Nepal lifts TikTok ban after app addresses cyber crime concerns
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Kathmandu bureau, editing by Shilpa Jamkhandikar
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab


Thousands of Australians without power as heavy rain, damaging winds lash Tasmania
Tens of thousands of people in Australia's southern island state of Tasmania were without power on Sunday after a cold front brought damaging winds and heavy rains, sparking flood warnings.

Cybercrime in Nepal
Whether or not nepalese legal standard address current and prospective modus operandi of cybercrime in nepal.

Diploma Thesis , 2014 , 56 Pages
Autor:in: Prabin Subedi (Author)
- eBook for only 18.99 € Download immediately. Incl. VAT Format: PDF and ePUB – for all devices
- Softcover for only 27.95 € Shipping worldwide
Broadly, the thesis aims to resolve two research questions. Firstly, whether or not the legal regime of cybercrime in Nepal has been able to address current or prospective modus operandi of cyber related crime? And secondly, whether Nepalese legal regime related to cybercrime is in line with the standards set forth in Convention on Cybercrime, 2001 for addressing the cybercrime?. The dissertation is substantially based on secondary resources such as scholar's article, books, and data from police, annual report of court and informal unstructured discussion with personnel from relevant authorities. Furthermore, the thesis has undertaken empirical study of cases and reports along with unstructured interview with relevant officials using random purposive sampling. After observation of secondary sources, unstructured interview, the paper has used primary sources such as treaties and laws to make a analytical study where the findings has been analyzed and conclusion has been drawn.
Table of Contents
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
CHAPTER I - INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background 1.2. Research Questions 1.3. Methodology
CHAPTER II – OVERVIEW ON CYBERCRIME 2.1. Introduction 2.2. What are Cybercrime? 2.3. Modus Operandi of Cybercrime
CHAPTER III – CYBERCRIME IN NEPAL 3.1. Nepalese Legal Regime governing Cybercrime 3.1.1. Electronic Transaction Act, 2008 3.1.2. Banking Offence and Punishment Act, 2008 3.1.3. Children's Act 1992 3.1.4. Some Public (Crime and Punishment) Act, 1970 3.1.5. The Patent, Design and Trademark Act, 1965 3.1.6. Copyright Act, 2002 3.1.7. Consumer Protection Act, 1998 3.1.8. Other 3.2. Threat of Cybercrime in Nepal 3.3. Present Scenario 3.3.1. Cases 3.3.2. Complaint registered tendency 3.4. Prospective threats that may arise
CHAPTER 4 – EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON CYBERCRIME 4.1. International perspective 4.2. European Convention on Cybercrime
CHAPTER V – ANALYSIS 5.1. Nepalese legal regime addressing current or prospective modus operandi of cybercrime 5.1.1. Substantive Legal Regime 5.1.2. Enforcement 5.2. Comparison of Nepalese legal regime with Convention on Cybercrime
CHAPTER VI – CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION 6.1. Conclusion 6.2. Recommendation
Bibliography

- Upload your own papers! Earn money and win an iPhone X.
- Culture & Lifestyle

- Madhesh Province
- Lumbini Province
- Bagmati Province
- National Security
- Koshi Province
- Gandaki Province
- Karnali Province
- Sudurpaschim Province
- International Sports
- Brunch with the Post
- Life & Style
- Entertainment
- Investigations
- Climate & Environment
- Science & Technology
- Visual Stories
- Crosswords & Sudoku
- Corrections
- Letters to the Editor
- Today's ePaper
Without Fear or Favour UNWIND IN STYLE

What's News :
- Palesha Goverdhan
- Nepal’s biomass potential
- Conflict-era explosives
- Discontent in Congress
- Disenchantment with political parties
How Nepalis’ vulnerability grows amid changing nature of cyber crimes

Cyber crimes have become a global, borderless phenomena. The rapid growth of internet connectivity and information technology has created ample opportunities for criminals. Nepal too is at a high risk of cyber crimes as the country does not have proper legal procedures to address the ever-evolving cyber crimes. In the past few years the country has faced many security breaches on government websites; in late January, about 1,500 government websites were shut down.
The impact of cybercrimes on an individual level is still more alarming. According to the Bhotahity-based cyber bureau of Nepal Police, in the past four years a total of 16,190 complaints have been lodged. It gets an average of 60 to 70 complaints a day, the majority of them related to the hacking of email, social media passwords and other general issues. Officials at the bureau say they are struggling to tackle complex cyber cases without the aid of specialised technical analysis as well as certified experts.
Here is what you need to know about the changing trend of cyber crimes in Nepal:
What are cyber crimes?
Cyber crimes refer to criminal activities that are done with the help of computers, the internet and digital technologies. These include activities like digital identity theft, hacking, cyberstalking, cyberbullying, phishing and other forms of fraud with the use of the internet and electronic devices. They have emerged as a new challenge to the economy, security, social harmony as well as individual well-being.
According to Statista , an online platform specialised in market and consumer data which offers statistics and reports, as of January this year, there were 5.16 billion internet users worldwide, which is 64.4 percent of the global population. Cybercrime statistics show that by 2022, a minimum of 422 million individuals had been impacted.
The internet and new technologies have made peoples’ lives easier. However, they have also brought many negative consequences due to weak cybersecurity measures and lax law enforcement. As technology continues to advance, cyber crimes are likely to be a more persistent threat.
Recently, cyberspace has also been used for geo-political attacks. The recent distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack on Nepal’s websites has mostly been used in geo-political conflicts, notably in the Russian-Ukraine war. Netscout, a US-based cybersecurity company, reported over six million DDoS attacks in the first half of 2022, most of which corresponded with national or regional tensions. DDoS attacks in Finland increased by 258 percent year-on-year in response to its announcement to apply for NATO membership.
Nepal’s National Information Technology Centre (NITC) reported that no data was compromised in the recent attack but given the gravity of DDoS attacks, experts highlight the necessity of thorough digital forensic examinations. As per the Global Cybersecurity Index, which measures the commitments of countries to assess legal, technical, and organisational measures, and capacity development and cooperation, Nepal moved up to the 94th position in 2020 from 106th in 2018. But the country’s overall score remains low at 44.99 (out of 100 points) among 182 countries indexed.
How have cyber crimes evolved in Nepal?
Initially, they started with cases of email and SMS blackmails. But as social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp, Skype and LinkedIn became popular, people with criminal mindsets were encouraged to target governments, institutions and individuals.
In January 2017 , Nepal saw one of the biggest breaches of the government computer systems, with as many as 58 government websites hacked by a group called “Paradox CyberGhost”. Just two years ago the official website of the President of Nepal was also hacked. And the most recent attack was in Singha Durbar . In late January, about 1,500 government websites were shut, which also affected flights from the Tribhuvan International Airport, raising questions over Nepal’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
Meanwhile, in the past four years, the cyber bureau has recorded 16,190 cases of cyber crimes under different categories like online financial fraud, revenge porn, ransomware attack, defamation, hacking, unauthorised access, among others.
The bureau’s data shows that in the fiscal year 2019-2020 there were only 2,301 cases of cyber crimes lodged. This fiscal year, the number has increased three-fold, to 6,297.
“The number of cyber crimes is steadily inching up, and we are struggling to address all complaints,” said Pashupati Kumar Ray, the bureau’s spokesperson.
Most recorded cybercrimes in Nepal in the past four years are linked to Facebook (4,730), followed by Tik-Tok (447), Instagram (434) and WhatsApp (181). Other platforms such as Twitter, Viber, IMO, and digital wallets are also used by digital fraudsters. Website and email hacking have also become headaches for the victims and the police.
Emerging trends in Nepal
According to the bureau’s data for the past eight months, IT-related financial frauds were the most common cybercrimes. At 955, financial frauds made up 20 percent of the total online crimes in the country, followed by 901 cases of revenge porn , according to Ray. Financial crimes include phishing (attempting to acquire sensitive data such as bank account numbers under a guise), lottery scam including fraudulent offers of work from home and online shopping.
Cases of fake profiles on social media come third, with 898 complaints registered. There were 799 complaints for online blackmailing, and 700 cases of online defamation aimed at assassinating the complainant’s character. In the same period, 648 cases of online harassment and 36 cases of online child sexual abuse were filed.
Why are more Nepalis being targeted?
Cyber crime and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) experts say many people are victimised mainly because they are not literate about cyber security or lack digital awareness. They pointed out Nepalis’ negligence to adopt security measures as another reason.
Cyber security expert Vivek Rana said the youths in the IT sector who used to outsource work are now jobless. They are now looking to make some quick bucks. “We also don’t have cyber regulations and laws to punish offenders. Most of all, the carefree nature of Nepali internet users is to blame.”
Besides that, the lure of easy money has led Nepalis into the traps of online fraudsters.
Who is more vulnerable?
According to cyber bureau, of the total complaints in the past eight months, 36 were of online child sexual abuse.
“Children are more vulnerable because we have found many predators grooming children through online gaming, gifts, and then abusing or exploiting them in some way,” said bureau spokesperson Ray.
There were 38.38 million internet subscribers in the country as of mid-October 2022, according to the Nepal Telecommunications Authority. Internet penetration in the country has now reached far and wide.
Rana says teenagers in rural parts of the country, plus elderly people, are more vulnerable. Many elderly people use mobile phones without understanding the implications of random clicks. The same is true of children. This is why cyber criminals often prey on them.
“They don’t know much about digital safety. Most of the elderly people share their one time passport [OTP], which is a dangerous practice,” said Rana.
Nepal’s laws and manpower
The country has the Electronic Transaction Act, 2008 as its cyber law. But due to lack of necessary amendments, it fails to cover the ever-evolving cyber crimes or to add to the security of a country’s online infrastructure. The Cybercrime Act-2018 is yet to see the light of the day. With weak laws on online security, Nepal’s cyberspace has become a gold mine for innovative hackers.
Although the government in the first week of March formed a high-level panel to draft a cyber security policy, no one knows when the panel will start working.
What is the way ahead?
Cyber experts say the best way out is to make people digitally aware, for which the government should play a proactive role. ICT expert Satish Krishna Kharel said there should be a nationwide awareness campaign to check the rise in cybercrimes.
He says awareness should start from schools, while the government should also train and mobilise digital forensic experts in all the seven provinces to prevent large-scale cybercrimes.
Experts further stress the need to give jurisdiction over cybercrimes to all district courts. Plus, all district police offices should have at least a small unit to handle cases of cyber crime locally.
Rana says the banking service providers and digital wallets should adopt and implement online fraud management systems to decrease the risk of financial cybercrimes.
Similarly, the focus should be on creating opportunities for adept ethical hackers who can keep abreast of current evolutions in cybercrimes.
Anup Ojha Anup Ojha was a reporter for The Kathmandu Post primarily covering social issues, crime, and human interest stories since 2011. Before moving to the social beat, Ojha covered arts and culture for the Post for four years.
Related News

