is summed up to the value of government expenditure and overall consumer expenses and is measured against the income value1. The […]
- Macroeconomics and Reality This demand is affected by the price of the car, the price of other models of cars, tastes and preferences of consumers among others. Many of the models in the article are also difficult to […]
- Macroeconomic Policy Settings in Australia Monetary policies on the other hand are policies used by the reserve bank of Australia to monitor the flow of money in the economy.
- Macroeconomic Policy Settings in Australia The economic growth in Australia is aimed at reducing the unemployment rates in the future. The country has succeeded in achieving economic growth and prosperity in the face of the global recession.
- Macroeconomics: Collapse of the United States Housing Market Such was the experience that the economy of the United States faced in the year 2009 following the crisis that was realized in the housing market.
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Policies The rate of interest will lower to such an extent that the aggregate demand will start to rise until it is equalized with the addition supply of funding.
- Macroeconomics: Determination of GDP It is the market value of these final goods and services that is referred to as gross domestic product. A general rise in the average price of goods and services in an economy is referred […]
- Macroeconomics: Demand of Super Bowl Tickets Rovel argues that the prices of Super Bowl tickets are plummeting because there are very few short sellers and that the location of New Orleans is not optimal since it is not easy to make […]
- Macroeconomic Study about Argentina Despite the growth in the real GDP of the country, the aforementioned statistics shows a consistent rise in the rate of inflation in the country.
- The Impact of Premature Financial Liberalisation on Macroeconomic and Financial Stability Effects on rate of savings and investment One of the roles of liberalisation is to remove rigidity in the control of rates of exchange and rates of interest, compulsory allocation of credits from banks, and […]
- Comparative Analysis of Macroeconomic Indicators of USA and Brazil The rationale is that unemployment refers to a proportion of the population that has skills and is willing to provide the skills to the labor market.
- Conceptual Study on Macroeconomics Notions The law of demand states that the higher the costof the good or service, the less people will demand it, while the law of supply states that the higher the price of a commodity, the […]
- Macroeconomic Coordination Process The graph, which is one diagram, will show the relationship between the level of interest on the vertical axis and the degrees of GDP, APE and ASF on the horizontal axis.
- A Macroeconomic And Financial Outlook Of New Zealand Some of this factors are the level of consumption of the country’s population, the level of savings and investment and the government’s fiscal and monetary policies.
- Measuring Macroeconomic Concepts As a matter of fact, it can also be referred to as the rate at which the purchasing power of individuals’ changes as time goes by. The country is in a stable period of prices […]
- Great Britain’s Macroeconomics In Relation To The US The mammoth economy was however destabilized by the innumerable costs accrued to the first and the second world wars and the great depression in the ninety’s.
- Rapidly Developing Macroeconomics in Chile The history of macroeconomic reforms in Chile dates back to the beginning of the 1990s, when the military government initiated the first economic reform.
- Principles of Macroeconomics: Supply and Demand Relationship In conclusion, supply and demand relationship tries to describe macroeconomic variables like price levels and amount of quantity in the economy.
Did you figure out the basic economic terms and concepts? Congratulations! Now, you are ready to go to the next step of your task completing. It is a topic search. Take this step responsibly because a compelling topic is a key to a successful paper.
The process of idea selection may become a real struggle for students. But not for you! We created a list of macroeconomics paper topics. The ideas are divided into several sections based on the type of assignment you need to complete. The macroeconomics topic choice has never been so easy!
Unemployment Rates
Unemployment is a vital macroeconomic indicator representing a nation’s economic performance. It points to labor underutilization, which results in lost goods and services. It’s critical to note that the term “unemployed” applies only to those people without jobs who actively search for one. It excludes those unable to work, those who have ceased job-seeking, and unpaid domestic workers.
Causes of Economic Recessions
Economic recessions can stem from interruptions in the supply or demand sides of the economy. Supply shocks, like oil shortages, can provoke price hikes and economic unease. Moreover, ill-timed government policies, financial crises, or housing market crashes can also induce a decline in spending and economic activity.
A Solution to the Child Labor Problem
Child labor is a growing problem, affecting 160 million children worldwide. A one-size-fits-all solution will not work for this global issue. Instead, the responses must be adapted to the diverse environments in which child labor happens. Besides, governments must implement robust child labor legislation alongside dedicated enforcement resources to end child exploitation in supply chains and on other levels.
Economic Consequences of Population Aging
Industrialized nations are experiencing a demographic shift with a rapidly aging population. The result is a double-edged sword: a lack of qualified workers to fill essential roles and a strain on social programs. With fewer working individuals, the cost of paying for healthcare, pensions, and other programs grows, posing a considerable challenge to governments.
Government Budget Balance
The government’s budget balance, a vital economic metric, depicts the authorities’ fiscal discipline, ability to manage their finances, and economic impact. A regular pattern of deficits raises concerns about the government’s capacity to satisfy its financial responsibilities, whereas surpluses help to reduce debt and increase economic stability.
📄 Macroeconomics Essay Topics
- Effect of oil prices on different countries’ GDP.
- The political economy of international trade.
- Limitations of GDP as a measure of economic welfare.
- The significance of Adam Smith’s “invisible hand” concept in modern economics.
- Remittances role in spurring global economic growth.
- Economic factors of Dubai tourism demand.
- The effects of inflation targeting.
- The interactions of economic and political science.
- The nature of the catch-up growth phenomenon in developing countries.
- The benefits of medical tourism to the world economy.
- The economic recession of 2007-2009 . Conduct an economic analysis of the worldwide crisis of 2007-2009. What were the causes and effects of the recession? Analyze the role of monetary and fiscal policies. What role do they play in reducing the risks of a total financial collapse during the crisis?
- The tourism industry in the state of Oregon . Investigate traveling commerce in Oregon from an economic perspective. How thousands of tourists help to maintain the appropriate level of economic growth? Explore the impact of tourism on the economy of Oregon and the USA. Look at them separately.
- The impact of the COVID -19 outbreak on the global economy . Explore the influence of the pandemic on the different branches of the economy. Analyze the readiness of the countries to face financial difficulties. Were the governments’ reactions to the risks of recession effective enough?
- Practical problems of active economic stabilization policy . There are three key negative effects of stabilization policy: – recognition lag – decision lag – impact lagDiscuss how these lags may lead to destabilization of the economy instead of stabilization. Why can a stabilization policy be useful for one class of enterprises? Why can it be ineffective for another one?
- Neoclassical economists. Analyze the scientific impact of three the most famous neoclassical economists: -Thorstein Veblen -Eliot Roy Weintraub -George Joseph StiglerCompare and contrast their approaches to macroeconomic objectives. How did these figures contribute to the development of the modern economy?
Globalization refers to the ever-increasing interdependence of economies around the world. It is fueled by technical breakthroughs, trade liberalization, and multinational corporations. It influences macroeconomics and international trade, namely trade balances, currency rates, capital flows, and competitiveness.
Here are some ideas to research macroeconomics in the context of globalization:
- The long-term effects of globalization on structural inflation in various economic systems.
- Globalization and its primary challenges for central banks in managing monetary policy.
- The relationship between labor market trends and globalization.
- How does globalization affect the level of unemployment in developing countries?
- International institutions and their regulatory function in the global economy.
🖥️ Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation
- Sustainable economic development. The four greens.
- European macroeconomic policies and risks.
- International environmental concerns in economics.
- Macroeconomic environment: self-correction of the economy .
- Economic systems types: free market and a mixed economy.
- Abu Dhabi commercial bank and financial regulation.
- Economic inequality as a result of globalization.
- Cultural differences and ethics of international trading.
- Economic analysis of criminal law.

