

How to Do a T Test in Excel (2 Ways with Interpretation of Results)
Download the Practice Workbook
T Test.xlsx
T Test Types
There are two types of t-tests. They are:
- One-tailed t-test
- Two-tailed t-test
Each of them has 3 subtypes. They are:
- Two sample equal variance
- Two sample unequal variance
How to Do a T-Test in Excel: 2 Effective Ways
Method 1 – using the excel t.test or ttest function for a t-test, case 1.1 – two sample equal variance t-test.
In the dataset, you will see the prices of different laptops and smartphones. Here is a formula that performs a T-Test on the prices of these products and returns the t-test result.
=T.TEST(B5:B14,C5:C14,2,2)
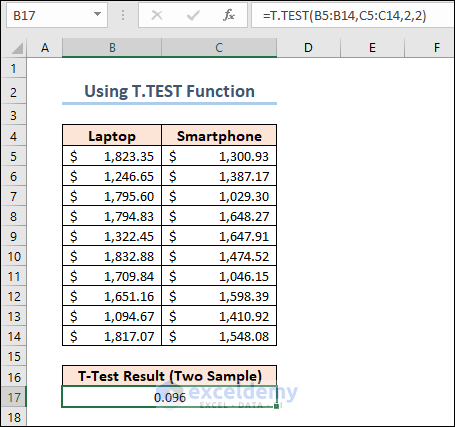
We set the 3rd argument of the function to 2 as we are doing a two-tailed t-test on the dataset. The 4th argument should be 2 for a two-sample equal variance t-test.
Case 1.2 – Paired T-Test
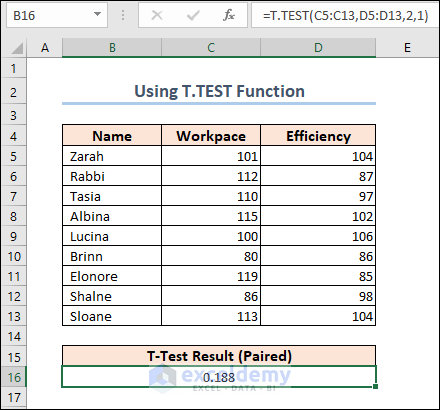
We are going to apply another formula to calculate the Paired T-Test . The following dataset shows the performance mark of some employees in two different criteria.
=T.TEST(C5:C13,D5:D13,2,1)
Note: The explanation of the results is described in the following sections.
Method 2 – Using the Analysis ToolPak
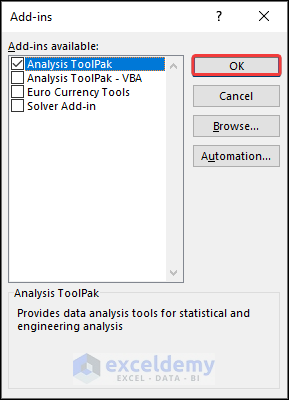
- Go to the Options window.
- Select Add-ins and click on the Go button in the Manage section.

- The Add-ins window will appear. Select Analysis ToolPak and click OK again.
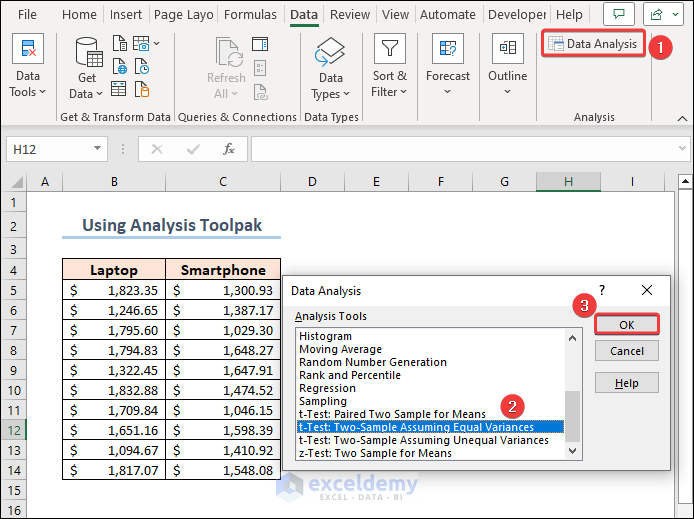
Case 2.1 – Tw-Sample Equal Variance T-Test
- Click on the Data Analysis button from the ribbon of the Data tab.
- The Data Analysis features will appear. Select t-Test: Two Sample Assuming Equal Variances and click OK .
- Set up the parameters for the t-test operation. Insert the Laptop and Smartphone prices as Variable 1 Range and Variable 2 Range. Include the headings in the range and check Labels.
- Set the value of Hypothesized Mean Difference to 0 .
- Select an Output option of your preference and click OK .
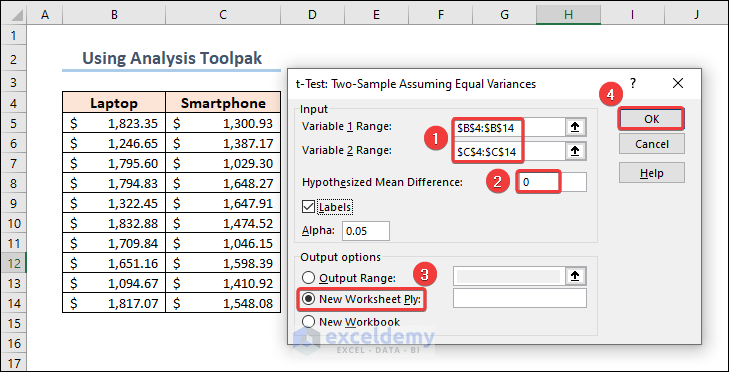
- As we have chosen a New Worksheet for the outputs, we will see the results in a new sheet.
Comments on Results
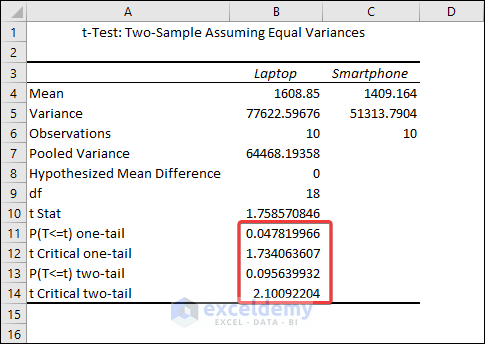
The output shows that the mean values for Laptops and Smartphones are 1608.85 and 1409.164 respectively. We can see from the Variances row that they are not precisely equal, but they are close enough to be assumed to have equal variances. The most relevant metric is the p-value .
The difference between means is statistically significant if the p-value is less than your significance level. Excel calculates p-values for one- and two-tailed T Tests .
One-tailed T Tests can detect only one direction of difference between means. A one-tailed test, for example, might only evaluate whether Smartphones have higher prices than Laptops . Two-tailed tests can reveal differences that are larger or smaller than. There are some other disadvantages to utilizing one-tailed testing, so I’ll continue with the conventional two-tailed results.
For our results, we’ll utilize P(T=t) two-tail, which is the p-value for the t-test’s two-tailed version. We cannot reject the null hypothesis because our p-value ( 0.095639932 ) is greater than the conventional significance level of 0.05 . The hypothesis that the population means differ is supported by our sample data. The mean price of Laptops is greater than the mean price of Smartphones’ .
The Analysis ToolPak also returns results for a one-tailed t-test . Here, the one-tailed P value of the two-sample equal variance t-test is 1.734 .
Case 2.2 – Paired T-Test
Select the t-Test: Paired Two Samples for Mean when you open the Data Analysis window.
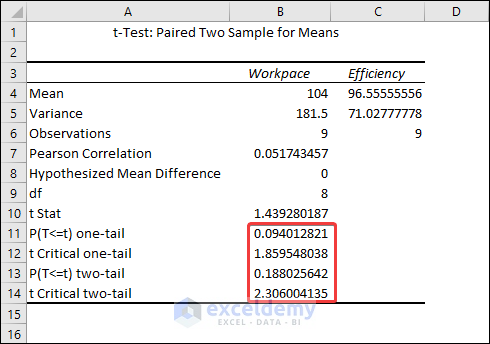
The result shows that the mean for the Workpace is 104 and the mean for the Efficiency is 96.56 .
The difference between means is statistically significant if the p-value is less than your significance level. For our results, we’ll utilize P(T=t) two-tail, which is the p-value for the t-test’s two-tailed version. We cannot reject the null hypothesis because our p-value ( 0.188 ) is greater than the conventional significance level of 0.05 . The hypothesis that the population means differ is supported by our sample data. In particular, the Workpace mean exceeds the Efficiency mean.
How to Interpret T-Test Results in Excel
Let’s bring out the results again.
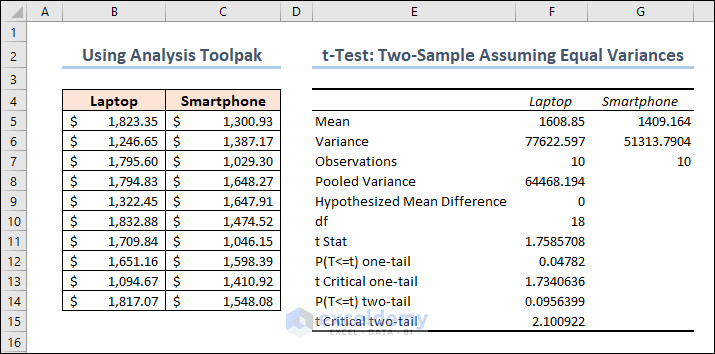
- The mean of laptop prices = 1608.85
- The mean of smartphone prices = 1409.164
ii. Variance
- The variance of laptop prices = 77622.597
- The variance of smartphone prices = 51313.7904
iii. Observations
The number of observations for both laptops and smartphones are 10 .
iv. Pooled Variance
The samples’ average variance, calculated by pooling the variances of each sample.
The mathematical formula for this parameter is:
((No of observations of Sample 1-1)*(Variance of Sample 1) + (No of observations of Sample 2-1)*(Variance of Sample 2))/(No of observations of Sample 1 + No of observations of Sample 2 – 2)
So it becomes: ((10-1)*77622.59676+(10-1)*51313.7904)/(10+10-2) = 64468.19358
v. Hypothesized Mean Difference
We “hypothesize” that the number is the difference between the two population means. In this situation, we chose 0 because we want to see if the difference between the means of the two populations is zero.
It indicates the value of the Degrees of Freedom. Formula for this parameter is:
No of observations of Sample 1 + No of observations of Sample 2 – 2 = 10 + 10 – 2 = 18
vii. t-Stat
The test statistic value of the t-Test operation.
The formula for this parameter is given below.
(Mean of Sample 1 – Mean of Sample 2)/(Square root of (Pooling Variance* (1/No of observations of Sample 1 + 1/No of observations of Sample 2)))
So it becomes: (1608.85 – 1409.164)/Sqrt(64468.19358 * (1/10 + 1/10)) = 1.758570846
viii. P(T<=t) two-tail
A two-tailed t-test’s p-value. This value can be found by entering t = 1.758570846 with 18 degrees of freedom into any T Score to P Value Calculator.
In this situation, the value of p is 0.095639932 . Because this is greater than 0.05 , we cannot reject the null hypothesis. This suggests that we lack adequate evidence to conclude that the two population means differ.
ix. t-Critical two-tail
This is the test’s crucial value. A t-Critical value Calculator with 18 degrees of freedom and a 95% confidence level can be used to calculate this number.
In this instance, the critical value is 2.10092204 . We cannot reject the null hypothesis because our test statistic t is less than this number. Again, we lack adequate information to conclude that the two population means are distinct.
Things to Remember
- Excel demands that your data be arranged in columns, with data from each group in a separate column. The first row should have labels or headers.
- Clearly state your null hypothesis (usually that there is no significant difference between the group means) and your alternative hypothesis (the opposite of the null hypothesis).
- As a result of the t-test, Excel returns the p-value. A small p-value (usually less than the specified alpha level) indicates that the null hypothesis may be rejected and that there is a substantial difference between the group means.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I perform a t-test on unequal sample sizes in Excel?
Yes, you can use the T.TEST function to do a t-test on unequal sample sizes. When calculating the test statistic, Excel automatically accounts for unequal sample sizes.
What is the difference between a one-tailed and a two-tailed t-test?
A one-tailed t-test determines if the means of the two groups differ substantially in a given direction (e.g., greater or smaller). A two-tailed t-test looks for any significant difference, regardless of direction.
Can I calculate the effect size in Excel for t-tests?
While there is no built-in tool in Excel to calculate effect size, you can manually compute Cohen’s d for independent t-tests and paired sample correlations for paired t-tests using Excel’s basic mathematical operations.
<< Go Back to Excel for Statistics | Learn Excel
What is ExcelDemy?
Tags: Statistical Significance in Excel

Md. Meraz Al Nahian has worked with the ExcelDemy project for over 1.5 years. He wrote 140+ articles for ExcelDemy. He also solved a lot of user problems and worked on dashboards. He is interested in data analysis, advanced Excel, statistics, and dashboards. He also likes to explore various Excel and VBA applications. He completed his graduation in Electrical & Electronic Engineering from Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET). He enjoys exploring Excel-related features to gain efficiency... Read Full Bio
Leave a reply Cancel reply
ExcelDemy is a place where you can learn Excel, and get solutions to your Excel & Excel VBA-related problems, Data Analysis with Excel, etc. We provide tips, how to guide, provide online training, and also provide Excel solutions to your business problems.
See Our Reviews at

- User Reviews
- List of Services
- Service Pricing
- Create Basic Excel Pivot Tables
- Excel Formulas and Functions
- Excel Charts and SmartArt Graphics
- Advanced Excel Training
- Data Analysis Excel for Beginners

Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions PDF

Master Hypothesis Testing In Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide

Table of Contents :
Mastering hypothesis testing in Excel can significantly enhance your data analysis capabilities. Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that allows you to make inferences or draw conclusions about a population based on sample data. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to performing hypothesis tests using Excel, accompanied by practical examples and easy-to-follow instructions.
What is Hypothesis Testing? 🤔
Hypothesis testing is a statistical technique used to determine whether a statement (hypothesis) about a population is true based on sample data. The process involves:
Formulating the Null and Alternative Hypotheses :
- Null Hypothesis (H0) : The hypothesis that there is no effect or no difference.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1) : The hypothesis that there is an effect or a difference.
Choosing a Significance Level (α) : Commonly set at 0.05, this level determines the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis.
Selecting the Appropriate Test : Depending on the data type and sample size, you may choose a t-test, z-test, chi-square test, etc.
Calculating the Test Statistic : This statistic will help determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Making a Decision : Based on the calculated p-value or test statistic, you can make conclusions about your hypothesis.
Why Use Excel for Hypothesis Testing? 📊
Excel is a widely used tool for data analysis due to its user-friendly interface and robust functionalities. Here are some reasons why it’s beneficial for hypothesis testing:
- Accessibility : Most people have access to Excel, making it easier for them to apply statistical methods.
- Built-in Functions : Excel has numerous built-in functions for various statistical tests, simplifying calculations.
- Visualization : Excel allows for easy charting and visualization of data, which can help in understanding results better.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hypothesis Testing in Excel
Step 1: set up your data.
Before you start with hypothesis testing, you need to have your data organized in Excel. For example, let’s say you have the following data of test scores for two classes:
Step 2: Formulate Your Hypotheses
Assuming you want to test whether Class A has a higher average score than Class B, your hypotheses would be:
- H0 : μA ≤ μB (Class A's average score is less than or equal to Class B's)
- H1 : μA > μB (Class A's average score is greater than Class B's)
Step 3: Choose a Significance Level
In most cases, the significance level (α) is set at 0.05. This means you are willing to accept a 5% chance of making a Type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis).
Step 4: Calculate the Test Statistic
To perform a t-test in Excel, follow these steps:
- Go to the Data tab in Excel.
- Click on Data Analysis . If this option is not visible, you may need to enable the Analysis ToolPak add-in.
- Select t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Equal Variances or the appropriate t-test based on your data.
Fill in the input ranges for Class A and Class B, set your hypothesized mean difference to 0, and choose the output range for the results.
Step 5: Interpret the Results
Once you run the t-test, you will receive an output that includes:
- t Stat : The calculated t-statistic.
- P(T<=t) one-tail : The p-value for a one-tailed test.
- t Critical one-tail : The critical value against which your t Stat is compared.
You can create a simple decision table for clarity:
<table> <tr> <th>Test Statistic</th> <th>Critical Value (t)</th> <th>P-value</th> <th>Decision</th> </tr> <tr> <td>Calculated t Stat</td> <td>t Critical one-tail</td> <td>P(T<=t) one-tail</td> <td>Reject H0 if t Stat > t Critical</td> </tr> </table>
Step 6: Make a Decision
- If t Stat > t Critical : Reject the null hypothesis (H0) and accept the alternative hypothesis (H1). This suggests that Class A has a significantly higher average score than Class B.
- If t Stat ≤ t Critical : Fail to reject the null hypothesis, indicating that there is not enough evidence to conclude that Class A scores higher than Class B.
Important Notes 📝
"When interpreting your p-value, remember that a p-value less than 0.05 typically indicates statistical significance, meaning you can reject the null hypothesis."
Step 7: Visualize Your Results
Visualization can enhance understanding and presentation. Use Excel’s charting tools to create a bar chart comparing the average scores of Class A and Class B. This can provide a clear visual representation of your findings.
Mastering hypothesis testing in Excel is an invaluable skill for anyone involved in data analysis. This step-by-step guide has provided you with a solid framework to perform hypothesis testing using Excel, making the process efficient and accessible. With practice, you will become proficient in using Excel for various statistical analyses, enabling you to derive meaningful insights from your data. Happy analyzing! 🎉
Latest Posts
- Why Text Formula Is Not Working In Excel Nov 14, 2024
- Why Cant I Save My Excel File Nov 14, 2024
- Why Is My Excel File So Large Nov 14, 2024
- Why Cant I Unhide Rows In Excel Nov 14, 2024
- Which Of The Following Characters Precedes Excel Functions Nov 14, 2024
Featured Posts
- How To Graph A Function In Excel Nov 14, 2024
- Excel Wheel Chair Mds808210are Nov 14, 2024
- How To Calculate Change In Percentage In Excel Nov 14, 2024
- How To Transfer Excel To Tsv Nov 14, 2024
- How To Make Dot Plot In Excel Nov 14, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO