

Watershed Management Framework
Jan 31, 2012
440 likes | 895 Views
Watershed Management Framework. Mission of watershed management
Share Presentation
- basic treatments
- dry periods
- riparian forest buffer
- storm events
- water yield vh vh

Presentation Transcript
Watershed Management Framework • Mission of watershed management • Coordinate and integrate the programs, tools, and resources of multiple stakeholder groups to better protect, maintain, and restore the ecological structure and function of watersheds and support the sustainable uses of watersheds.
Form Interagency Workgroup • Design and implement a framework to facilitate the transition from a program-centered to a resource-based approach to holistic management of watershed.
Resource Management Goals • Conserve and enhance public health. • Conserve and enhance watershed ecosystems. • Support watershed resource use to achieve water quality standards and conservation goals. • Conserve and improve ambient conditions. • Reduce or prevent pollutant loadings and other stressors.
Goals Achieved Through Operational Objectives • Identify indicators of watershed integrity • Increase communications and consensus among all stakeholder • Implement integrated solutions by coordinating activities on targeted watersheds • Provide a forum for program networking • Develop stronger partnerships with regional, county, and local governments • Coordinate public communication and education forums, • Coordinate existing means and develop new avenues for broad participation • Promote stronger resource conservation ethics
Major Elements – • Stakeholder involvement • Basin-wide management units • Tool kit of programs NRCS Conservation Reserve Program Wildlife Habitat Incentives Program Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program Wetland Reserve Program
Forests as Source of NPS Pollution • Forests not a major source of NPS • Especially true in flat lands • Potential for erosion increases with slope and soil type • Forests used as buffer against more intensive land uses • Agriculture • Urbanization
Knowledge of Precipitation Amounts and Patterns • Plan drainage structures • Size temporary culverts to handle storm events during period of operations • Size permanent drainage structure to handle 100 year storms
Knowledge of Precipitation Amounts and Patterns • Time operations • Expose soil during dry periods if possible • Establish vegetative cover as soon as possible • Use native vegetation whenever possible
What Happens to Precipitation? • Hydrologic cycle P = RO + ET + S, where • P ≡ precipitation • RO ≡ runoff • ET ≡ evapotranspiration • S ≡ storage
Evapotransporation • Loss of water from a given area during a specified time by evaporation from the soil surface and by transpiration from the plants. • Supports plant life • Reduces water yield
Relationship of Forest Cover to Water Flows • Erosion • Impacts of • Roads • Harvests • Water flows • Storm events • Storage • Water yield • Amount • Timing
Timber Harvesting • Major factor in control of water quality in forested watersheds • Felling, limbing and bucking – avoid riparian zones and exclude slash from channel
Timber Harvesting • Skidding and yarding – minimize soil compaction and disturbance • Use high lead systems in sensitive and steep areas
Timber Harvesting • Roads and skid trails – layout and construct according to BMP’s
Impact of Harvesting on Water Quantity and Quality Stone, Swank, and Hornbeck. 1978. “Impacts of Timber Harvest Regeneration Systems on Stream Flow and Soils in the Eastern Deciduous Region,” Forest Soils and Land Use, Proceedings Fifth North Am. Forest Soils Conf.
Low Flow Water Yield VH VH H H M M L L VL VL uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut Peak Flow Sedimentation VH VH poor roads & skid trails poor roads & skid trails H H M M L L Good control of roads & skid trails VL VL uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut
Dissolved Nutrient Loss Nutrient Removal by Harvest – Average Annual VH VH Thick organic layer H H M M L L VL VL uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut Maximum Stream Temperature Reduction in Surface Soil Organic Matter VH Without shade VH H H M M L L With shade strip VL VL uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut uncut selection shelter- wood clear- cut intensive clearcut
NPS: Sediment • Total suspended solids (TSS), i.e., sediment is major NPS pollution of concern Cropland – 1 to 20 tons per acre per year Forestland – 1 lb. to 0.5 tons per acre per year Issue is amount of sediment loading relative to expected amount. Usually zero for streams in forested watersheds.
NPS: Nitrogen • Water soluble • Some converted to gaseous forms by microbial action • Enters surface and goundwater
NPS: Phosphorus • Major nutrient leading to water pollution • Binds to soil particles – correlated with silt load • Leads to low dissolved oxygen from excessive plant growth
Logging and Forestry BMP’s • Planning • Roads • Skid Trails • Stream Crossings • Riparian Zones • Log Landings • Fuel
Related BMP’s • Equipment breakdown and spills • Litter • Site preparation • Mechanical and hand clearing • Chemical site preparation • Planting and weed control • Forest chemicals • Fire and fire control lines • Woodland grazing • Recreation trails
Streamside Forest as Sediment Filter • Sediment settles as speed of surface flow reduced by forest floor • Sediment is filtered out as sediment loaded water percolates into porous forest floor
Benefits of Buffers • Control surface runoff and shallow ground water • Nutrients • Sediment • Shade streams • Ameliorate effects of some pesticides • Provide dissolved and particulate organic food for aquatic and terrestrial systems Sheet erosion on crop land
Underlying Principles of Buffers • Vegetation and soil filters sediments • Vegetation takes up nutrients which can be removed from portion of site by harvesting timber and forage. Clearfield Creek in PA, stable structure but polluted by mine drainage
Riparian Forest Buffer: Design
Total Buffer Width: Streamside • Determine based on • Soil hydrographic group • Total area of source • Soil capability class
Midwest Issue • Field drain tiles empty into drainage ditches that flow directly to waterways. • Methods need to buffer tile water before it enters ditches. • Nitrogen is pollutant
Water Movement Below Surface • Groundwater issues • Recharge areas • Inorganic pollutants • Soil trafficability • Location of roads and skid trails • Operating seasons Abandoned wells are most common source of ground water pollution, not surface applied chemicals.
Groundwater Issues • Groundwater recharge zones should receive special protection
Management for Water Yield • Basic treatments • Removal of woody vegetation – limited application • Weather modification – not practical • Construction of “catchments” – best technique but with high ecological cost
Control of Stream Flow Regimen • Objectives • Prevent deterioration of regimen because of altered land uses • Improve natural stream flow regime by management of hydrology • Rehabilitate deteriorated watersheds Stable banks
Primary considerations • Irregular flow • Volume of high and low flows • Duration of high and low flows • Capacity of structures to handle high flows • Management of aquatic ecosystems Hyetograph
Conflict Resolution • Watershed management involves multiple • Stakeholders • Landowners • High likelihood of conflicting • Values, • Cultures • Threat to economic security The Colorado Internet Center for Environmental Problem Solving, University of Colorado
Conflict Resolution • Resolution should be based on a participatory process led by non-stakeholder • Agree on discussion process • Identify points of • agreement • disagreement • Agree on major issues • Identify possible solutions • Implement representative solutions
Forest Certification • Way to “guarantee” BMP’s are implemented for multiple objectives, • Water quality • Timber production • Biodiversity • Response to interest groups wanting to • Stop timber harvests • Buy products from sustainably managed forests Forest Stewardship Council is a major certifying agency
What Is Certification • Loose definition - Verification by a first-, second, or third-party of compliance with principles, objectives and performance measures established by a recognized organization. • Strict definition - Independent verification of conformity to a standard.
Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI)® Program • Sustainable Forestry • To practice forestry to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs by practicing a land stewardship ethic which integrates the reforestation, managing, growing, nurturing, and harvesting of trees for useful products with conservation of soil, air and water quality, wildlife and fish habitat and aesthetics.
Definitions • Principle – The vision and direction for sustainable forest management • Objective – A fundamental goal of sustainable forest management • Performance measure – A means of judging whether an objective has been fulfilled
- More by User