- Economic fluctuations in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
- Theory of liquidity preference . Analyze Keyne’s theory of liquidity preference. Can interest rate adjustments indeed bring money supply and demand in balance? Use visual aids (graphs, charts) to make the understanding of the topic more accessible.
- Who leads the economy: economists or politicians? Explore the influence of politics on the economic sector. Why economics and politics cannot exist independently? Investigate the positive and negative outcomes of economic and political interactions. List all the key ideas on the slides. Appropriate illustrations will help the audience comprehend your ideas more effectively.
- Money laundering as one of the most critical financial crimes . Explain the mechanisms of economic crimes that occur in modern society. What criminal procedures are applied to deal with money laundering? What are the possible ways to reduce the risks of crimes against the property?
- Short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply differences. Explore the notions. What do they mean? How are they familiar? To make your presentation more professional, use slides. Demonstrate the correlation of short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply curves on the graph.
- Keynesian economics . Briefly introduce John Maynard Keynes. What were his economic approaches? Illustrate his models (the liquidity trap, IS-LM plot, Keynes–Samuelson cross). Highlight the significance of Keynesian discoveries for modern economics.
Monetary and fiscal policies function in a coordinated manner to direct economic activity. The central bank employs monetary policy to regulate the availability of credit and the money supply. Meanwhile, fiscal policy is employed to modify the government’s spending and taxation levels. Both instruments can be used as gas and brakes – stimulating growth during a slowdown or cooling down a booming economy.
Check out some research topics on macroeconomic policy:
- How does monetary policy influence corporate investment?
- What are the adverse aspects of expansionary fiscal policy?
- The government’s principal reasons for using expansionary monetary policy.
- How can fiscal policy address poverty and inequality?
- Does monetary policy affect greenhouse gas emissions?
📊 Macroeconomics Project Topics
- The costs and benefits of incurring an annual federal budget deficit.
- Cause and effects of the mortgage crisis.
- The effects of the introduction of the national minimum wage on employment.
- GDP growth rate and economic future of the United States.
- Alternative policies towards the exchange rate.
- Economic tools: alcohol abuse problem-solving.
- Optimizing production in the food industry.
- Automatic economic stabilizers.
- Methods of sustainable economic development.
- The role of China and the USA for the international economy. Compare and contrast the impact of both countries for global economic development.
- Strategies to overcome economic recession . Develop your ways to deal with economic obstacles. How to be ready for a financial crisis? How to reduce the negative consequences of the recession? State your ideas clearly and structure them wisely.
- Ways to reduce the unemployment level . Examine the causes and effects of unemployment. What would be possible mechanisms of dealing with the issue of lack of working places in a country? Explore the concept of the natural unemployment level and consider it while developing your project.
- Business establishment. Imagine you are planning to open a company. Applying economic concepts, develop a business plan for your enterprise. Organize the funds’ distribution within a company. What macroeconomic concepts should be used for this project

- Inflation vs. deflation. Investigate the positive and negative sides of inflation and deflation. What causes more harm to the national economy? Develop a strategic plan of dealing with the obstacles of inflation and deflation.
- Overconsumption of goods: beneficial for the producers, bad for the environment. Comment on the problem of unreasonable goods’ purchases. Why don’t people consider the lack of environmental resources while buying useless stuff? Develop a mechanism to control the consumption of the products to save the environment.
📈 Macroeconomics Presentation Topics on Economic Growth
Economic growth is an economy’s ability to manufacture more goods and services over time. It can be fueled by several factors, including capital goods, labor force, technology, and human resources. Economic growth is usually measured using indicators like GDP.
If you are looking for fresh topics on economic growth for your presentation, see the ones we listed below:
- Extensive and intensive types of economic growth.
- How does economic upturn impact quality of life?
- The key factors affecting economic upswing.
- The link between social welfare spending and economic growth.
- How do natural disasters hinder economic growth?
👩💻 Macroeconomic Topics for Research Paper
- Different forms of currency regimes and their impact on economic determinants.
- The implications of internet-banking on bank profitability.
- The trickle-down economics definition and aspects .
- Effects of increasing interest rates in Africa.
- The structure, history, and activities of the World Bank.
- Analysis of economic indicators for the United States and South Korea.
- The impact of demographic fluctuations within a country on its economic performance.
- The importance of the governmental support of small and medium businesses.
- The causes of economic inequality, poverty of underdeveloped countries.
- Macroeconomic implications of the healthcare sector development.
- The real exchange rate and the nominal exchange rate. Conduct research and analyze the differences between real and nominal exchange rates. What are the reasons for utilizing a real exchange rate? Support your ideas with arguments and appropriate examples.
- Theory of effective demand. Explore the significance of a balanced demand for the global economy. What place does Keynesianism take in this theory? For convenience, demonstrate your findings in the graphs.
- The bright future of the economy of ASEAN countries . Explain how the ASEAN (the Association of Southeast Asian Nations) can become a leading economic force globally. What opportunities and benefits do these countries have? Using economic thinking, suggest the right direction for the economic growth of ASEAN countries.

- How the Coronavirus outbreak affected stock prices and growth expectations? The worldwide pandemic noticeably weakened international economic performance. Discuss the adverse effects of COVID-19 on stock prices. What strategies did the governments implement to maintain a stable financial situation in a country?
- The impact of immigration on the national economy. What are the positive and negative effects of immigration? Develop an economic strategy to reduce the drawback of immigration on the national economy and maximize the benefits.
✍️ Macro Topics for Term Paper
- Unemployment rate as the most prominent national economy challenge .
- The nation’s budget deficit and how it relates to economic theory and crisis .
- Market elasticity in the banking industry.
- Minimum wages and their effects on the hospitality industry .
- New liquidity standards and implications.
- Corporate entrepreneurship and new business venturing.
- Economic factors on the stock market.
- The threat of Norwegian commercial banks for the economic stability of a country.
- Indicators of the upcoming recession and the strategies to prevent it.
- Influence of consumers’ tastes and preferences on market growth.
- The Economy of France between 1980 and 2012 . Provide a brief background of France’s economy and an overview of five variables. Analyze the country’s economy. What would be some possible policy recommendations? Provide graphs, charts, or tables if necessary.
- Strategies for raising the country’s per capita gross domestic product. Explore the possible ways to increase the GDP per capita. How will the rise of GDP stimulate the country’s economic growth? Provide clear arguments to support your opinion.
- The benefits of investments in innovative technologies . Explain why business owners should invest in innovations. How will it help them to increase the profitability of the companies? Examine the future of economics. Will the high-quality production be possible without modern technologies?
- Profit maximization strategies. Analyze the existing ways of maximizing the firms’ profit. What are the benefits and drawbacks of these strategies? Develop your profit-maximizing method. What macroeconomic principles and theories would you use for it? State your ideas clearly and provide examples to support your position.

- Globalization: an opportunity or a threat to the international economy? Analyze the positive and negative effects of globalization. What obstacles does globalization cause to small entrepreneurial organizations? How does globalization influence huge corporations? Present bright examples to solidify your ideas.
🔥 20 More Hot Topics in Macroeconomics
Did you look through our ideas and still unsure of which one to select? Then, take a look at the following section. Here, you can find the most popular and effective macroeconomics paper topics. Use one of the ideas from this list, and don’t worry that it will be inappropriate.
- International political economy perspectives.
- An invisible network of demand and supply.
- Factors affecting marketing and production decisions.
- The impact of monetary policy on economic stabilization.
- Behavioral finance and economics.
- Elasticity and its crucial role in business development.
- Sustainability and trends of the global trade imbalance.
- Financial economics for infrastructure and fiscal policy.
- The ways to increase the stockholders’ equities after the settlement of liabilities.
- Core-Econ: what economic data offers this online platform?
- The causes and effects of inflationary and deflationary gaps.
- The most effective ways to reach market equilibrium.
- The application of the macroeconomic concepts in real-life situations.
- Price discrimination problem. Introduce the phenomenon of price discrimination in the modern economic environment. What are the causes of the problem? What are the possible solutions? After the problem is solved, suggest future directions to prevent further concerns about price discrimination.
- The impact of the governmental regulations on the national economy. This is a topic of multiple-purpose. Are you searching for an idea for a term paper, presentation, or a capstone project? Then use this topic. It is quite relatable and offers a wide variety of sources to explore.
- The impact of biology progress on economic growth . Explain how biological innovations improve the production capacities of firms. What impact do such changes have on the healthcare, food, and agricultural industries? Refer to statistical data from reliable sources to support your ideas.
- Economic ethics . Analyze the progress of economic ethics from middle ages to contemporary times. Why is the following of moral rules while developing a business essential? Provide solid arguments and clear examples to prove your position.
- The importance of GDP for investors. Explain how investors make their decisions based on the GDP of a country. What factors do the investors take into consideration while investing money?

- Unemployment and inflation rates correlation. Explore the relationship between inflation and unemployment in the short-run and the long-run. Why do the outcomes of their correlation are different in the short-run and long-run? Refer to the Philips curve line graph to demonstrate your findings.
- Securities market structures. There are four types of securities market structures: – Quote-driven markets – Order-driven markets – Hybrid markets – Brokered markets Compare and contrast them. What structure is the most transparent and effective? How to minimize the risks of the securities market collapse?
- What Is Macroeconomics in Economics?
- What Are Macroeconomics and Examples?
- What Are the Five Macroeconomics?
- What Are the Four Main Factors of Macroeconomics?
- Which Is the Main Objective of Macroeconomics?
- Why Is Macroeconomics Important?
- What Are the Primary Tools of Macroeconomics?
- How Do Macroeconomics Factors Affect SMEs?
- How Does the Study of Microeconomics Differ From That of Macroeconomics?
- How Does Macroeconomics Affect Business?
- How Does Macroeconomics Affect Managerial Decision Making?
- How Well Can the New Open Economy Macroeconomics Explain the Exchange Rate?
- What Can Civil Society Expect From Academic Macroeconomics?
- What’s Wrong With Modern Macroeconomics?
- What Does the Entrepreneurial Problem Reveal About Keynesian Macroeconomics?
- What Are the Consequences for Macroeconomics During the Past 60 Years?
- Where Did Modern Macroeconomics Go Wrong?
- Which Way Forward for Macroeconomics and Policy Analysis?
- Why Does Macroeconomics Not Supervene on Microeconomics?
- Will the New Keynesian Macroeconomics Resurrect the IS-LM Model?
- Does Akerlof and Shiller’s Animal Spirits Provide a Helpful New Approach to Macroeconomics?
- Does Macroeconomics Need Microeconomic Foundations?
- How Macroeconomics Different From Microeconomics?
- How Can Macroeconomists Use Microeconomic Theory to Guide Them in Their Work?
- Macroeconomics: Should the Minimum Wage Increase?
- Macroeconomics: What Are the Main Causes of Unemployment in an Economy?
🔨 Tricks to Nail a Macroeconomics Paper
You are likely to have a general idea of essay writing. A thesis statement, five-paragraph structure, and arguments with supporting evidence are all part of it. Your paper on macroeconomics will probably follow the same old formula as well. However, we found a few tricks that will make the writing process less complicated. They can be used for any paper on macroeconomics.
- Find out the type of assignment beforehand. The structure of the project will differ drastically from that of the research paper. If it’s an essay, determine whether its an argumentative, informative, cause and effect, etc. Follow the structure If you need to prepare a presentation. Make appropriate slides to help the audience get your ideas. But remember to make the PowerPoint presentation professional. Use a readable font and suitable design to impress your listeners.
- academic style;
- suitable writing formats;
- reliable sources;
- proper citations.
- Change the central idea. The first viewpoint that comes to your mind can be erroneous. Any piece of academic writing requires a thought-out message. If you’re not sure what to state in your thesis, search for another macroeconomic topic for a paper. And don’t be afraid of changing it if necessary. Remember, a well-developed central idea is a key to a high grade. So, take enough time to compose a strong thesis statement.
- Research before writing. Macroeconomics is a broad field, so you have to make sure you see all the angles of the issue. Look for related macroeconomic topics or overlapping areas of study. If needed, improve your research question or change the perspective of your research. Make sure to select only credible sources. And don’t forget to cite them properly. Are you unsure about formatting requirements? Double-check the rules of the writing format you use.
- Outline your paper. Any writing guide will tell you that this is a great way to ensure the logical order. A well-developed outline will help you to structure your paper correctly. Thus, the readers will get your ideas without any difficulties. Moreover, fixing it is easier than the written text. So, don’t skip this step. By spending some time on outlining, you will save a lot of time on writing.
- Set out the size of each part. Remember that the introduction and conclusion must be shorter than the body. Moreover, the central part of your paper has to be divided into several sections. Use a separate body paragraph for each key point. A long and complicated text unit will only distract the readers’ attention. So, each part should follow its purpose and deliver the idea effectively.
- Find examples . Appropriate examples always improve the quality of a paper. Firstly, the readers understand the ideas more deeply when the writer presents the illustrations. Secondly, well-selected cases establish the credibility of a document. So, you can use them for reference. But be careful. To avoid confusion, make sure you provide suitable and relatable examples.
- Use online grammar correctors. We are not robots, and we make mistakes. That’s natural! Fortunately, we have an opportunity to use online grammar correctors. Such tools will ensure you haven’t missed an error while proofreading. One of the most useful and efficient ones is Grammarly . Besides correcting your spelling or grammar mistakes, it will also suggest style and vocabulary improvements. Why not use the benefits of correcting tools if there is such an opportunity?

Thank you for visiting our page! We hope your article was helpful. Don’t forget to share your macroeconomic topics and essay writing tips with your friends!
🔗References
- Macroeconomics: Economics and Finance, Khan Academy
- Macroeconomics: Articles, Research, & Case Studies on Macroeconomics, HBS Working Knowledge
- Top 100 Economics Blogs Of 2020: Prateek Agarwal, Economics Theory & News, Intelligent Economist
- Hot Topics in the U.S. Economy: US Economy and News, The Balance
- Writing Economics: Robert Neugeboren with Mireille Jacobson, Harvard University
- Macroeconomics Essay: Bartleby
- Organizing an Essay: Writing Advice by Jerry Plotnick, University College Writing Centre, University of Toronto
- Academic Essay Writing, Some Guidelines: Department of Economics, Carleton University
- Sample Business and Economics Essay: Research & Learning Online, Monash University
- Macroeconomics: Britannica
- Studies in Macroeconomic History: Cambridge Core, Cambridge University Press
- 14 Types of Essay Hooks with Samples And How to Write Them: EduPeet
- Budget Ideas
- Forecasting Questions
- Marxism Essay Ideas
- Collective Bargaining Essay Titles
- Economic Inequality Questions
- Market Research Titles
- Unemployment Essay Topics
- Trade Questions
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, October 17). 248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/
"248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research." IvyPanda , 17 Oct. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research'. 17 October.
IvyPanda . 2024. "248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research." October 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research." October 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "248 Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation & Research." October 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
Resources: Discussions and Assignments
Module 3 assignment: problem set — supply and demand.
You can click on the link to download the problem set for this module: Supply and Demand Problem Set.
Supply and Demand Problem Set [1]
Use the following graph to answer questions 1 through 3:.

- Plot the following Price and Quantity combinations: (4, 8), (1, 2), (5, 10)
- Is your graph more likely to be a demand curve or a supply curve? Why?
- Using the equation of a line, and P for price and Q for quantity, what is the algebraic formula of this curve?
Use the following graph to answer questions 4 and 5:

- Plot the following Price and Quantity combinations. Note that the points are given in the format (Quantity, Price).(0, 50), (2, 40), (4, 30), (6, 20), (8, 10)
- Using the equation of a line, what is the algebraic formula of this demand curve?
Use the following information to answer questions 6 through 10:
Suppose the equation of the line changes to [latex]P=-5\times Q+70[/latex]. Compute the quantity demanded at each indicated price.
- Price: $50, Quantity:
- Price: $40, Quantity:
- Price: $30, Quantity:
- Price: $20, Quantity:
- Price: $10, Quantity:

Use the following graph to answer questions 11 through 14:
- Let’s call the original demand curve (from Question 4) D1 and the new demand curve (from Questions 6-10) D2. Plot both of the demand curves on the graph above.
Use the formulas for the two demand curves to compute the quantity demanded shown by each curve at a price of $34.
- Demand Curve D1: Price: $34, Quantity:
- Demand Curve D2: Price: $34, Quantity:
- Describe what has happened to demand in this problem.
Use the following information to answer questions 15 and 16:
Use the following two equations for the demand and supply curves to compute the equilibrium price value.
Demand curve: [latex]Q_d=3300-2P[/latex]
Supply curve: [latex]Q_s=500+8P[/latex]
- What is the value of the equilibrium price?
- What is the equilibrium quantity?
Use the following information to answer questions 17 and 18:
Suppose Congress cuts personal income tax rates.
- Draw a simple supply and demand graph to show how this would affect the market for refrigerators.
- Why does this shift occur? How does that affect the equilibrium price and quantity? Explain.
Use the following information to answer questions 19 and 20:
Suppose that scooter workers accept a pay cut of 2 dollars per hour.
- Draw a graph to show how this would affect the market for scooters.
[1] This assignment by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. You can access an alternative means to plotting points at https://www.desmos.com/calculator .
- Supply and Demand Problem Set. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
Macroeconomics Practice Quiz Questions And Answers

Are you looking for practice material for an upcoming assignment or test in macroeconomics? Check out these macroeconomics practice quiz questions and answers and test your knowledge for the same. Macroeconomics is the field of economics that deals with the performances, structure, behavior, and decision-making of economies as a whole. The quiz below will test how well you know its basics and concepts. Are you ready to take this test? Go for it, then.
(16).jpg)
Diffrence between Real and Nominal GDP is:
Measured by excluding some of the sectors
That real GDP is always smaller than Nominal GDP.
Change in price level from base year to current year.
None of the above.
Rate this question:
(11).jpg)
GDP is the market value of all the final goods:
Produced domestically.
Produced by domestic factors of production.
Produced by all factors of production.
All of the above.
(12).jpg)
When comparing a nation's economic position with another, one should see its:
Per Capita GDP.
Currency in circulation.
(11).jpg)
Verticle intercept of consumption function indicates:
Average propensity to consume.
Consumption at zero level of income.
Both of the above.
(11).jpg)
In consumption function, c = a+by
B is intercept
Slope of the function
(10).jpg)
In Keynesian Framework, Income is measured along:
45 degree line
Verticle axis.
Horizontal axis.
All are correct.
(12).jpg)
If investment is exogenous to the Income determination model it can be shown as
Verticle line.
Horizontal line.
(13).jpg)
In closed economy GDP equals
(13).jpg)
In the model Y=C+I+G and C=a+by, Where b=0.8, the expenditure multiplier is
None of the above
The negative relationship between inflation and unemployment is characterized by ___________ in macroeconomics.
The Engle curve
The indifference curve
Okun’s law
The Phillips curve
Quiz Review Timeline +
Our quizzes are rigorously reviewed, monitored and continuously updated by our expert board to maintain accuracy, relevance, and timeliness.
- Current Version
- Jul 10, 2024 Quiz Edited by ProProfs Editorial Team
- Aug 28, 2008 Quiz Created by Mohammad Akram
Related Topics
Recent Quizzes
Featured Quizzes
Popular Topics
- Economic Development Quizzes
- Elasticity Quizzes
- Inflation Quizzes
- Microeconomics Quizzes
- Price Quizzes
- Scarcity Quizzes
- Supply And Demand Quizzes

Related Quizzes
Wait! Here's an interesting quiz for you.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.3 GDP and Economic Well-Being
Learning objectives.
- Discuss and give examples of measurement and conceptual problems in using real GDP as a measure of economic performance and of economic well-being.
- Explain the use of per capita real GNP or GDP to compare economic performance across countries and discuss its limitations.
GDP is the measure most often used to assess the economic well-being of a country. Besides measuring the pulse of a country, it is the figure used to compare living standards in different countries.
Of course, to use GDP as an indicator of overall economic performance, we must convert nominal GDP to real GDP, since nominal values can rise or fall simply as a result of changes in the price level. For example, the movie Avatar , released in 2009, brought in $761 million—the highest amount to date in gross box office receipts, while Gone with the Wind , released in 1939, earned only $199 million and ranks 117th in terms of nominal receipts. But does that mean that Avatar actually did better than Gone with the Wind ? After all, the average price of a movie ticket in 1939 was about 25 cents. At the time of Avatar , the average ticket price was about $7.50. A better way to compare these two movies in terms of popularity is to control for the price of movie tickets—the same strategy that economists use with real GDP in order to determine whether output is rising or falling. Adjusting the nominal box-office receipts using 2012 movie prices to obtain real revenue reveals that in real terms Gone with the Wind continues to be the top real grosser of all time with real box-office receipts of about $1.6 billion. Avatar ’s real box-office receipts amounted to a mere $776 million. [1] As illustrated by this example on revenues from popular movies, we might draw erroneous conclusions about performance if we base them on nominal values instead of on real values. In contrast, real GDP, despite the problems with price indexes that were explained in another chapter, provides a reasonable measure of the total output of an economy, and changes in real GDP provide an indication of the direction of movement in total output.
We begin this section by noting some of the drawbacks of using real GDP as a measure of the economic welfare of a country. Despite these shortcomings, we will see that it probably remains our best single indicator of macroeconomic performance.
Measurement Problems in Real GDP
There are two measurement problems, other than those associated with adjusting for price level changes, in using real GDP to assess domestic economic performance.
The first estimate of real GDP for a calendar quarter is called the advance estimate. It is issued about a month after the quarter ends. To produce a measure so quickly, officials at the Department of Commerce must rely on information from relatively few firms and households. One month later, it issues a revised estimate, and a month after that it issues its final estimate. Often the advance estimate of GDP and the final estimate do not correspond. The recession of 2001, for example, began in March of that year. But the first estimates of real GDP for the second and third quarters of 2001 showed output continuing to rise. It was not until later revisions that it became clear that a recession had been under way.
But the revision story does not end there. Every summer, the Commerce Department issues revised figures for the previous two or three years. Once every five years, the department conducts an extensive analysis that traces flows of inputs and outputs throughout the economy. It focuses on the outputs of some firms that are inputs to other firms. In the process of conducting this analysis, the department revises real GDP estimates for the previous five years. Sometimes the revisions can paint a picture of economic activity that is quite different from the one given even by the revised estimates of GDP. For example, revisions of the data for the 1990–1991 recession issued several years later showed that the recession had been much more serious than had previously been apparent, and the recovery was more pronounced. Concerning the most recent recession, the first estimates of fourth quarter 2008 GDP showed that the U.S. economy shrank by 3.8%. The first revision, however, showed a drop of 6.8%, and the second revision showed a drop of 8.9%!
The Service Sector
Another problem lies in estimating production in the service sector. The output of goods in an economy is relatively easy to compute. There are so many bushels of corn, so many pounds of beef. But what is the output of a bank? Of a hospital? It is easy to record the dollar value of output to enter in nominal GDP, but estimating the quantity of output to use in real GDP is quite another matter. In some cases, the Department of Commerce estimates service sector output based on the quantity of labor used. For example, if this technique were used in the banking industry and banking used 10% more labor, the department would report that production has risen 10%. If the number of employees remains unchanged, reported output remains unchanged. In effect, this approach assumes that output per worker—productivity—in those sectors remains constant when studies have indicated that productivity has increased greatly in the service sector. Since 1990 progress has been made in measurement in this area, which allows in particular for better estimation of productivity changes and price indexes for different service sector industries, but more remains to be done in this large sector of the U.S. economy (Triplett & Bosworth, 2008).
Conceptual Problems with Real GDP
A second set of limitations of real GDP stems from problems inherent in the indicator itself. Real GDP measures market activity. Goods and services that are produced and exchanged in a market are counted; goods and services that are produced but that are not exchanged in markets are not. [2]
Household Production
Suppose you are considering whether to eat at home for dinner tonight or to eat out. You could cook dinner for yourself at a cost of $5 for the ingredients plus an hour or so of your time. Alternatively, you could buy an equivalent meal at a restaurant for perhaps $15. Your decision to eat out rather than cook would add $10 to the GDP.
But that $10 addition would be misleading. After all, if you had stayed home you might have produced an equivalent meal. The only difference is that the value of your time would not have been counted. But surely your time is not worthless; it is just not counted. Similarly, GDP does not count the value of your efforts to clean your own house, to wash your own car, or to grow your own vegetables. In general, GDP omits the entire value added by members of a household who do household work themselves.
There is reason to believe this omission is serious. Economists J. Steven Landefeld and Stephanie H. McCulla of the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis estimated in a 2000 paper the value of household output from 1946 to 1997. Their estimate of household output in 1946 was 50% of reported GDP. Since then, that percentage has fallen, because more women have entered the workforce, so that more production that once took place in households now occurs in the market. Households now eat out more, purchase more prepared foods at the grocery store, hire out child-care services they once performed themselves, and so on. Their estimate for 1997, for example, suggests that household production amounted to 36% of reported GDP (Landefeld & McCulla, 2000).
This problem is especially significant when GDP is used to make comparisons across countries. In low-income countries, a much greater share of goods and services is not exchanged in a market. Estimates of GDP in such countries are adjusted to reflect nonmarket production, but these adjustments are inevitably imprecise.
Underground and Illegal Production
Some production goes unreported in order to evade taxes or the law. It is not likely to be counted in GDP. Legal production for which income is unreported in order to evade taxes generally takes place in what is known as the “underground economy.” For example, a carpenter might build a small addition to a dentist’s house in exchange for orthodontic work for the carpenter’s children. Although income has been earned and output generated in this example of bartering, the transaction is unlikely to be reported for income tax or other purposes and thus is not counted in GDP. Illegal activities are not reported for income taxes for obvious reasons and are thus difficult to include in GDP.
Leisure is an economic good. All other things being equal, more leisure is better than less leisure.
But all other things are not likely to be equal when it comes to consuming leisure. Consuming more leisure means supplying less work effort. And that means producing less GDP. If everyone decided to work 10% fewer hours, GDP would fall. But that would not mean that people were worse off. In fact, their choice of more leisure would suggest they prefer the extra leisure to the goods and services they give up by consuming it. Consequently, a reduction in GDP would be accompanied by an increase in satisfaction, not a reduction.
The GDP Accounts Ignore “Bads”
Suppose a wave of burglaries were to break out across the United States. One would expect people to respond by buying more and louder burglar alarms, better locks, fiercer German shepherds, and more guard services than they had before. To the extent that they pay for these by dipping into savings rather than replacing other consumption, GDP increases. An epidemic might have much the same effect on GDP by driving up health-care spending. But that does not mean that crime and disease are good things; it means only that crime and disease may force an increase in the production of goods and services counted in the GDP.
Similarly, the GDP accounts ignore the impact of pollution on the environment. We might produce an additional $200 billion in goods and services but create pollution that makes us feel worse off by, say, $300 billion. The GDP accounts simply report the $200 billion in increased production. Indeed, some of the environmental degradation might itself boost GDP. Dirtier air may force us to wash clothes more often, to paint buildings more often, and to see the doctor more often, all of which will tend to increase GDP!
Conclusion: GDP and Human Happiness
More GDP cannot necessarily be equated with more human happiness. But more GDP does mean more of the goods and services we measure. It means more jobs. It means more income. And most people seem to place a high value on these things. For all its faults, GDP does measure the production of most goods and services. And goods and services get produced, for the most part, because we want them. We might thus be safe in giving two cheers for GDP—and holding back the third in recognition of the conceptual difficulties that are inherent in using a single number to summarize the output of an entire economy.
International Comparisons of Real GDP and GNP
Real GDP or GNP estimates are often used in comparing economic performance among countries. In making such comparisons, it is important to keep in mind the general limitations to these measures of economic performance that we noted earlier. Further, countries use different methodologies for collecting and compiling data.
Three other issues are important in comparing real GDP or GNP for different countries: the adjustment of these figures for population, adjusting to a common currency, and the incorporation of nonmarket production.
In international comparisons of real GNP or real GDP, economists generally make comparisons not of real GNP or GDP but of per capita real GNP or GDP , which equals a country’s real GNP or GDP divided by its population. For example, suppose Country A has a real GDP of about $4,000 billion and Country B has a real GDP of about $40 billion. We can conclude that Country A produced 100 times more goods and services than did Country B. But if Country A has 200 times as many people as Country B (for example, 200 million people in Country A and 1 million in Country B), then Country A’s per capita output will be half that of Country B ($20,000 versus $40,000 in this example).
Figure 6.7 “Comparing Per Capita Real GNP, 2010” compares per capita real GNP for 11 countries in 2010. It is based on data that uses a measure called “international dollars” in order to correct for differences in the purchasing power of $1 across countries. The data also attempt to adjust for nonmarket production (such as that of rural families that grow their own food, make their own clothing, and produce other household goods and services themselves).
Figure 6.7 Comparing Per Capita Real GNP, 2010
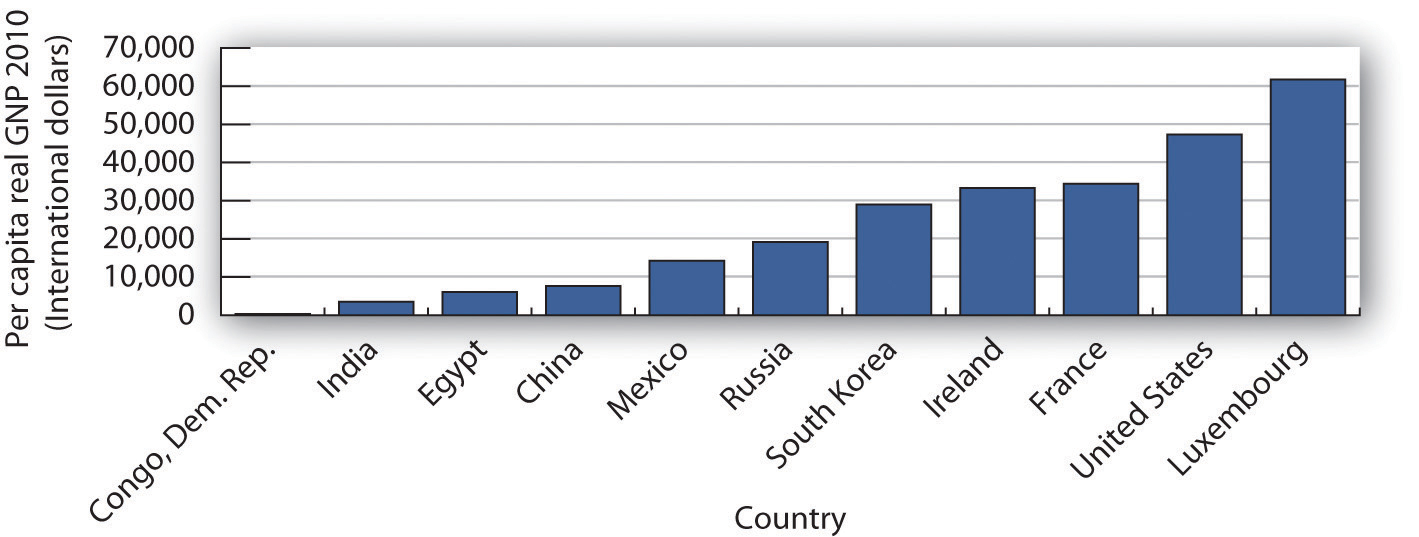
There is a huge gap between per capita income in one of the poorest countries in the world, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and wealthier nations such as the United States and Luxembourg.
Source : World Bank, World Development Indicators Online
The disparities in income are striking; Luxembourg, the country with the highest per capita real GNP, had an income level nearly 200 times greater than the Democratic Republic of Congo, the country with the lowest per capita real GNP.
What can we conclude about international comparisons in levels of GDP and GNP? Certainly we must be cautious. There are enormous difficulties in estimating any country’s total output. Comparing one country’s output to another presents additional challenges. But the fact that a task is difficult does not mean it is impossible. When the data suggest huge disparities in levels of GNP per capita, for example, we observe real differences in living standards.
Key Takeaways
- Real GDP or real GNP is often used as an indicator of the economic well-being of a country.
- Problems in the measurement of real GDP, in addition to problems encountered in converting from nominal to real GDP, stem from revisions in the data and the difficulty of measuring output in some sectors, particularly the service sector.
- Conceptual problems in the use of real GDP as a measure of economic well-being include the facts that it does not include nonmarket production and that it does not properly adjust for “bads” produced in the economy.
- Per capita real GDP or GNP can be used to compare economic performance in different countries.
What impact would each of the following have on real GDP? Would economic well-being increase or decrease as a result?
- On average, people in a country decide to increase the number of hours they work by 5%.
- Spending on homeland security increases in response to a terrorist attack.
- The price level and nominal GDP increase by 10%.
Case in Point: Per Capita Real GDP and Olympic Medal Counts

David Pilbrow – Adam Gemili – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
In the popular lore, the Olympics provide an opportunity for the finest athletes in the world to compete with each other head-to-head on the basis of raw talent and hard work. And yet, contenders from Laos tend to finish last or close to it in almost any event in which they compete. One Laotian athlete garnered the unenviable record of having been the slowest entrant in the nearly half-century long history of the 20-kilometer walk. In contrast, U.S. athletes won 103 medals at the 2004 Athens Olympics and 110 medals at the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Why do Laotians fare so poorly and Americans so well, with athletes from other countries falling in between?
Economists Daniel K. N. Johnson and Ayfer Ali have been able to predict with astonishing accuracy the number of medals different countries will win on the basis of a handful of factors, including population, climate, political structure, and real per capita GDP. For example, they predicted that the United States would win 103 medals in Athens and that is precisely how many the United States won. They predicted 103 medals for the United States in Beijing; 110 were won. They did not expect the Laotians to win any medals in either Athens or Beijing, and that was indeed the outcome.
Johnson and Ali estimated that summer game participant nations average one more medal per additional $1,000 of per capita real GDP. With per capita real GDP in Laos less than the equivalent of $500 compared to per capita real GDP in the United States of about $38,000, the results for these two nations could be considered a foregone conclusion. According to Johnson and Ali, “High productive capacity or income per person displays an ability to pay the costs necessary to send athletes to the Games, and may also be associated with a higher quality of training and better equipment.” For example, a Laotian swimmer at Athens, Vilayphone Vongphachanh, had never practiced in an Olympic-size pool, and a runner, Sirivanh Ketavong, had worn the same running shoes for four years.
The good news is that as the per capita real GDP in some relatively poor countries has risen, the improved living standards have led to increased Olympic medal counts. China, for instance, won 28 medals in 1988 and 63 in 2004. As the host for the 2008 games, it won an impressive total of 100 medals.
While not a perfect measure of the well-being of people in a country, per capita real GDP does tell us about the opportunities available to the average citizen in a country. Americans would surely find it hard to imagine living at the level of consumption of the average Laotian. In The Progress Paradox: How Life Gets Better While People Feel Worse , essayist Gregg Easterbrook notes that a higher material standard of living is not associated with higher reported happiness. But, he concludes, the problems of prosperity seem less serious than those of poverty, and prosperity gives people and nations the means to address problems. The Olympic medal count for each nation strongly reflects its average standard of living and hence the opportunities available to its citizens.
Sources : Gregg Easterbrook, The Progress Paradox: How Life Gets Better While People Feel Worse (New York: Random House, 2003); Daniel K. N. Johnson and Ayfer Ali, “A Tale of Two Seasons: Participation and Medal Counts at the Summer and Winter Olympic Games,” Social Science Quarterly 84, no. 4 (December 2004): 974–93; David Wallechinsky, “Why I’ll Cheer for Laos,” Parade Magazine , August 8, 2004, p. 8.
Answer to Try It! Problem
- Real GDP would increase. Assuming the people chose to increase their work effort and forgo the extra leisure, economic well-being would increase as well.
- Real GDP would increase, but the extra expenditure in the economy was due to an increase in something “bad,” so economic well-being would likely be lower.
- No change in real GDP. For some people, economic well-being might increase and for others it might decrease, since inflation does not affect each person in the same way.
Landefeld, J. S. and Stephanie H. McCulla, “Accounting for Nonmarket Household Production within a National Accounts Framework,” Review of Income & Wealth 46, no. 3 (September 2000): 289–307.
Triplett, J. E. and Barry P. Bosworth, “The State of Data for Services Productivity Measurement in the United States,” International Productivity Monitor 16 (Spring 2008): 53–70.
- Based on estimates at “Domestic Grosses Adjusted for Ticket Price Inflation,” Box Office Mojo, accessed April 10, 2012, http://boxofficemojo.com/alltime/adjusted.htm . ↵
- There are two exceptions to this rule. The value of food produced and consumed by farm households is counted in GDP. More important, an estimate of the rental values of owner-occupied homes is included. If a family rents a house, the rental payments are included in GDP. If a family lives in a house it owns, the Department of Commerce estimates what the house would rent for and then includes that rent in the GDP estimate, even though the house’s services were not exchanged in the marketplace. ↵
Principles of Macroeconomics Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Trending Courses
Course Categories
Certification Programs
Free Courses
Economics Resources
- Career Guides
- Interview Prep Guides
- Free Practice Tests
- Excel Cheatsheets
By Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
(ex. J.P. Morgan & CLSA Equity Analyst with 20+ years of training experience)

Macroeconomics
Last Updated :
21 Aug, 2024
Blog Author :
Wallstreetmojo Team
Edited by :
Ashish Kumar Srivastav
Reviewed by :
Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
Table Of Contents
Macroeconomics Definition
Macroeconomics is a 'top-down approach; it gives a birds' eye view of the economy. It focuses on aspects and phenomena that are important to the national economy and the world economy at large. The economy is impacted by GDP, growth, inflation, government spending, borrowings (fiscal policies), unemployment, and monetary policy.
The prices of products and services are interlinked, and macroeconomics studies the changes in these prices during economic ups and downs. Governments and institutions strategize policies based on this study. John Maynard Keynes is widely regarded as the pioneer in macroeconomics.
Table of contents
Macroeconomics explained, macroeconomics theories, #1 - reduce unemployment, #2 - exchange rate stability, #3 - control inflation, #4 - economic development, #5 - balance of payment equilibrium, #6 - decrease government borrowings, macroeconomics examples, scope and importance, limitations of macroeconomics, frequently asked questions (faqs), recommended articles.
- Macroeconomics is the economics discipline that concentrates on problems that affect the whole nation or region instead of an individual or household. It focuses on poverty, unemployment, inflation, national income, and economic growth.
- Governments and statutory bodies rely on this study. It is an essential parameter used in formulating fiscal and monetary policies.
- John Maynard Keynes is considered the father of macroeconomics. In 1936, he reshaped macroeconomics concepts.
- This economics discipline aims to facilitate sustainable economic development, stability of price, stable exchange rates, improved employment conditions, and balance of payment.
Between micro and macroeconomics, the latter is more fascinating. It elucidates a global economic picture, a bird's eye view. It is a 'top-down' approach. The study highlights how the output levels of different products and services are correlated. For example, if the price of fuel rises, then the price of goods like fruits, vegetables, and groceries will also rise. This is brought about by high transportation costs. Thus, this economics discipline aims to interlink different phenomena.

Historically, issues like trade, prices, output, unemployment, and growth have been discussed earlier by great economists like John Stuart Mill and Adam Smiths. However, it was the famous British economist John Maynard Keynes who combined all these economic factors. As a result, the modern concept of macroeconomics was introduced. In 1936, Keynes published The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money . Keynes' modern economics contradicted the classic theory of the self-regulating market. After the 1929's Great Depression, the US and Europe faced severe unemployment levels. Consequently, the aggregate output also fell drastically. Keynes studied the whole economy and correlated the behavior of different sectors and the economic factors to identify the reasons behind the fluctuation.
In macroeconomics, demand and supply refer to a broad range of aspects as both are aggregate by nature. Keynes favored demand-side economics , which impacts real GDP by increasing aggregate demand. This involves improving income levels, stabilizing unemployment, and checking government spending. The aim was to boost the spending ability of people. Supply-side economics tries to impact real GDP by increasing aggregate supply. This includes adjusted tax rates, deregulation, infrastructure support, privatization, and educational reforms.
Macroeconomics focus on the following concepts.
- Theory of General Price Level : The prices of products and services are interlinked; economists study the changes in these prices during the economic ups and downs.
- Theory of National Income : The country's budgeting, income, and expenditure impacts the nation's overall growth. This measure aims to facilitate economic equality in society.
- Economic Growth and Development : The nation's gross domestic product and per capita income are development indicators.
- Theory of Employment : It is equally important to determine the unemployment level of a nation. Unemployment affects a nation's income, consumption, demand, supply, and GDP.
- Theory of International Trade : Countries are highly affected by cross-border selling and purchase. As trade is necessary for improving economic conditions, the stability of exchange rates is essential. Preferably, the barriers for import and export should also be minimal.
- Theory of Money : The central bank policies control monetary circulation. Therefore, the economists give due consideration to central bank policies and their consequences.
Macroeconomics Objectives
In 1929, the US and apparently the whole world faced a great economic depression. Most economists failed to interpret this downfall. Following are the objectives of the macroeconomics theories:
Macroeconomics highlights how consumer demand impacts employment levels. A fall in demand causes employee layoffs. Therefore, measures increasing demand improve the employment conditions of a nation.
Exchange rate fluctuations greatly impact the cross-border selling of goods and services. Favorable export and import duties can promote economic growth.
A macroeconomic analysis identifies inflation. It further highlights measures that can reduce the adverse impact of inflation.
We have often read about business cycle fluctuations; the economy is dynamic. This is why economists, governments, and statutory bodies try to anticipate fluctuations. They plan based on the predictions. Therefore, despite unavoidable changes, economic growth can be ensured by making policies diligently.
International trade activities are essential for a nation's development. This is why economists match export receipts to import payments. They identify a surplus or deficit. If import exceeds export, the surplus is termed as the balance of payment.
Governments borrow funds from other countries to fulfill short-term and long-term requirements or to repay previous loans. However, excessive borrowings can negatively impact a nation's economy. Therefore, checking government borrowings is a vital part of this economics discipline.
Let us discuss an example of macroeconomic analysis. The actual gross domestic product of Puerto Rico decreased by 2.4% in 2018. However, in 2019, GDP went up by 0.3% due to a 0.7% increase in exports. Also, a 9.1% decline in imports subsided the effects of reduced consumer and government spending. The credit for this goes to the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
Moreover, in 2019, the government reduced its expenditure on disaster recovery activities by 11.4%. This was possible because major damage repair of the power grid was accomplished in 2018 itself. Further, consumer spending in 2019 fell by 0.5%, and durable goods sales fell by 3.6%. This was caused by the 2018 reduction in compensation offered by the government and insurance companies.
United States Current Account deficit is another example. They simply consume more than they earn. But how does the US finance this spending then? The government borrows money by issuing sovereign debt. Thus, the US runs a Capital Account Surplus.
The scope of macroeconomics is described below.
- Curtail the Impact of Recession or Inflation : Though the economic cycles cannot be avoided, their impact can be reduced significantly by implementing macroeconomic policies.
- Economic Problem Solving : Macroeconomic research and analysis identify the root cause behind a country’s economic crisis. It further facilitates the development of a problem-solving mechanism.
- Sustainable Economic Growth : The study helps deal with various macro-level issues like inflation, unemployment, and price level fluctuations.
- Policy Formation : The government and the statutory bodies make use of macroeconomic analysis for devising fiscal policies and monetary policies. These are reforms for correcting the economy.
- Social Welfare : The study also facilitates proper resource allocation to ensure economic equality.
- Business Cycle Analysis : With the regressive study of macroeconomic conditions, economists can interpret business cycle fluctuations. As a result, necessary steps are taken to reduce the impact of economic adversities.
Macroeconomic analysis may go wrong since it emphasizes future predictions based on past incidents. In reality, things may not fall in the same way. Moreover, a particular situation can result from multiple economic changes, which require an expert's knowledge and efforts.
There are numerous theories for conducting such an analysis; however, these theories ignore the practical aspects like government regulations and taxation. Further, it is a complex and specialized stream that requires a high level of skill and learning.
Macroeconomists analyze a nation's economic growth and business cycle fluctuations. They aid governments and business entities in decision-making. To control and stabilize macroeconomic changes, governments use fiscal policy measures. This involves increasing or decreasing government spending and tax rates. Additionally, statutory bodies like the central bank implement monetary policies. For example, the reduction or increase in interest rates and money supply is a monetary policy.
Listed below are some of the principal aims behind macroeconomic analysis: 1. Controlling inflation, 2. Maintaining the balance of payment, 3. Stabilizing exchange rates, 4. Ensuring sustainable economic development, and 5. Reducing unemployment
The British economist John Maynard Keynes is renowned as the father of macroeconomics. In 1936, Keynes compiled the significant economic issues and variables to propose this concept. He published this in a book, The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money.
This has been a Guide to what is Macroeconomics and its Definition. Here we explain macroeconomics objectives, theories, & importance using examples. You may learn more about from these economics recommended articles below –
- Best Macroeconomics Books
- Economies of Scale vs Economies of Scope
- Microeconomics
- Behavioural Economics

Principles of Macroeconomics: Exam Questions Assignment
Monroe College Instructor: Carlo Augusta Student name : James Demesnes Macroeconomics l. Current event questions Take home test 2 a. Summarize the history (creation) of the Central Bank of the US Re: The First Bank of the United States was founded after the revolutionary war in 1795 – 1797 . The United States was in debts cause by the War. Therefore, President Alexander Hamilton advised of the bank to handle the colossal war debt and also create some kind of currency. B.
Give the full name of and time in office for the current chairman of the Federal Reserve Bank and his predecessor Re: Since February 3, 2014, Janet Yelled is the current chairperson for Federal Reserve Bank and her predecessor is Ben S. Brenan. II. Theoretical questions 1. Define macroeconomics and explain its roots Re:(A) Macroeconomics is study of a country’s larger economic issues, such as how firms compete, the effects of government policies, and how an economy maintains and allocates its scarce resources.
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
Re:(B) As the world economy has experienced a range of perplexity , such as mass unemployment rate during the Great depression f the sass, rapid inflation in the sass and other recessions in the early sass through sass. As a result many economists have analyze them and somehow came up with an solution called macroeconomics. Which study the over whole the behavior of an economic system. 2. State and explain the three different macroeconomics policies Re(A): The three different macroeconomics policies are: Economic Growth, Low Unemployment and Low inflation. B) Economic Growth is the increase of the total physical output of the final goods and services of an economy. C) Low unemployment occur when the natural rate is a below due to some changes in the economy . (D)Low inflation is decrease in the overall price level. 3. Explain the three different market arenas Re(A) Goods and Services Market is when the household seller , the government and outsiders buy goods and services from firms. (B) Labor market is when firms and the government purchase labor from households. (C)Money Market or financial markets is when households ,other firms and outsiders purchase stocks and bonds from firms.
Output market in other hand is where finished goods are traded 4. Discuss the trends and cycles of the US economy Principles of Macroeconomics: Exam Questions By Jadedness 5 Define GAP, explain its two types , and discuss its limitations Re:The total output measured by the market value of all final amount of goods and services produced by an economy during a given period of time, usually a year. (B) Nominal GAP is when the value of goods and services are articulated in current prices 6. Define unemployment and discuss the different types of unemployment Ill.
Practicum questions 1. Let the price of Barbarous (the Haitian Rum) be $15 a bottle in 2000 and $25 in 2010, and its production 5000 and 7500 bottles respectively for the two years. Let the price of a bag of rice be $20 in 2000 and $35 in 2010, when its production is 10000 and 25000 bags for the same two years. Let the price of a bag of beans be $30 in 2000 and $40 in 2010, when its production is 8000 and 20000 bags of the two years respectively. Using the year 2000 as the base year, compute: a. The Nominal GAP for both years b. The real GAP for both year .
The Implicit Price Deflator for GAP for both years d. The ICP for both years. 2. Suppose that the economy of an island H is described by the following equations: GAP (Y) = 8000, government expenditures (G) = 600, Taxes (T) = 1000, Consumption (C) = 400 + 3/4 (Y-T), and investment (I) = 800 – err a. Write the equation of the GAP b. Compute 1. Private saving 2. Public saving 3. National saving 4. Equilibrium interest rate 5. What can you conclude about the economy of Island H (in term of type of budget and type of economy? ) Explain why.
How to cite this assignment
Related assignments:.
- Testbank for macroeconomics canada in the global Assignment
- How macroeconomics is different from microeconomics. Assignment
- Macroeconomics Sample Exam Paper Assignment
- Questions in Macroeconomics Assignment
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page

IMAGES
VIDEO