Blast of conflict-era explosive reopens old wounds

Nepal Oil Corporation slashes fuel prices

No more anarchy and violence in Nepal: Prime Minister Oli

Lightning kills one in Sindhuli

China welcomes authentication of transitional justice bill

Minister Bhattarai points out need for policy revision in education sector
Most read from national.

Nepal lifts its ban on TikTok

Nepal asks China to turn Pokhara airport loan into grant

FM Rana meets Modi, Jaishankar

Nepal, China to issue five-year passes for Himalayan districts

Sri Lanka to allow visa free access to 35 countries including Nepal
Editor's picks.

Remittance, tourism drive economy. Other sectors lag

Justice delayed for consumer court

Tigers major threat to rhino calves in Chitwan

Early warning system saves lives

Nepal has a long way to go before it is Olympics-ready
E-paper | september 01, 2024.
- Read ePaper Online
- News & Events
- SCHOLARSHIPS
- About Islington
- University Partner
- Facilities & Infrastructure
- Schedule an Appointment
Our Programmes
- MSc IT & Applied Security
- BSc (Hons) Computing
- BSc (Hons) Computing with Artificial Intelligence
- BSc (Hons) Computer Networking & IT Security
- BSc (Hons) Multimedia Technologies
Business Degree
- Masters of Business Administration
- BA (Hons) Accounting & Finance
- BA (Hons) Business Administration
- How to Apply?
Student Life
- Student Area
- Islington Experience
- Islington Spirit
- International Exposure
- Scholarship

Cyber security in Nepal | Importance, Scope and Types

Cyber security is the technique of securing computers, electronic systems, networks, and data from online malicious attacks. It is also known as Information technology security. It focuses on keeping cybercriminals and malicious hackers from gaining access, disrupting, or changing the systems and applications without the owner's consent. Cyber security in Nepal started its peak in 2017 when 58 different governmental sites were hacked by a group of hackers named “Paradox Cyber Ghost”. They leaked the customers' information and citizens' information creating a threat to the general public as well as governmental organizations.
Because an organization’s assets are composed of a variety of different platforms, a strong cyber security posture requires coordinated efforts across all of its systems.
What is the importance of Cyber security in Nepal?
Cyber security in Nepal is important to protect personal, government data, information and server from theft, damage, and malware. Without cybersecurity, neither an organization nor an individual will be able to defend their data from cyber-attacks. The level of cybercrimes is increasing day by day and becoming more vulnerable. Many innocent users get affected by cybercrimes through different cyber-attacks that are attempted by hackers. It has become as risky in the present world as the world is digitizing and technologies are developing and more hackers are evolving and inventing new ideas to attempt cybercrime.
Due to the increasing number of cybercrimes, cyber security in Nepal is very important and a greater necessity to keep personal and confidential data, information safe. Different organizations are implementing cyber security to protect confidential data and information and to protect servers and networks. One of the great information security scandals to be remembered was the 2019 Facebook record breaking 5 billion dollar fine which Facebook agreed to pay to the US Federal Trade Commission. At the highest levels of government and business, the need to protect confidential information is a top priority.
Related: Reasons to study IT in Nepal
What are the cyber security issues in Nepal?
Some of the major cybersecurity issues reported in Nepal include ransom, phishing, and data breach, banking frauds, defamation, slander, online identity theft and individual cybercrimes.
In June 2017, a group of Turkish hackers hacked the Department of Passport Official website leaving a threat to reveal government's data. In October, the Swift system of NIC Asia bank was hacked by an unidentified hacker. Similarly in April 2020, data of more than 160,000 customers of Vianet Communication were leaked through twitter handles. Due to this act, various companies have started to provide dynamic cyber security services to help businesses and organizations cope with data breaches.
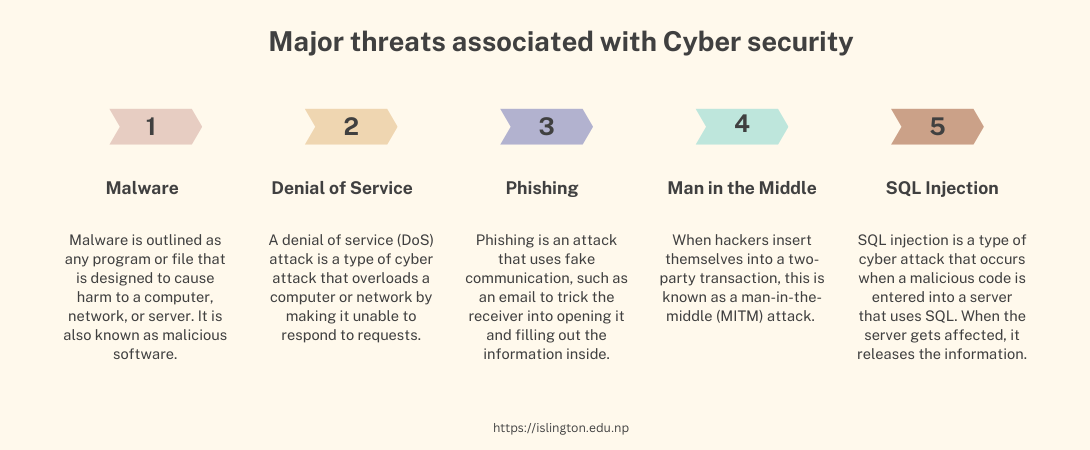
Major threats associated with Cyber security
Cyber security threats are attacks that menace and put information in danger. It is an attempt to unlawfully gain access to networks and accounts without the owner's consent, steal confidential information, or corrupt data. The various cyber security threats are:
Malware is outlined as any program or file that is designed to cause harm to a computer, network, or server. It is also known as malicious software. It is activated when a user clicks on a malicious link or attachment.
Denial of Service:
A denial of service (DoS) attack is a type of cyber-attack that overloads a computer or network by making it unable to respond to requests. A distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack accomplishes the same thing, but the attack originates on a computer network.
Phishing is an attack that uses fake communication, such as an email to trick the receiver into opening it and filling out the information inside (such as providing a credit card number, password, etc.)
According to Cisco, "the goal is to steal sensitive data such as credit card and login information or to install malware on the victim's machine."
Man in the Middle:
When hackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction, this is known as a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack. According to Cisco, after interfering with traffic, they can filter and steal data. MITM attacks are common when a visitor connects to an unsecured public Wi-Fi network. Attackers place themselves between the visitor and the network, then use malware to install software and manipulate data.
SQL injection:
SQL injection is a type of cyber-attack that occurs when a malicious code is entered into a server that uses SQL. When the server gets affected, it releases the information. A website's search box is used to submit vulnerable malicious code with ease.
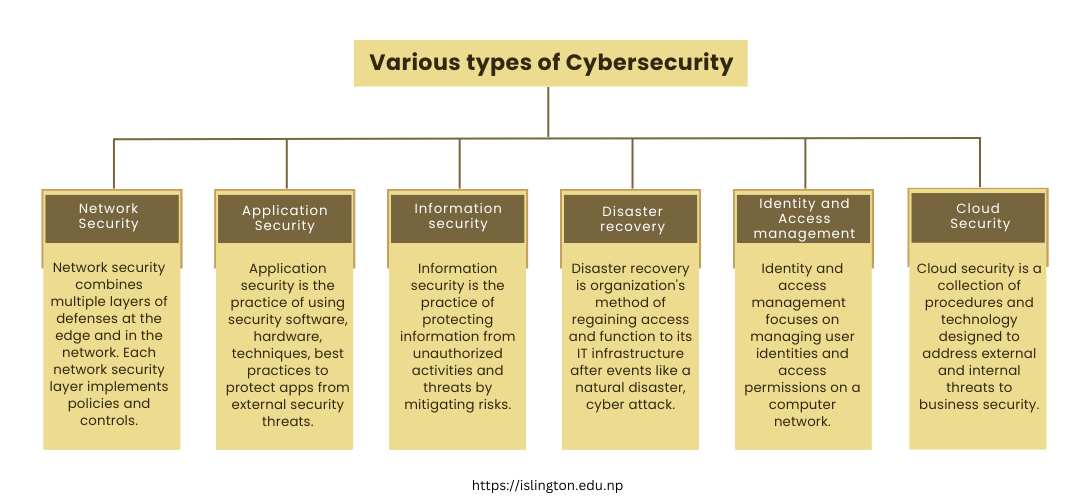
Various types of Cybersecurity
Knowing the various cybersecurity domains is also essential for preparing you for the knowledge requirements if you decide to work in the industry.
Network security:
Network security is one domain that helps secure a computer network from intruders like attackers or malware. There is the implementation of both hardware and software techniques to secure the network from unwanted access, disruptions, and misuse.
Application security:
Application security focuses on keeping software and devices free from threats. There is the installation of various defenses within the software of an organization to protect data against a wide variety of threats.
Information security:
Data integrity and privacy are protected by information security in both storage and transit. Application software helps in keeping the information safe and secured.
Disaster recovery:
Disaster recovery and business continuity define how an organization responds to a cyber-security incident or any other event that causes the loss of operations or data. Disaster recovery policies dictate how the organization restores its operations and information to return to the same operating capacity as before the event.
Business continuity is the plan the organization falls back on while trying to operate without certain resources. DR&BC deals with processes, monitoring, alerts, and plans that help organizations prepare for keeping business vital systems online during and after a disaster, as well as restarting lost operations and systems.
Identity and Access management:
Identity management refers to the frameworks, processes, and activities that enable legitimate individuals to access information systems within an organization. Implementing strong information storage techniques that assure data security at rest and in transit is part of data security.
Cloud Security:
Cloud Security includes the practices and tools that protect cloud computing environments from both external and internal cyber threats. It involves prevention from unauthorized access and keeping data, information in public, private and hybrid cloud secure from various threats.
What skills are needed for a job in cyber security?
For working in a job in cyber security, an individual must require to know basic technical skills in network and system administration, operating systems and virtual machines, network, programming skills, digital forensics, data management, and cloud security.
For personal or soft skills an individual requires to have an analytical thinking and problem-solving mindset, as well in researching, management skills, and communication skills. Mixing knowledge of technical skills and soft skills is required in cybersecurity.
To become a cybersecurity professional one must have a degree in IT security or Computer Science. Courses on cyber security like CEH, CISSP, and CISA have equivalency with the IT degree mentioned above. The certificates of completion of these courses or a degree are required to become a cybersecurity professional. Becoming a cybersecurity professional an individual must have a wider and broader concept of IT security, basic knowledge of Computer Science, and various personal and technical skills.
What is the Scope of Cybersecurity in Nepal?
Due to recent threats in many financial institutions and digitization, cybersecurity is alarmingly increasing. In the Global Cybersecurity Index, Nepal is ranked 94th. With the rise of various Cyber Security company in Nepal such as Eminence ways, Vairav Tech, Bugv, Cynical Technology. Cybersecurity in Nepal has been adopted by numerous FinTech businesses, the Nepali telecom authority, organizations, and commercial banks. As a result, Cybersecurity degree in Nepal has emerged as one of the most sought field in tech.
Cybersecurity specialists are in great demand all over the world. Both the public and private sectors are prone to cyber-attacks. The need of the digital world today requires cyber security to defend against cyber-attacks.
But Nepal also struggles with a general lack of appropriate IT policies, programs to raise security awareness, and knowledge of new technologies, which has led to a lot of spamming, phishing, and password piracy issues.
Find out everything about BSc IT in Nepal at islington college
Some job roles in Cybersecurity in Nepal are:
Cybersecurity specialist: An authority in the field of information technology security is a "cyber security specialist." They are responsible for safeguarding the software development process. They protect networks from outside threats like hackers who want access for unlawful purposes.
Information security analyst: To secure computer networks, information security analysts install software like firewalls. They develop and implement security measures to safeguard a company's computer networks and systems.
Penetration tester: Penetration tester helps organizations in locating and addressing security flaws that affect their digital assets and computer networks.
Network security engineer: Network security safeguards your network and data against breaches, privacy violations, and other threats. This is a broad and all-encompassing term that refers to processes, rules, and configurations relating to network use, accessibility, and overall threat protection, as well as hardware and software solutions.
Software security engineer: Software security engineering tests services, processes, techniques, and tools to figure out any security-related issues.
No new notice found.

Anamnagar, Kathmandu

+977-1- 4102849
Appointment

Cyber Crime Laws in Nepal
Cyber Crime in Nepal | Cyber Crime Laws in Nepal | Cyber Crime Lawyer in Nepal | Cyber Crime Law Expert in Nepal
What is Cybercrime?
- Cybercrime is a crime relating to any illegal behavior committed by or in relation to a computer system or network, including such crime as illegal possession or distribution of information by means of a computer system or network. In short, cybercrime is a crime committed through cyber.
CYBERCRIME AND INTERNET CRIME: UNDERSTANDING
- Unauthorized access to another’s a computer, deleting data or jeopardizing the data, or destroying the computer by virtue, etc. can also be cybercrime.
- And specifically in the case of internet crime, one has to use the internet as the medium E:g hacking, phishing, E: mail bombing, spam, etc. [note: internet crime is also cybercrime]
What makes cybercrime?
- When there is the presence of the following:
- illegal act
- using computer
- with or without internet
- must have malafide intention
- the harm caused to the property or life of the person.
What are the elements of cybercrime?
- To prove one act as cybercrime: it requires the following elements:
- Actus Reus (physical element)
- Mens Rea (mental element)
- Modus Operendi (computer,internet)
What is the emerging trend in cybercrime?
- botnet attacks(robot)
- voice over IP communication
- cloud computing
- not only methods but impacts also changed.
What are the major cybercrimes in Nepal?
- IP theft and privacy
- photo mutilation
- email fraud for ransom
- pornography
- cyber bullying
- online gambling
- child trafficking
- sexting, sextortion, etc.
What are the legal provisions of cybercrime in Nepal?
- In Nepal, the Nepal Police have been using the Electronic Transactions Act 2063 (Hereafter referred ETA ) to regulate cybercrimes. Section 47 of the Act is the most used section to prevent cybercrime in Nepal. This section stipulates that if a person publishes or displays material against morals, etiquette, hatred, or malice on a computer, internet, and other electronic media, the culprit can be punished with a fine of 1 lakh rupees or imprisonment for up to 5 years or both.
- Section 48 of the Act is also used customarily, which stipulates that if any person who has access to any record, book, register, correspondence, information, documents or any other material under the authority conferred under this Act or Rules framed hereunder divulges or causes to divulge confidentiality of such record, books, registers, correspondence, information, documents or materials to any unauthorized person, he/she shall be liable to the punishment with a fine not exceeding Ten Thousand Rupees or with imprisonment not exceeding two years or with both, depending on the degree of the offense.
What is the punishment provisioned by the law of Nepal relating to pirating, destroying, or altering computer source data?
- As per the ETA, 2063 (section 44) , if any person, knowingly or with malafide intention, pirates, destroys, alters computer sources code to be used for any computer, computer programmer, computer system or computer network or cause, other to do so, he/she shall be liable to the punishment with imprisonment not exceeding three years or with a fine not exceeding two hundred thousand Rupees or with both.
Is unauthorized access to computer materials, a cybercrime?
- Unauthorized Acess is an offense punishable by law. If any person to have access to any program, information, or data of any computer, uses such a computer without authorization of the owner of or the person responsible for such a computer or even in the case of authorization, performs any act to have access in any program, information or data contrary to from such authorization, such a person shall be liable to the punishment with the fine not exceeding Two Hundred thousand rupees or with imprisonment not exceeding three years or with both depending on the seriousness of the offense.[ Section 45, ETA 2063]
What are the provisions regarding damage to any computer and information system?
- If any person knowingly and with a mala fide intention to cause wrongful loss or damage to any institution destroys, damages, deletes, alters, disrupts any information of any computer source by any means or diminishes value and utility of such information or affects it injuriously or causes any person to carry out such an act, such a person shall be liable to the punishment with the fine, not exceeding two thousand Rupees and with imprisonment not exceeding three years or with both.[ Section 46, ETA 2063]
Is the publication of illegal materials in electronic form allowed?
- No, it is not. If any person publishes or displays any material in electronic media including computer, internet which is prohibited to publish or display by the prevailing law or which may be contrary to public morality or decent behavior or any type of material that may spread hate or jealousy against anyone or which may jeopardize the harmonious relations subsisting among the peoples of various castes, tribes and communities shall be liable to the punishment with the fine not exceeding One Hundred Thousand Rupees or with the imprisonment not exceeding five years or with both .[Section 47, ETA 2063]
What are the provisions of the law of Nepal regarding computer fraud?
- If any person, intending to commit any fraud or any other illegal act, creates, publishes, or otherwise provides a digital signature certificate or acquires benefit from the payment of any bill, the balance amount of any one’s account, any inventory or ATM card in connivance of or otherwise by committing any fraud, amount of the financial benefit so acquired shall be recovered from the offender and be given to the person concerned and such an offender shall be liable to the punishment with a fine not exceeding one hundred thousand Rupees or with imprisonment not exceeding two years or with both.[ Section 52, ETA2063]
What is the punishment for a person who abets others to commit a computer-related offense?
- If any person abuts another to commit an offense relating to computer under ETA Act or who attempts or is involved in a conspiracy to commit such an offense shall be liable to the punishment of a fine not exceeding fifty thousand Rupees or imprisonment not exceeding six months or with both, depending on the degree of the offense.[ Section 53, ETA 2063]
What is the punishment for an offence committed outside Nepal?
- If any person commits any act which constitutes an offense under ETA Act and which involves the computer, computer system, or computer network system located in Nepal, even though such an act is committed while residing outside Nepal, a case may be filed against such a person and shall be punished accordingly . [Section 55, ETA 2063]

BagBazar, Ktm
Opposite to PK Campus
- +9779804495818
24/7 SMS support
Sun - Fri: 9:00 - 17:30
Saturdays: 10am-2pm
Cybercrime in Nepal : Types and Laws for Cybersecurity
Table of contents.
Cybercrime refers to criminal activities that are carried out through the use of digital devices or the internet. Cybercrime has become a widespread problem around the world, and Nepal is no exception. The country has seen a significant increase in cybercrime in recent years, which can be attributed to the rapid growth of the internet and the increasing use of digital devices. Cybercriminals in Nepal use various methods to carry out their illegal activities, including phishing scams, hacking, identity theft, and malware attacks. In this article, we will understand various types of cyber crimes and further guide you on where and how to report cyber crimes in Nepal.
Common Types of Cybercrime in Nepal
Online fraud.
Online fraud is a type of cybercrime that involves using deception to obtain money or valuable information through the internet. Phishing scams are a common form of online fraud in Nepal, where criminals trick victims into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. These scams often come in the form of fraudulent emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or a government agency.
Other types of online fraud in Nepal include lottery scams, where victims are promised a large sum of money if they pay a fee or provide personal information, and fake online shopping websites, where criminals set up fake websites to steal credit card information from unsuspecting customers. Job scams are also prevalent in Nepal, where criminals pose as employers and ask for personal information or payment for job applications. It is important to be cautious when providing personal information online and to verify the authenticity of websites and emails before taking any action.
Hacking is a form of cybercrime that involves gaining unauthorized access to a computer system or network. In Nepal, hacking has become a prevalent issue, with many hackers targeting businesses and government agencies. Hacking can result in the theft of sensitive information, such as customer data or financial records, and can cause significant damage to the reputation and operations of affected organizations.
Hackers in Nepal often use techniques such as social engineering, phishing, and malware to gain access to computer systems and networks. They may also exploit vulnerabilities in software and operating systems to gain access. To combat hacking, it is essential to implement strong cybersecurity measures, such as using up-to-date software and firewalls, regularly backing up data, and educating employees on safe computing practices. It is also important to report any suspected hacking incidents to law enforcement agencies.
Identity theft
Identity theft is a type of cybercrime that involves the unauthorized use of someone’s personal information, such as their name, address, or social security number. In Nepal, cybercriminals often use identity theft to commit various types of fraud, such as opening bank accounts or applying for loans in someone else’s name.
Identity theft can have severe consequences for victims, including damage to their credit score, financial losses, and even legal issues. Cybercriminals in Nepal use a variety of tactics to obtain personal information, such as phishing scams, hacking, and malware. They may also steal physical documents or personal devices that contain sensitive information.
To protect against identity theft, it is advised to safeguard personal information, such as by using strong and unique passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks, and regularly monitoring bank and credit card statements for suspicious activity. It is also critical to report any suspected incidents of identity theft to law enforcement agencies and credit bureaus.
Impact of Cybercrime in Nepal
Impact on businesses.
Cybercrime has a significant impact on businesses in Nepal. Many businesses are not adequately prepared to deal with cyber threats, and a successful cyberattack can cause significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and loss of sensitive data.
To protect against cyber threats, businesses in Nepal should implement strong cybersecurity measures, such as using firewalls and antivirus software, regularly backing up data, and conducting regular security audits. Businesses should also educate their employees on safe computing practices, such as how to recognize phishing scams and how to create strong passwords.
It is also significant for businesses to have an incident response plan in place in case of a cyberattack. This plan should include steps for isolating affected systems, notifying stakeholders, and contacting law enforcement agencies. By taking proactive steps to prevent cyberattacks and having a plan in place to respond to incidents, businesses can better protect themselves against the harmful effects of cybercrime.
Impact on Individuals
Individuals in Nepal are also vulnerable to cybercrime. Cybercriminals often use social engineering tactics to trick people into providing personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. This can lead to financial losses and identity theft.
To protect against cyber threats, individuals should take steps such as using strong and unique passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks, and being cautious when sharing personal information online. It is also important to regularly monitor bank and credit card statements for suspicious activity and to report any suspected incidents of identity theft or fraud to the appropriate authorities.
In addition, individuals can protect themselves by staying informed about the latest cyber threats and by using security software, such as antivirus programs and firewalls, on their devices. By taking these steps, individuals can reduce their risk of falling victim to cybercrime in Nepal.
Measures to Combat Cybercrime in Nepal
Legal framework for cybersecurity in nepal.
Nepal has enacted various laws and regulations to combat cybercrime. The Electronic Transactions Act, 2063 (2008) provides a legal framework to regulate electronic transactions and prevent cybercrime. The act includes provisions for punishing cybercriminals and protecting the rights of victims.
Under the act, cybercrime is defined as any activity carried out with the intent to harm or deceive someone through the use of electronic means. This includes unauthorized access to computer systems, hacking, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime.
The act also provides for the establishment of a Cyber Bureau within the Nepal Police to investigate and prosecute cybercrime cases. The Cyber Bureau has the authority to seize and examine electronic devices and to work with international law enforcement agencies to track down cybercriminals.
In addition, Nepal has ratified the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, which provides a framework for international cooperation in the investigation and prosecution of cybercrime. By enacting these laws and regulations and working with international partners, Nepal is taking important steps to combat cybercrime and protect its citizens against the harmful effects of cybercrime.
Cybersecurity awareness campaigns in Nepal
To combat cybercrime, the Nepalese government has launched various cybersecurity awareness campaigns to educate the public about cyber threats and how to protect themselves from cybercriminals. These campaigns include seminars, workshops, and training programs.
The government has partnered with private sector organizations, such as banks and telecommunications companies, to reach a wider audience with these campaigns. The goal is to increase public awareness of cyber threats and to promote safe online behavior.
In addition to these campaigns, the government has also launched a website dedicated to cybersecurity awareness. The website provides information on common cyber threats, tips for staying safe online, and resources for reporting cybercrime incidents.
These efforts to raise awareness about cyber threats and promote safe online behavior are an important part of Nepal’s strategy to combat cybercrime. By educating the public about the risks and providing resources for staying safe online, the government can help to reduce the number of cybercrime incidents in Nepal.
Law enforcement agencies
In Nepal, the Central Investigation Bureau (CIB) is responsible for investigating cybercrime. The CIB has established a Cyber Crime Investigation Cell to investigate and prosecute cybercriminals. The government has also established a National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) to coordinate efforts to combat cybercrime.
The Cyber Crime Investigation Cell is responsible for conducting investigations into cybercrime cases and bringing cybercriminals to justice. The cell has trained investigators who use specialized tools and techniques to analyze digital evidence and track down cybercriminals.
The NCSC is responsible for developing policies and strategies for combating cybercrime and for coordinating efforts between government agencies, private sector organizations, and international partners. The center also provides advice and support to businesses and individuals on how to protect themselves from cyber threats.
These law enforcement agencies play a critical role in combating cybercrime in Nepal. By investigating and prosecuting cybercriminals and by coordinating efforts to combat cybercrime, these agencies are helping to create a safer online environment for Nepalese citizens and businesses.
Where and How to report cyber crime in Nepal
To report cybercrime in Nepal, you can follow these steps:
- Contact the Cyber Bureau: The Cyber Bureau is responsible for handling cybercrime cases in Nepal. You can reach them through various means.
- Email: Email the Cyber Bureau at [email protected]. Include all relevant information about the cybercrime incident, such as details of the incident, any evidence you have, and your contact information.
- Visit the website: Access the official website of Nepal Police at https://www.nepalpolice.gov.np/index.php/cyber-bureau?start=3. You can find more information about reporting cybercrime and any updates on the process.
- Phone: You can also contact the Cyber Bureau by phone. The contact number provided on the website is 9851286770. You can call this number or reach out to the main police line at 014219044.
When reporting cybercrime, make sure to provide as much detail as possible about the incident. Include any evidence, such as screenshots, emails, or other relevant documents that can assist in the investigation. It is important to provide accurate contact information so that the authorities can reach you if needed.
Remember to always keep copies of any correspondence or evidence related to the cybercrime incident. It’s advisable to cooperate fully with the authorities and provide any additional information or assistance they may require during the investigation.
Cybercrime is a growing threat in Nepal, and it is essential to take measures to combat it. By enacting strong laws and regulations, raising cybersecurity awareness, and investing in law enforcement agencies, Nepal can take significant steps towards preventing cybercrime and protecting its citizens and businesses from the harmful effects of cyber threats.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
I wann complain about a person who theareating me
A tiktoker hack my I’d
My sister tiktok I’d fack I’d and hat speech tiktok live I’d fake name=@ramsem_ramsem
I was scamed 20k To buy a phone I have his citizen card number can police can trace him?? I’m really sad😞
iPhone 15 thousands vanayra mero paisa khayo Happy mobile shop KO Manche lay
Mero facebook account hack vayo 2 month agadi ekdam private account ho life barbaad hune vo mero abo sucide garna matra baki xa
my id has hacked plz help me
My Facebook account was hacked and he/she is posting annoying things of my id. Hacker phone number 9826450071 Please arrest him/her and recover my id and money.मलाई instagram बाट invest and earn more money भनेर messages garer ahile facebook I’d hack garer jpt post gardai xa please help me
I’d has been hack
I need help plz in fake facebook id to blackmale
Auta keto le mero photo Facebook ma halera naramro comment gardai xa please help
Hello sir , my self krishna Jaiswal . My id has been hacked. help me sir please
One man do prank with fake account of girls and says i love you and do you want something
My Facebook account has been hacked
Someone scam my 5.5k money from messenger he can’t return my money please help.
Someone hacked my Facebook I’d ,and changed password,now he scamming lots of people through my Facebook I’d,I need your help
My fake I’d in Facebook for blackmail others people for me plz help me
Recover my account
My fb account was hacked.
How can I find who hack my account
Subject: Urgent Assistance Needed: Hacked Facebook Account
Dear Cyber Security Team,
I hope this email finds you well. I am writing to seek urgent assistance regarding a security issue I am facing with my Facebook account.
Recently, I purchased a Facebook account for gaming purposes related to Freefire. The transaction involved a significant amount of money, approximately 11k, and unfortunately, I have fallen victim to a scam. The seller deceived me and not only took my money but also seized control of the Facebook account I purchased.
This situation has caused me great distress and financial loss. I am reaching out to your esteemed cyber security team with the hope that you can help me regain access to my hacked Facebook account and possibly identify the perpetrator behind this fraudulent activity.
I understand the gravity of the situation and assure you of my full cooperation in any investigation or process required to resolve this matter. Please let me know what information or documentation you may need from my end to assist in the recovery process.
I sincerely appreciate your prompt attention to this matter and eagerly await your guidance and support.
Thank you for your understanding and assistance.
Warm regards, Lalit Budha 9865716696
There is a girl who posted me by saying Maya rough thi g
Aauta kti leh malai dheri naramro vanerw Facebook ko story ma hala ko xaa 🙂 Ani aayela ma dipression ma xu usko I’d Lai band gardinu paryo na Vaya ma aatmahatya garxu 🙂
I ordered iphone 6s during this I got scammed and also I have his esewa account bank account his fake pan card and transfered money details
Sir jay nepal Mero facebook account hack vayo Kasari report garne ho
- [email protected]
- Yeti Plaza, Bagbazar, Kathmandu
- Company Registration
- Marketing Plan
- Bookkeeping
- Management Consulting
- StudentsNepal
- Best Consultancy
- Developables

© All rights reserved
Quick Support
♠ 9804495818
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Cyber Crime, Cyber Law, Cyber Ethics and Cyber Security in Nepal

2019, Nepal Academy of Science and Technology
Huge numbers of illegal activities are increasing day by day using ICT tools and applications. The government organizations, citizens, business are being victims by cyber crime, attack and threat. The purpose this paper is to explore about cyber crime, cyber law, cyber ethics and cyber security in Nepal. The study has completed by using content analysis, analysis of various national and international survey reports; and in-depth interviews with subject experts. The study claims that risk of cyber crime attract, and threat have been increasing unexpectedly. Within a decade, our technology turned against human being and being more sophisticated day to day. The study concludes that cyber law should pursue strictly in the nation to control the cyber crime. Cyber ethics is only one moral weapon to reduce the cyber crime. Strong cyber security precautions and technologies must adopt during installation of ICT automation. The government of Nepal should appoint all rounder of cyber security personnel in government service so that expert team could be able to fight against the cyber crime, attract and threat. Don't delay to enhance the capability of cyber security force. The Government ought to not delay to form a new force 'Cyber Army'.
Related Papers
IJCSMC Journal
Measuring effectiveness analysis of civil service is not so easy job as we think. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is being a fundamental tool of human being which is making our daily life activities easy, smart and simplify. ICT has played a role of pool between civil service and day to day service delivery. In this study, the author is trying to examine and investigate the effectiveness analysis of civil service using ICT in Nepal. Survey research with qualitative research technique has applied to collect primary data from civil servants of government organizations, whose primary role is to deliver public service. This paper concludes that the successful, effective civil service delivery of the country has been in itself a harbinger of national peace, progress and prosperity. The success of government is dependent on the trust and honesty of ruling political leaders; the civil servants; conscious people and one door delivery system. Researcher claims that ICT has been recognized as a critical component for the successful delivery of many existing services of government and it enables the service delivery to build on these successes and use ICT to operate in a more efficient, shared and integrated manner across all the government sectors. The government should create ICT awareness for the people, trust on technology and e-governance by decreasing the digital divide between common people and other citizens. People should adopt their ownership towards the electronic service delivery system. The service delivery system in Nepal seems poor in the sense of efficiency and effectiveness.
Pramana Journal
Dr. Shailendra Giri
Human life is depending on online services which are making daily life easy and smart but facing various challenges of cyber attract, threat and security. Huge numbers of criminal activities are increasing day by day using ICT tools and applications. Government organizations, citizens, business is being victims by cyber crime and threats. The risks of cyber attract and threat is very high. The cyber security strategies, policies, plan and law, help to protect e-government systems against threat and attack; and detect abnormal activities. The aim of this paper is to explorer cyber crime and cyber threat and security strategies and law. The content analysis and survey methods are used for this research. The study concluded that the government must conduct a professional analysis of cyber crime, cyber threat, cyber security, and cyber strategies. This article has discussed about the legal requirements of cyber security. If we are not able to design systems that secure human life and distinguish that usable solutions are not sufficient and a crucial component of strong security in the future. As we know that within a decade, observe our technology turned against us in continued and being more sophisticated day to day and how it made destructive attacks and threats. It shows that our future will not really happy and healthy due to cyber insecurity.
International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology
The approach of e-governance is constantly changing the way government system execute its service to the people. E-service encompasses a series of necessary steps for institutions to develop and administer to ensure successful implementation of services at large. This paper discusses the growth trend of e-service, its effectiveness and challenges to overcome the situation for effective service delivery. Content analysis and survey approach was used to generate data in the case study. The study claims that the virtual nature of the internet, and its dynamic aspects, can multiply the service of government to the people and novice users to its considerable capacity to do no harm in e-service. The study has concludes that e-government service is essential for managing future complications and responding to current and past incidents to build trust from people. The insight on reducing current and future inefficiencies, the probabilities of effectiveness, and the costs associated with potential outcomes support their mitigation. Some of the issues related to e-service can be regulatory, legal, technical and procedural measures as well as civil service personnel's education, capacity building and continuous upgrading the technology. Manage the three level of employees and administration smooth way that is Federal, province and local level and coordinate and cooperate each other are the major challenges of civil service.
Journal of Institute of Engineering, Pulchok Lalitpur, Nepal.
E-government uses information and communication technologies (ICTs) tools and systems to provide better public services. Database Management System (DBMS) is a very significant part in e-governance activities and process in the nation. Security of the data is a main concern of the organizations and private. Proper database management and data security are the major issues in present era. The aim of the paper is to try analyzing necessity of database management and data security. The author used survey methods during research to collect the data and analyze it. This paper concludes that the data backup is key profession while using computer in an institute or people. Hard disk, external hard disk, pen drive, memory card, server and open drive are the major storage Medias. People and employees don't create backup of data due to lack of knowledge, device and don't know about importance. The authors conclude that using Antivirus on computer, password on file and computer system, data and information backup, firewall, encryption and decryption technology are the data security tools. Data security protect against the unauthorized use, disclosure, access, destruction, modification and loss of data. Confidential password security and regular monitoring on password are very necessary to secure data. An online security system, as well as manual security systems, should be managed attentively.
IJCSMC Journal , Dr. Shailendra Giri
The proper use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has made human daily activities easy and fast. The service delivery mechanism of government, department and business organization has been fast, efficient and reliable. The primary motive of government is to deliver public services transparently, effectively and efficiently. Civil service is one of the most important mechanisms for public service delivery. The primary objective of this research paper is to explore current ICT status and use of ICT in service delivery mechanism by government organization to its People. The researchers have applied survey research to collect primary data from employees of government organizations whose primary role is to deliver public service and adopted quantitative research technique. This paper concludes that use of ICT for public service delivery can be more effective through integration, linkage and inter-operability among government organizations, departments and business entities. And regular programme for capacity development of service providers towards new ICT tools and systems is essential.
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology
Civil servants are often charged not providing effective services though they have sufficient resources and technological knowhow. The authors is trying to explore the challenges of effective service delivery in civil service as implementing e-governance in Nepal. Survey method was used to generate data and adopted quantitative research technique. The study has claimed that Nepal has been facing numerous challenges during service delivery while implementing e-governance. Infrastructure development, human resource development and management, digital divide, are identified as the major challenges. Unnecessary influence of middleman and syndicate created by some hidden groups make government service holdup. Needless expansion of government agencies and its employees; too many layers in decision-making process; more process oriented service delivery rather than result oriented, failure to make individual officials responsible; and a lack of decentralization of necessary authority to the officials are the other challenges.
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
Technology-Based Training provides a practical and highly useful perspective on how to tackle the world of learning and technology. The trend of technology based training is in fashion of late in the academies. Training with Technology is being essential in every training institution to deliver training contents in easy and smart way so that learner can achieve the knowledge and skill without doubt. People are searching for ways to fully utilize the recent achieve in technology to improve work performance. Nepal has been also practicing use of technology in training since few years. This paper examines the ongoing practices and explorers recent advances in technology based training as well as examines different trainings and software applications available in the marketplace. Likewise, this article compares the costs and benefits of technology based training and identify several other factors that influence effectiveness of training. Finally, the paper concludes with a few guidelines on how training centers can effectively use technology to better deliver training and meet their human capital development needs. Training not only provides skills and knowledge to the learners but also changes the attitude and behavior of trainees.
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
The aim of this paper is to the purposed a roadmap of digital Nepal and trying to explorer the various dimensions of the digital Nepal framework. The content analysis method was used for the study. The researcher claims that Digital Nepal is a broad conception of the Government of Nepal. The Government's big plan Digital Nepal is designed to facilitate Nepal to connect its driving socioeconomic growth of citizens which will help and support to achieve the sustainable development goal. The Digital Nepal Framework encompasses one nation, eight sectors, 80 digital initiatives. The study claims that there are eight dimensions of the Digital Nepal framework. They are the digital foundation, agriculture, health, education, energy, tourism; finance and urban. They will help to guide Nepal on its journey toward becoming a digital state in days to come. The Government of Nepal is successes in information and communication development in the nation. The possible roadmap of digital Nepal is clearly mentioned in two parts as infrastructure development and service and application. The way of digital Nepal is not so easy but the recent trends in the development of ICT in the country show that the true digital Nepal isn't as for as we think.
Pranama Journal
Within very short span of time, developing countries are showing their pace in the development of the e-Government which has changed the peoples' day to day life style though they have been lagging behind in e-government use as compared to developed countries. E-government development in developing countries have the potential to build better relationships between government and the public by making interaction with citizens smoother, easier and more efficient. Nepal is facing numerous emerging challenges while e-government development and government activities as well as service delivery. The aim of this paper is trying to explore the e-government development in developing countries and to analyses the emerging challenges of e-government, ICT policy and legal issues in Nepal. The content analysis method is used during research. This paper concludes that Nepal is facing numerous challenges whole implementing e-government like poor ICT infrastructure development, law and public policy, insufficient human resources development and management, digital divide and e-literacy. Some other challenges are political issues, inadequate human resources, lack of a legal framework, low per capita income, little public awareness about ICT and new technology. For authentication and regularization of the recognition, validity, integrity, and reliability; it is essential to make legal provisions. Nepal requires a bold set of institutional reforms aimed at achieving better governance while enforcing the rule of law. The reason of success and failure of e-government is the lack of comprehensive regulatory framework and good coordination between regulation implementing agencies of government. Citizens play a major role to make government success or failure. There are not sufficient act and policy in ICT sector so different sector wise law, policy and plan should formulate in time for regulating the e-government activities in the nation.
SONE/UK Conference Proceedings, London
Ramhari Poudyal
Solar energy is present in abundant quantities in Nepal, although it is not widely exploited to improve the energy situation of households. In order to promote utilisation of solar energy, this paper assesses the energy potential of a typical photovoltaic rooftop module installation in Kathmandu. In particular, the current-voltage and power-voltage characteristics of the P.V. module are obtained, assuming a simplified equivalent electrical circuit with a single diode. The model is implemented and simulated in Matlab/Simulink. Simulation results are compared with different types of P.V. modules and the corresponding datasheets. The comparison verifies that the developed P.V. model can provide accurate predictions for deploying the actual P.V. modules. Furthermore, using the real weather data for Kathmandu, our results indicate that solar radiation is a viable source of energy which can be promoted on a large scale in households across the city. This would mitigate the present deficiency in electricity supply leading to frequent power outages and enhance the energy security of the country.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Nepal Academy of Science and Technology
Proceedings of Science Globe International Conference, 10th June, 2018, Bengaluru, India
Stefano Manacorda
ONODUGO CHRIS
Conference Proceedings of Second International Conference of SASCV.
Megha Shree , Dr.Debarati Halder,Ph.D
Asad Munir Lecturer Mass Communication , Asad Munir
Matthew Hall
Bushra Elamin
Future Governance: The Internet, Vulnerability, Social Change, and State-Society Relationship in Nigeria
Okey Uzoechina
Philip Ndubueze
6th International Report CRIME PREVENTION AND COMMUNITY SAFETY: Preventing Cybercrime
Matthew Hall , Jeff Hearn
Dr.Debarati Halder,Ph.D
AIPFU Journal of School of Sciences (AJSS)
Augustine C Onuora
IJCSMC Journal , Rajendra Man Banepali
Champa Sarker
Emmanuel Olusegun Adekoya
Mahboob Usman
Raj Kumar Dhungana
LBEF RESEARCH JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
Colin Maclay
Archives of Business Research
Tareq Alshammari , Harman Singh
Tanusree Chakraborty
Tade Oludayo
Rakesh Chandra
CYBER CRIMINOLOGY IN MODERN TANZANIA
COSMAS MASIMO
Subhajit Basu
Prabinda Joshee
Ramandeep Kaur
Susan Nepal
Journal of Computer Science IJCSIS
The 4th International Conference on Energy, Environmental and Information System (ICENIS 2019)
Mochammad Fahlevi , Mohamad Saparudin
Pranita Upadhyaya , Manish Pokharel
Proceedings of International Conference on Gender Equality through the Strategy of Gender Mainstreaming
Dr. Md. Mamun U R Rashid
lekhnath bhusal
mwale clinton
IT for Change
Bedadyuti Jha
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Octopus Cybercrime Community
Status regarding Budapest Convention
Cybercrime policies/strategies.
In 2015, the Government of Nepal, through its Ministry Of Communications And Information Technology , issued its National Information and Communication Technology Policy (ICT Policy 2072) (NE) which presents various objectives to guide the digitalization of the country. The document sets the targets of digitalization in terms of infrastructure and Internet access, implying a transition towards an e-administration and e-economy to follow in the upcoming years. In this context, fighting cybercrime, enhancing cybersecurity and data protection are mentioned as means to build confidence and security and increase the use of ICT among citizens.
To meet these expectations, in the ICT Policy 2072 the government commits to improve existing legislation on cybercrime and cybersecurity, and to increase the capabilities of law enforcement agencies and prosecution services on cybercrime matters. The policy establishes also new units within existing government institutions or agencies to enforce the law, such as the Computer Crimes Investigation Unit, the National Electronic Communication Security Centre and an Information Security Response Team (NPCERT).
The 2019 Digital Nepal Framework proposes to finish setting up the National Electronic Communication Security Centre by 2021. In general, cybercrime is subsumed under the umbrella of cybersecurity, which is evident in this most recent digital framework when it comes to developing relevant legislation.
Cybercrime legislation
State of cybercrime legislation.
Provisions within Nepal’s current legal framework correspond only to some extent to the Budapest Convention. The current legal framework on cybercrime and electronic evidence in Nepal mostly addresses crimes against electronic and financial transactions through its Electronic Transactions Act, 2063 (2008)/ETA and Banking Offence and Punishment Act 2064 (2008).
Substantive law
The piece of legislation that provides substantive law provisions criminalizing some online offences is the Electronic Transactions Act , 2063 (2008). The Act provides definitions such as computer system, computer, computer network, computer resource, computer database, data, originator (Section 2), unauthorized access (Section 45), damage to any computer and information systems (Section 46) etc., but they are not edited and conceived as a criminal law on cybercrime. However, the Act’s focus is on ensuring and regulating the safety, authenticity and security of electronic transactions, leaving room for legislation that would address the full spectrum of cybercrimes and the use and handling of electronic evidence in traditional crimes.
Other relevant pieces of legislation are:
The Banking Offence and Punishment Act 2064 (2008) codifies a number of relevant offences in Ch. 2 – Banking Offences:
- Section 5: unauthorized withdrawals or payments;
- Section 6: unauthorized payments via electronic means;
- Section 12: alterations to account/ledger, forgery or fraud.
- Punishments are prescribed in Ch. 3.
The Children's Act, 2048 (1992), 2049/2/7 (May 1992 A.D.) offers some limited protection from online exploitation in Ch. 2 – Rights and Interests of Children, Section 16. (1-3) and Ch. 6 – Miscellaneous, Section 53: punishment.
The Copyright Act, 2059 (2002) addresses infringements to copyrights in Sections 25-29 (Ch. 6).
The National Penal Code Act (2017) (EN):
- Section 35: prohibition of abetment;
- Section 276: prohibition of forgery;
- Section 298: prohibition of breaching privacy through electronic means;
- Section 300: prohibition of writing letters with dishonest intention of causing annoyance;
- Section 307: punishment for libel.
Procedural law
We find some safeguards in various legal sources, as listed below, however serious concerns persist with proposed draft legislation and the apparent misuse of current legislation to control certain freedoms (e.g. freedom of speech, association) as outlined above in the State of Cybercrime Legislation section:
Constitution of Nepal :
- Part 3: Fundamental Rights and Duties16. Right to live with dignity
17. Right to Freedom
18. Right to equality
19. Right to communication
20. Right to justice
22. Right against torture
23. Right against preventive detention
27. Right to information
28. Right to privacy
- Part 25: National Human Rights Commission
National Penal Code Act (2017) (EN):
- Section 302: prohibition of unauthorized entry into other’s residence;
Related laws and regulations
- Constitution of Nepal ;
- National Penal Code Act (2017) (EN);
- National Criminal Procedure Code Act (2017; EN);
- ETA: The basic law in cybercrime related matters in Nepal is the Electronic Transactions Act, 2063 (2008) (EN);
- Banking Offence and Punishment Act 2064 (2008, EN);
- ETR: In exercise of the powers conferred by Section 78 of the Electronic Transaction Act, 2063 (2007), the Government of Nepal has framed the following Rules: Electronic Transactions Rules 2064 (2007).
- GC: The Muluki Ain (General Code) Act Number 67 of the year 2019 is the general law that contains the procedural law as well as the substantive law provisions, which are applicable when no specific laws are applicable.
- CA: The Children's Act, 2048 (1992), 2049/2/7 (May 20, 1992 A.D.) is the Act relating to protect the rights and interest of Children
- TA: The Nepal Communications Act 2053 (1997)
- CRA: The Copyright Act, 2059 (2002)
- Consumer Protection Act 2075 (2018)
- EA: The Nepal Evidence Act, 2031 , Date of Authentication and publication 2031.7.5 (1974 Oct. 21).
- MLA: Mutual Legal Assistance 2070 (2014, EN), Date of Authentication and Publication 2070.12.12;
- Mutual Legal Assistance Regulation 2070 (2014, EN);
- Extradition Act, 2070 (2014, EN – starting page 39), repealed the Extradition Act, 2045 (1988).
Specialised institutions
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs : via diplomatic channels, seems to be the default Central Authority for mutual legal assistance and extradition matters. However, the Mutual Legal Assistance 2070 (2014) provides that the Central Authority for MLA would be decided for each bilateral treaty upon publication in the Nepal Gazette.
- Ministry of Home Affairs : according to the Extradition Act, 2070 (2014) Section 9, once the request for extradition reaches the Ministry of Foreign Affairs through diplomatic channels, the request is then forwarded to the Ministry of Home Affairs for processing.
- Cyber Bureau : part of the Nepali Police, the office was set up in 2018 to: (1) investigate cybercrimes (including on critical infrastructure); (2) undertake capacity building; (3) coordinate and cooperate on information exchange and cybercrime investigations with national and international organisations/bodies and security agencies; (4) form the national CERT. Contact information here .
- Information Security Response Team Nepa l (NPCERT): established in 2016, was created to deal with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing, to help identify and respond to cyber risks (and limit their impact on operations), and to coordinate with other domestic and international CSIRTs (Computer Security Information Response Team) and related organisations.
International cooperation
Competent authorities and channels.
The Mutual Legal Assistance 2070 (2014), Section 3, provides a general rule that legal assistance can be provided to a foreign country on the basis of a bilateral treaty or on the basis of reciprocity commitment from the foreign country.
The Extradition Act, 2070 (2014) , Sections 3 and 5, covers the conditions to offer and refuse extradition. Extraditable offences are presented in Section 4.
Even though Nepal has bilateral relations with some 169 countries and international entities (e.g. European Union), it appears none have integrated MLAs for criminal justice international cooperation.
Jurisprudence/case law
Sources and links.
ICT Policy 2072 (2015);
2019 Digital Nepal Framework ;
Cyber Bureau ;
President Yadav certifies 10 different Acts (27 Mar 2014), The Kathmandu Post;
Compendium of Bilateral and Regional Instruments for South Asia: International Cooperation in Criminal Matters (2015). United National Office on Drugs and Crime;
Cyber Security and Internet Governance in Nepal (Apr 2020), Manish Jung Pulami, Nepal Institute for International Cooperation and Engagement;
Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Bilateral Relations .

- Cybercrime website
- Template: Mutual Legal Assistance Request for subscriber information (Art. 31 Budapest Convention). English and bilingual versions available.
- Template: Data Preservation Request (Articles 29 and 30 Budapest Convention). English and bilingual versions available.
Analysis of Law Relating to Cybercrime in Nepal
- First Online: 14 February 2018
Cite this chapter

- Balram Prasad Raut 3
1246 Accesses
Science , technology, and law share unique relationship. Technological advancement has tendency to alter human relations and social ethos, posing new challenges to the existing laws in the context of society. As the function of law is to regulate social conflicts and deliver justice, law must be restructured to meet the exigencies and suit itself to cater to the new issues that have science and technological derivatives.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Cybercrime: Concerns, Challenges and Opportunities

Combating Cyber Dependent Crimes: The Legal Framework in the UK

Cyberspace as an Area of Legal Regulation
Durgambini Patel, “ Digital Revolution and Good Governance—A New State in Making ”, Paper presented in the 13th ICT Conference held on February 8–9, 2013 in Kathmandu, Nepal, organized by Computer Association of Nepal and Internet Society Nepal Chapter, Kathmandu.
Zibber Mohiuddin, “ Cyber Law in Pakistan ”, Paper was presented in the workshop related with Cyber Law, 2012.
Lokendra Sharma, Criminal Law (Lumbini Publication, Kathmandu, 2010) at 195.
Approved by the President of Nepal in February 2013, The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) compelled the Government of Nepal to make law relating to organized crime, otherwise Nepal Will be under the blacklisted, meaning thereby that Letter of Credit (LC) will not be accepted by other banks of the world.
Based on the presentation made by Nepal Police on “ Cyber Crime in Nepalese Perspectives ” Police Head Quarter, Naxal, Kathmandu.
The Central Investigation Bureau of Nepal Police, Press Released on 19/05/2012.
Id., on 08/06/2012.
Id., on 11/05/2012.
Id., on 04/05/2012.
Id., on 22/8/2012.
Supra note 1.
The Attorney General, Annual Report of 2011/12.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nepal Law Campus, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal
Balram Prasad Raut
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
National University of Study and Research in Law, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
B.C. Nirmal
Faculty of Law, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India
Rajnish Kumar Singh
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Raut, B.P. (2018). Analysis of Law Relating to Cybercrime in Nepal. In: Nirmal, B., Singh, R. (eds) Contemporary Issues in International Law. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6277-3_29
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6277-3_29
Published : 14 February 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-6276-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-6277-3
eBook Packages : Law and Criminology Law and Criminology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nepal's previous government banned the app in November, citing concerns around its misuse. More than 1,600 TikTok-related cyber crime cases were registered over four years in the Himalayan nation ...
Nepal's previous government banned the app in November, citing concerns around its misuse. More than 1,600 TikTok-related cyber crime cases were registered over four years in the Himalayan nation ...
The purpose of this paper shall be to deal with the following issues:to determine and analyse cases pertai. ng to cybercrimes in Nepal (with data) and the nature of such cases.to identify the strengths and weaknesses in the criminal justice delivery system (investigation, prosecution, and adjudi.
Essay on Cyber crime in Nepali#साइबरअपराध#निबन्ध #साइबर विद्युतीय अपराध वा साइबर अपराध ...
साइबर अपराध निबन्ध नेपाली | Essay on Cyber crime in Nepali | Cyber Crime Essay in Nepali🟪Your Queries:-साइबर अपराध ...
नेपालमा बढ्दाे साइबर अपराध Increasing Cyber Crime in NepalInterview with the spokesperson of Nepal Cyber Bureau Mr. Nabinda Aryal.#cybercrime # ...
साइबर अपराधको रोकथाम | Cyber Aparadhko Roktham | निबन्ध सिकाइ सन्दर्भ सामग्री कक्षा ९ विषय ...
Nepalese legal regime addressing current or prospective modus operandi of cybercrime. 5.1.1. Substantive Legal Regime. 5.1.2. Enforcement. 5.2. Comparison of Nepalese legal regime with Convention on Cybercrime. CHAPTER VI - CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION. 6.1.
Law Campus, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu. ABSTRACT. Cybercrime is becoming a serious issue in Nepal, with a rising number of cases being reported. each year. In response to this growing problem ...
The cyber security strategies, policies, plan and law, help to protect e-government systems against threat and attack; and detect abnormal activities. The aim of this paper is to explorer cyber ...
The objective of this article are; to know the basic concept of cyber crime and reasons for cyber crime, evaluate different provisions relating to computer and computer related crimes under ICT Act,2006 (amended 2013), analyze the role of police power of arrest without warrant under this Act etc. Secondary sources have been used during the time ...
Nepal too is at a high risk of cyber crimes as the country does not have proper legal procedures to address the ever-evolving cyber crimes. In the past few years the country has faced many security breaches on government websites; in late January, about 1,500 government websites were shut down.
Cyber security in Nepal is important to protect personal, government data, information and server from theft, damage, and malware. Without cybersecurity, neither an organization nor an individual will be able to defend their data from cyber-attacks. The level of cybercrimes is increasing day by day and becoming more vulnerable.
NATIONAL JUDICIAL ACADEMY, NEPAL
Section 47 of the Act is the most used section to prevent cybercrime in Nepal. This section stipulates that if a person publishes or displays material against morals, etiquette, hatred, or malice on a computer, internet, and other electronic media, the culprit can be punished with a fine of 1 lakh rupees or imprisonment for up to 5 years or both.
22071352423-Final a Study on Cyber Crime Cases in Nepal, 2022 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides a preface and background for a study on cyber crime cases in Nepal. It discusses the rapid growth of internet usage in Nepal and the corresponding rise in cyber crimes. The study aims to analyze cyber crime cases in Nepal, identify ...
1.3.2 Objectives. es of the curriculum are:To impart the theoretical and practical knowledge of cyber law and cyber crime in na. onal and global context.To sensitize all the participants regarding the cyberspace, yber law and cybercrime.To enhance the quality and understanding of the participants regarding principles and nuances of the cyberspace,
The inculpated had hacked the Nepal Electronic Payment System (NEPS), an interface that sanctions the transaction of money deposited in a bank by utilizing cards issued by other member banks. On April 15, a group of hackers that had managed to gain unauthorized access to WebPages and data systems in Nepal launched a cyber-attack.
In this article, we will understand various types of cyber crimes and further guide you on where and how to report cyber crimes in Nepal. Common Types of Cybercrime in Nepal Online fraud. Online fraud is a type of cybercrime that involves using deception to obtain money or valuable information through the internet. Phishing scams are a common ...
3. Methodology Cyber crime is one of the fastest growing areas of crime around the globe. Nepal is not an exception to attract, threat of cybercrime. Increasing internet and computer users and the growth of technology are grooming cyber crime. Nepal faces a huge hindrance due to its limited policies and regulation.
595 International Youth Conference on Science, Technology and Innovation 2019, October 21-23, Kathmandu, Nepal Cyber Security in Nepal: ICTs are use in various sectors in our daily activities and US government has followed different cyber security strategies to control the cyber crime [11] [12].
Provisions within Nepal's current legal framework correspond only to some extent to the Budapest Convention. The current legal framework on cybercrime and electronic evidence in Nepal mostly addresses crimes against electronic and financial transactions through its Electronic Transactions Act, 2063 (2008)/ETA and Banking Offence and Punishment Act 2064 (2008).
सामाजिक सञ्जाल दुरुपयोगका मामिला बढे, एक वर्षमै १५ हजारभन्दा बढी उजुरी
Recently, the questions papers of entrance examination of Institute of Engineering, Tribhuvan University was published through Facebook. ... Based on the presentation made by Nepal Police on "Cyber Crime in Nepalese Perspectives" Police Head Quarter, Naxal, Kathmandu. 7. The Central Investigation Bureau of Nepal Police, Press Released on 19 ...
E-governance is required to deal with various risks and responding to current and beyond incidents and attacks to build trust from people. Managing the future risk related to cyber space and future vulnerabilities and how to prevent or the way to mitigate them. Responding to present and beyond incidents and attacks required knowledge. What has ...