Integrated Watershed Management Programme
Integrated Watershed Management Programme. State Level Nodal Agency Uttarakhand WMD , Dehradun . Progress . Watershed Management Directorate nominated as the State Level Nodal Agency (SLNA) as per the Common Guidelines vide G.O. No. 591/2008/XIII-II/51(5)/2005 dt. 11.09.2008.
863 views • 14 slides

Watershed Management Planning
1.24k views • 42 slides
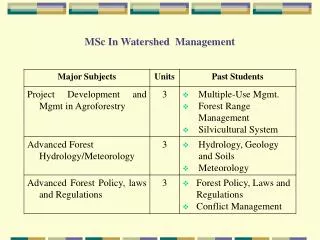
MSc In Watershed Management
MSc In Watershed Management. MSc in Watershed Management. Complementary Projects. Minor Field (6 units) - the students in consultation with the Advising Committee, should enroll 3 courses representing his chosen minor fields. Silviculture
420 views • 13 slides

Watershed Management Working Group
Watershed Management Working Group. Fred Beall, CFS Chris Knopp, USFS Ramon Cordoza Vazquez, CONAFOR. History. BOA meeting in Oct. 2001 requested a scoping paper on watershed management issues Commissioners approved creation of Watershed Management Working Group in Oct. 2002
284 views • 6 slides

WATERSHED MANAGEMENT
WATERSHED MANAGEMENT. WMA 510 Dr. J.A. Awomeso , Dr O.Z. Ojekunle , Dr. G.O. Oluwasanya Dept of Water Res. Magt . & Agromet UNAAB. Abeokuta. Ogun State Nigeria [email protected]. WATERSHED MANEGEMENT . WMA 510. Introduction.
18.12k views • 72 slides

Watershed Management in MA
Watershed Management in MA . The Deerfield River Watershed Action Plan. http://www.mass.gov/envir/water/publications/WAPs/Deerfield_WAP_2004.pdf. Kate Crawford, River Corridor Management, October 10, 2005. MA River Management . Watershed-scale management approach Emphasis on: Water quality
408 views • 14 slides


INTEGRATED WATERSHED MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
PRESENTATION ON . INTEGRATED WATERSHED MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME. SIKKIM Date:- 20-21/05/2010. Details of Projects Sanction During The Year 2009-10. Status of Implementation of Projects During The Year 2009-10. Status of Implementation of Projects During The Year 2009-10.
954 views • 15 slides

Collaboration in Watershed Management
Collaboration in Watershed Management. Mark Shea - Watershed Planning - Colorado Springs Utilities. Colorado Springs Utilities Who We Are. Four-service utility provider Electric, natural gas, water, wastewater Over 650,000 customers Local government oversight
234 views • 7 slides

Watershed Management Runoff models
Watershed Management Runoff models. Hydrology and Water Resources, RG744 Institute of Space Technology November 13, 2013. Runoff models. Peak runoff models Provide only the estimates of peak discharge from the watershed Continuous runoff models
1.34k views • 73 slides

Watershed Management in MA. The Deerfield River Watershed Action Plan. http://www.mass.gov/envir/water/publications/WAPs/Deerfield_WAP_2004.pdf. Kate Crawford, River Corridor Management, October 10, 2005. MA River Management. Watershed-scale management approach Emphasis on: Water quality
427 views • 14 slides

WATERSHED MANAGEMENT. WMA 510 Dr. J.A. Awomeso , Dr O.Z. Ojekunle , Dr. G.O. Oluwasanya Dept of Water Res. Magt . & Agromet UNAAB. Abeokuta. Ogun State Nigeria [email protected]. COURSE CODE : WMA 510 COURSE TITLE : Watershed Management COURSE UNITS : 3 Units
1.91k views • 77 slides

Strategic Watershed Management
Strategic Watershed Management. Session Chair: David Ward, Loudoun Watershed Watch Panelists: Gem Bingol, Piedmont Environmental Council Joe Ivers, PhD, Virginia Waters and Wetlands, Inc. Tom Turner, John Marshall Soil & Water District. March 24, 2010 Middleburg, VA. A Watershed Approach.
357 views • 5 slides

Watershed Management Wake County
Watershed Management Wake County. Monitoring Drivers. 2003 Watershed Plan Pollutant loads & trends Assess programs Develop strategies and projects Regulatory compliance. Monitoring Points. Falls watershed in 2007 Other watersheds 2009. Watershed Monitoring Parameters.
513 views • 14 slides

Watershed Management institutional aspect
Watershed Management institutional aspect. Land husbandry in dry prone area Module 556. By - Zeremariam G. Mosazghi 21/3/00. What is watershed. Watershed. Land area from which rainfall or snowmelt drains into single water body.
483 views • 11 slides

Forest Watershed Management
Forest Watershed Management. Course Objective:
1.31k views • 45 slides

WATERSHED MANAGEMENT. Muhammad Tayyab Nauman 2004- ag -1411 7 th Semester Department of Agronomy. Watershed. The area that drains into a river or other body of water. Actions in one part of a watershed will often have an impact throughout the watershed. Watersheds & Watershed Management.
1.47k views • 27 slides

Watershed Management What is a watershed?
Watershed Management What is a watershed? Line of separation between two catchments (UK) [Chambers dictionary] Watershed (USA) = Basin (USA) = Catchment (UK) [US usage is most common overseas] Frequently (incorrectly) used to refer to upper or steep part of watershed
964 views • 39 slides

WATERSHED MANAGEMENT. Module 23, part A – Social Component. Watershed management organization. Social Component Ecological Component Economic Component. Watershed management structure . A strong watershed structure uses sound science facilitates communication and partnerships
976 views • 32 slides

Watershed Development Department Government of Karnataka. Integrated Watershed Management Programme. NET PLANNING PROCESS. H.G Shivananda Murthy IFS Commissioner. Planning. Plan is the document, detailed proposal for doing or achieving something
528 views • 23 slides

Collaborative Watershed Management
Collaborative Watershed Management. Collaborative Watershed Management. Kansas NPS Management Plan. 1989 – Approved Policy, Implementation, Funding Short Term Goals, Long Term Goals, Action Plans First Overhaul – 2000 Broad Goals, Objectives, Strategies Second Overhaul – 2010-2011
318 views • 10 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO