
Work With Us
Private Coaching
Done-For-You
Short Courses
Client Reviews
Free Resources

Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
The “Big 6” Qualitative Methods + Examples
By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (D.Tech) | May 2020 (Updated April 2023)

If you’re new to the world of research, qualitative data analysis can look rather intimidating. So much bulky terminology and so many abstract, fluffy concepts. It certainly can be a minefield!
What (exactly) is qualitative data analysis?
To understand qualitative data analysis, we need to first understand qualitative data – so let’s step back and ask the question, “what exactly is qualitative data?”.
Qualitative data refers to pretty much any data that’s “not numbers” . In other words, it’s not the stuff you measure using a fixed scale or complex equipment, nor do you analyse it using complex statistics or mathematics.
So, if it’s not numbers, what is it?
Words, you guessed? Well… sometimes , yes. Qualitative data can, and often does, take the form of interview transcripts, documents and open-ended survey responses – but it can also involve the interpretation of images and videos. In other words, qualitative isn’t just limited to text-based data.
So, how’s that different from quantitative data, you ask?
Simply put, qualitative research focuses on words, descriptions, concepts or ideas – while quantitative research focuses on numbers and statistics . Qualitative research investigates the “softer side” of things to explore and describe , while quantitative research focuses on the “hard numbers”, to measure differences between variables and the relationships between them. If you’re keen to learn more about the differences between qual and quant, we’ve got a detailed post over here .
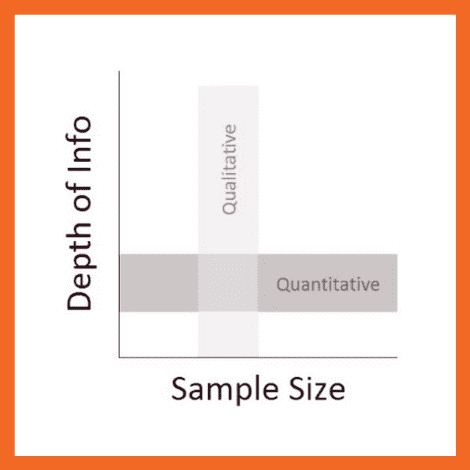
So, qualitative analysis is easier than quantitative, right?
Not quite. In many ways, qualitative data can be challenging and time-consuming to analyse and interpret. At the end of your data collection phase (which itself takes a lot of time), you’ll likely have many pages of text-based data or hours upon hours of audio to work through. You might also have subtle nuances of interactions or discussions that have danced around in your mind, or that you scribbled down in messy field notes. All of this needs to work its way into your analysis.
Making sense of all of this is no small task and you shouldn’t underestimate it. Long story short – qualitative analysis can be a lot of work! Of course, quantitative analysis is no piece of cake either, but it’s important to recognise that qualitative analysis still requires a significant investment in terms of time and effort.
Need a helping hand?
The “Big 6” Qualitative Analysis Methods
There are many different types of qualitative data analysis, all of which serve different purposes and have unique strengths and weaknesses . We’ll start by outlining the analysis methods and then we’ll dive into the details for each.
The 6 most popular methods (or at least the ones we see at Grad Coach) are:
- Content analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Grounded theory (GT)
- Interpretive phenomenological analysis (IPA)
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis
Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
With content analysis, you could, for instance, identify the frequency with which an idea is shared or spoken about – like the number of times a Kardashian is mentioned on Twitter. Or you could identify patterns of deeper underlying interpretations – for instance, by identifying phrases or words in tourist pamphlets that highlight India as an ancient country.
Because content analysis can be used in such a wide variety of ways, it’s important to go into your analysis with a very specific question and goal, or you’ll get lost in the fog. With content analysis, you’ll group large amounts of text into codes , summarise these into categories, and possibly even tabulate the data to calculate the frequency of certain concepts or variables. Because of this, content analysis provides a small splash of quantitative thinking within a qualitative method.
Naturally, while content analysis is widely useful, it’s not without its drawbacks . One of the main issues with content analysis is that it can be very time-consuming , as it requires lots of reading and re-reading of the texts. Also, because of its multidimensional focus on both qualitative and quantitative aspects, it is sometimes accused of losing important nuances in communication.
Content analysis also tends to concentrate on a very specific timeline and doesn’t take into account what happened before or after that timeline. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing though – just something to be aware of. So, keep these factors in mind if you’re considering content analysis. Every analysis method has its limitations , so don’t be put off by these – just be aware of them ! If you’re interested in learning more about content analysis, the video below provides a good starting point.
QDA Method #2: Narrative Analysis
As the name suggests, narrative analysis is all about listening to people telling stories and analysing what that means . Since stories serve a functional purpose of helping us make sense of the world, we can gain insights into the ways that people deal with and make sense of reality by analysing their stories and the ways they’re told.
You could, for example, use narrative analysis to explore whether how something is being said is important. For instance, the narrative of a prisoner trying to justify their crime could provide insight into their view of the world and the justice system. Similarly, analysing the ways entrepreneurs talk about the struggles in their careers or cancer patients telling stories of hope could provide powerful insights into their mindsets and perspectives . Simply put, narrative analysis is about paying attention to the stories that people tell – and more importantly, the way they tell them.
Of course, the narrative approach has its weaknesses , too. Sample sizes are generally quite small due to the time-consuming process of capturing narratives. Because of this, along with the multitude of social and lifestyle factors which can influence a subject, narrative analysis can be quite difficult to reproduce in subsequent research. This means that it’s difficult to test the findings of some of this research.
Similarly, researcher bias can have a strong influence on the results here, so you need to be particularly careful about the potential biases you can bring into your analysis when using this method. Nevertheless, narrative analysis is still a very useful qualitative analysis method – just keep these limitations in mind and be careful not to draw broad conclusions . If you’re keen to learn more about narrative analysis, the video below provides a great introduction to this qualitative analysis method.

QDA Method #3: Discourse Analysis
Discourse is simply a fancy word for written or spoken language or debate . So, discourse analysis is all about analysing language within its social context. In other words, analysing language – such as a conversation, a speech, etc – within the culture and society it takes place. For example, you could analyse how a janitor speaks to a CEO, or how politicians speak about terrorism.
To truly understand these conversations or speeches, the culture and history of those involved in the communication are important factors to consider. For example, a janitor might speak more casually with a CEO in a company that emphasises equality among workers. Similarly, a politician might speak more about terrorism if there was a recent terrorist incident in the country.
So, as you can see, by using discourse analysis, you can identify how culture , history or power dynamics (to name a few) have an effect on the way concepts are spoken about. So, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding culture or power dynamics, discourse analysis can be a powerful method.
Because there are many social influences in terms of how we speak to each other, the potential use of discourse analysis is vast . Of course, this also means it’s important to have a very specific research question (or questions) in mind when analysing your data and looking for patterns and themes, or you might land up going down a winding rabbit hole.
Discourse analysis can also be very time-consuming as you need to sample the data to the point of saturation – in other words, until no new information and insights emerge. But this is, of course, part of what makes discourse analysis such a powerful technique. So, keep these factors in mind when considering this QDA method. Again, if you’re keen to learn more, the video below presents a good starting point.
QDA Method #4: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis looks at patterns of meaning in a data set – for example, a set of interviews or focus group transcripts. But what exactly does that… mean? Well, a thematic analysis takes bodies of data (which are often quite large) and groups them according to similarities – in other words, themes . These themes help us make sense of the content and derive meaning from it.
Let’s take a look at an example.
With thematic analysis, you could analyse 100 online reviews of a popular sushi restaurant to find out what patrons think about the place. By reviewing the data, you would then identify the themes that crop up repeatedly within the data – for example, “fresh ingredients” or “friendly wait staff”.
So, as you can see, thematic analysis can be pretty useful for finding out about people’s experiences , views, and opinions . Therefore, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding people’s experience or view of something, thematic analysis can be a great choice.
Since thematic analysis is a bit of an exploratory process, it’s not unusual for your research questions to develop , or even change as you progress through the analysis. While this is somewhat natural in exploratory research, it can also be seen as a disadvantage as it means that data needs to be re-reviewed each time a research question is adjusted. In other words, thematic analysis can be quite time-consuming – but for a good reason. So, keep this in mind if you choose to use thematic analysis for your project and budget extra time for unexpected adjustments.

QDA Method #5: Grounded theory (GT)
Grounded theory is a powerful qualitative analysis method where the intention is to create a new theory (or theories) using the data at hand, through a series of “ tests ” and “ revisions ”. Strictly speaking, GT is more a research design type than an analysis method, but we’ve included it here as it’s often referred to as a method.
What’s most important with grounded theory is that you go into the analysis with an open mind and let the data speak for itself – rather than dragging existing hypotheses or theories into your analysis. In other words, your analysis must develop from the ground up (hence the name).
Let’s look at an example of GT in action.
Assume you’re interested in developing a theory about what factors influence students to watch a YouTube video about qualitative analysis. Using Grounded theory , you’d start with this general overarching question about the given population (i.e., graduate students). First, you’d approach a small sample – for example, five graduate students in a department at a university. Ideally, this sample would be reasonably representative of the broader population. You’d interview these students to identify what factors lead them to watch the video.
After analysing the interview data, a general pattern could emerge. For example, you might notice that graduate students are more likely to read a post about qualitative methods if they are just starting on their dissertation journey, or if they have an upcoming test about research methods.
From here, you’ll look for another small sample – for example, five more graduate students in a different department – and see whether this pattern holds true for them. If not, you’ll look for commonalities and adapt your theory accordingly. As this process continues, the theory would develop . As we mentioned earlier, what’s important with grounded theory is that the theory develops from the data – not from some preconceived idea.
So, what are the drawbacks of grounded theory? Well, some argue that there’s a tricky circularity to grounded theory. For it to work, in principle, you should know as little as possible regarding the research question and population, so that you reduce the bias in your interpretation. However, in many circumstances, it’s also thought to be unwise to approach a research question without knowledge of the current literature . In other words, it’s a bit of a “chicken or the egg” situation.
Regardless, grounded theory remains a popular (and powerful) option. Naturally, it’s a very useful method when you’re researching a topic that is completely new or has very little existing research about it, as it allows you to start from scratch and work your way from the ground up .

QDA Method #6: Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA)
Interpretive. Phenomenological. Analysis. IPA . Try saying that three times fast…
Let’s just stick with IPA, okay?
IPA is designed to help you understand the personal experiences of a subject (for example, a person or group of people) concerning a major life event, an experience or a situation . This event or experience is the “phenomenon” that makes up the “P” in IPA. Such phenomena may range from relatively common events – such as motherhood, or being involved in a car accident – to those which are extremely rare – for example, someone’s personal experience in a refugee camp. So, IPA is a great choice if your research involves analysing people’s personal experiences of something that happened to them.
It’s important to remember that IPA is subject – centred . In other words, it’s focused on the experiencer . This means that, while you’ll likely use a coding system to identify commonalities, it’s important not to lose the depth of experience or meaning by trying to reduce everything to codes. Also, keep in mind that since your sample size will generally be very small with IPA, you often won’t be able to draw broad conclusions about the generalisability of your findings. But that’s okay as long as it aligns with your research aims and objectives.
Another thing to be aware of with IPA is personal bias . While researcher bias can creep into all forms of research, self-awareness is critically important with IPA, as it can have a major impact on the results. For example, a researcher who was a victim of a crime himself could insert his own feelings of frustration and anger into the way he interprets the experience of someone who was kidnapped. So, if you’re going to undertake IPA, you need to be very self-aware or you could muddy the analysis.

How to choose the right analysis method
In light of all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve covered so far, you’re probably asking yourself the question, “ How do I choose the right one? ”
Much like all the other methodological decisions you’ll need to make, selecting the right qualitative analysis method largely depends on your research aims, objectives and questions . In other words, the best tool for the job depends on what you’re trying to build. For example:
- Perhaps your research aims to analyse the use of words and what they reveal about the intention of the storyteller and the cultural context of the time.
- Perhaps your research aims to develop an understanding of the unique personal experiences of people that have experienced a certain event, or
- Perhaps your research aims to develop insight regarding the influence of a certain culture on its members.
As you can probably see, each of these research aims are distinctly different , and therefore different analysis methods would be suitable for each one. For example, narrative analysis would likely be a good option for the first aim, while grounded theory wouldn’t be as relevant.
It’s also important to remember that each method has its own set of strengths, weaknesses and general limitations. No single analysis method is perfect . So, depending on the nature of your research, it may make sense to adopt more than one method (this is called triangulation ). Keep in mind though that this will of course be quite time-consuming.
As we’ve seen, all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve discussed make use of coding and theme-generating techniques, but the intent and approach of each analysis method differ quite substantially. So, it’s very important to come into your research with a clear intention before you decide which analysis method (or methods) to use.
Start by reviewing your research aims , objectives and research questions to assess what exactly you’re trying to find out – then select a qualitative analysis method that fits. Never pick a method just because you like it or have experience using it – your analysis method (or methods) must align with your broader research aims and objectives.

Let’s recap on QDA methods…
In this post, we looked at six popular qualitative data analysis methods:
- First, we looked at content analysis , a straightforward method that blends a little bit of quant into a primarily qualitative analysis.
- Then we looked at narrative analysis , which is about analysing how stories are told.
- Next up was discourse analysis – which is about analysing conversations and interactions.
- Then we moved on to thematic analysis – which is about identifying themes and patterns.
- From there, we went south with grounded theory – which is about starting from scratch with a specific question and using the data alone to build a theory in response to that question.
- And finally, we looked at IPA – which is about understanding people’s unique experiences of a phenomenon.
Of course, these aren’t the only options when it comes to qualitative data analysis, but they’re a great starting point if you’re dipping your toes into qualitative research for the first time.
If you’re still feeling a bit confused, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process to help you develop your best work.

Learn More About Qualitative:

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.
Structured, Semi-Structured & Unstructured Interviews
Learn about the differences (and similarities) between the three interview approaches: structured, semi-structured and unstructured.

Qualitative Coding Examples: Process, Values & In Vivo Coding
See real-world examples of qualitative data that has been coded using process coding, values coding and in vivo coding.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.

Process Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about process coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies exploring processes, actions and changes over time.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
88 Comments
This has been very helpful. Thank you.
Thank you madam,
Thank you so much for this information
I wonder it so clear for understand and good for me. can I ask additional query?
Very insightful and useful
Good work done with clear explanations. Thank you.
Thanks so much for the write-up, it’s really good.
Thanks madam . It is very important .
thank you very good
Great presentation
very informative. Thank you!!
This has been very well explained in simple language . It is useful even for a new researcher.
Great to hear that. Good luck with your qualitative data analysis, Pramod!
This is very useful information. And it was very a clear language structured presentation. Thanks a lot.
Thank you so much.
very informative sequential presentation
Precise explanation of method.
Hi, may we use 2 data analysis methods in our qualitative research?
Thanks for your comment. Most commonly, one would use one type of analysis method, but it depends on your research aims and objectives.
You explained it in very simple language, everyone can understand it. Thanks so much.
Thank you very much, this is very helpful. It has been explained in a very simple manner that even a layman understands
Thank nicely explained can I ask is Qualitative content analysis the same as thematic analysis?
Thanks for your comment. No, QCA and thematic are two different types of analysis. This article might help clarify – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nhs.12048
This is my first time to come across a well explained data analysis. so helpful.
I have thoroughly enjoyed your explanation of the six qualitative analysis methods. This is very helpful. Thank you!
Thank you very much, this is well explained and useful
i need a citation of your book.
Thanks a lot , remarkable indeed, enlighting to the best
Hi Derek, What other theories/methods would you recommend when the data is a whole speech?
Keep writing useful artikel.
It is important concept about QDA and also the way to express is easily understandable, so thanks for all.
Thank you, this is well explained and very useful.
Very helpful .Thanks.
Hi there! Very well explained. Simple but very useful style of writing. Please provide the citation of the text. warm regards
The session was very helpful and insightful. Thank you
This was very helpful and insightful. Easy to read and understand
As a professional academic writer, this has been so informative and educative. Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Its Great and help me the most. A Million Thanks you Dr.
It is a very nice work
Very insightful. Please, which of this approach could be used for a research that one is trying to elicit students’ misconceptions in a particular concept ?
This is Amazing and well explained, thanks
great overview
What do we call a research data analysis method that one use to advise or determining the best accounting tool or techniques that should be adopted in a company.
Informative video, explained in a clear and simple way. Kudos
Waoo! I have chosen method wrong for my data analysis. But I can revise my work according to this guide. Thank you so much for this helpful lecture.
This has been very helpful. It gave me a good view of my research objectives and how to choose the best method. Thematic analysis it is.
Very helpful indeed. Thanku so much for the insight.
This was incredibly helpful.
Very helpful.
very educative
Nicely written especially for novice academic researchers like me! Thank you.
choosing a right method for a paper is always a hard job for a student, this is a useful information, but it would be more useful personally for me, if the author provide me with a little bit more information about the data analysis techniques in type of explanatory research. Can we use qualitative content analysis technique for explanatory research ? or what is the suitable data analysis method for explanatory research in social studies?
that was very helpful for me. because these details are so important to my research. thank you very much
I learnt a lot. Thank you
Relevant and Informative, thanks !
Well-planned and organized, thanks much! 🙂
I have reviewed qualitative data analysis in a simplest way possible. The content will highly be useful for developing my book on qualitative data analysis methods. Cheers!
Clear explanation on qualitative and how about Case study
This was helpful. Thank you
This was really of great assistance, it was just the right information needed. Explanation very clear and follow.
Wow, Thanks for making my life easy
This was helpful thanks .
Very helpful…. clear and written in an easily understandable manner. Thank you.
This was so helpful as it was easy to understand. I’m a new to research thank you so much.
so educative…. but Ijust want to know which method is coding of the qualitative or tallying done?
Thank you for the great content, I have learnt a lot. So helpful
precise and clear presentation with simple language and thank you for that.
very informative content, thank you.
You guys are amazing on YouTube on this platform. Your teachings are great, educative, and informative. kudos!
Brilliant Delivery. You made a complex subject seem so easy. Well done.
Beautifully explained.
Thanks a lot
Is there a video the captures the practical process of coding using automated applications?
Thanks for the comment. We don’t recommend using automated applications for coding, as they are not sufficiently accurate in our experience.
content analysis can be qualitative research?
THANK YOU VERY MUCH.
Thank you very much for such a wonderful content
do you have any material on Data collection
What a powerful explanation of the QDA methods. Thank you.
Great explanation both written and Video. i have been using of it on a day to day working of my thesis project in accounting and finance. Thank you very much for your support.
very helpful, thank you so much
The tutorial is useful. I benefited a lot.
This is an eye opener for me and very informative, I have used some of your guidance notes on my Thesis, I wonder if you can assist with your 1. name of your book, year of publication, topic etc., this is for citing in my Bibliography,
I certainly hope to hear from you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Data Analysis in Research: Types & Methods
What is data analysis in research?
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense.
Three essential things occur during the data analysis process — the first is data organization . Summarization and categorization together contribute to becoming the second known method used for data reduction. It helps find patterns and themes in the data for easy identification and linking. The third and last way is data analysis – researchers do it in both top-down and bottom-up fashion.
On the other hand, Marshall and Rossman describe data analysis as a messy, ambiguous, and time-consuming but creative and fascinating process through which a mass of collected data is brought to order, structure and meaning.
We can say that “the data analysis and data interpretation is a process representing the application of deductive and inductive logic to the research and data analysis.”
Why analyze data in research?
Researchers rely heavily on data as they have a story to tell or research problems to solve. It starts with a question, and data is nothing but an answer to that question. But, what if there is no question to ask? Well! It is possible to explore data even without a problem – we call it ‘Data Mining’, which often reveals some interesting patterns within the data that are worth exploring.
Irrelevant to the type of data researchers explore, their mission and audiences’ vision guide them to find the patterns to shape the story they want to tell. One of the essential things expected from researchers while analyzing data is to stay open and remain unbiased toward unexpected patterns, expressions, and results. Remember, sometimes, data analysis tells the most unforeseen yet exciting stories that were not expected when initiating data analysis. Therefore, rely on the data you have at hand and enjoy the journey of exploratory research.
Create a Free Account
Types of data in research
Every kind of data has a rare quality of describing things after assigning a specific value to it. For analysis, you need to organize these values, processed and presented in a given context, to make it useful. Data can be in different forms; here are the primary data types.
- Qualitative data: When the data presented has words and descriptions, then we call it qualitative data . Although you can observe this data, it is subjective and harder to analyze data in research, especially for comparison. Example: Quality data represents everything describing taste, experience, texture, or an opinion that is considered quality data. This type of data is usually collected through focus groups, personal qualitative interviews , qualitative observation or using open-ended questions in surveys.
- Quantitative data: Any data expressed in numbers of numerical figures are called quantitative data . This type of data can be distinguished into categories, grouped, measured, calculated, or ranked. Example: questions such as age, rank, cost, length, weight, scores, etc. everything comes under this type of data. You can present such data in graphical format, charts, or apply statistical analysis methods to this data. The (Outcomes Measurement Systems) OMS questionnaires in surveys are a significant source of collecting numeric data.
- Categorical data : It is data presented in groups. However, an item included in the categorical data cannot belong to more than one group. Example: A person responding to a survey by telling his living style, marital status, smoking habit, or drinking habit comes under the categorical data. A chi-square test is a standard method used to analyze this data.
Learn More : Examples of Qualitative Data in Education
Data analysis in qualitative research
Data analysis and qualitative data research work a little differently from the numerical data as the quality data is made up of words, descriptions, images, objects, and sometimes symbols. Getting insight from such complicated information is a complicated process. Hence it is typically used for exploratory research and data analysis .
Finding patterns in the qualitative data
Although there are several ways to find patterns in the textual information, a word-based method is the most relied and widely used global technique for research and data analysis. Notably, the data analysis process in qualitative research is manual. Here the researchers usually read the available data and find repetitive or commonly used words.
For example, while studying data collected from African countries to understand the most pressing issues people face, researchers might find “food” and “hunger” are the most commonly used words and will highlight them for further analysis.
The keyword context is another widely used word-based technique. In this method, the researcher tries to understand the concept by analyzing the context in which the participants use a particular keyword.
For example , researchers conducting research and data analysis for studying the concept of ‘diabetes’ amongst respondents might analyze the context of when and how the respondent has used or referred to the word ‘diabetes.’
The scrutiny-based technique is also one of the highly recommended text analysis methods used to identify a quality data pattern. Compare and contrast is the widely used method under this technique to differentiate how a specific text is similar or different from each other.
For example: To find out the “importance of resident doctor in a company,” the collected data is divided into people who think it is necessary to hire a resident doctor and those who think it is unnecessary. Compare and contrast is the best method that can be used to analyze the polls having single-answer questions types .
Metaphors can be used to reduce the data pile and find patterns in it so that it becomes easier to connect data with theory.
Variable Partitioning is another technique used to split variables so that researchers can find more coherent descriptions and explanations from the enormous data.
Methods used for data analysis in qualitative research
There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods,
- Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented information from text, images, and sometimes from the physical items. It depends on the research questions to predict when and where to use this method.
- Narrative Analysis: This method is used to analyze content gathered from various sources such as personal interviews, field observation, and surveys . The majority of times, stories, or opinions shared by people are focused on finding answers to the research questions.
- Discourse Analysis: Similar to narrative analysis, discourse analysis is used to analyze the interactions with people. Nevertheless, this particular method considers the social context under which or within which the communication between the researcher and respondent takes place. In addition to that, discourse analysis also focuses on the lifestyle and day-to-day environment while deriving any conclusion.
- Grounded Theory: When you want to explain why a particular phenomenon happened, then using grounded theory for analyzing quality data is the best resort. Grounded theory is applied to study data about the host of similar cases occurring in different settings. When researchers are using this method, they might alter explanations or produce new ones until they arrive at some conclusion.
Choosing the right software can be tough. Whether you’re a researcher, business leader, or marketer, check out the top 10 qualitative data analysis software for analyzing qualitative data.
Data analysis in quantitative research
Preparing data for analysis.
The first stage in research and data analysis is to make it for the analysis so that the nominal data can be converted into something meaningful. Data preparation consists of the below phases.
Phase I: Data Validation
Data validation is done to understand if the collected data sample is per the pre-set standards, or it is a biased data sample again divided into four different stages
- Fraud: To ensure an actual human being records each response to the survey or the questionnaire
- Screening: To make sure each participant or respondent is selected or chosen in compliance with the research criteria
- Procedure: To ensure ethical standards were maintained while collecting the data sample
- Completeness: To ensure that the respondent has answered all the questions in an online survey. Else, the interviewer had asked all the questions devised in the questionnaire.
Phase II: Data Editing
More often, an extensive research data sample comes loaded with errors. Respondents sometimes fill in some fields incorrectly or sometimes skip them accidentally. Data editing is a process wherein the researchers have to confirm that the provided data is free of such errors. They need to conduct necessary checks and outlier checks to edit the raw edit and make it ready for analysis.
Phase III: Data Coding
Out of all three, this is the most critical phase of data preparation associated with grouping and assigning values to the survey responses . If a survey is completed with a 1000 sample size, the researcher will create an age bracket to distinguish the respondents based on their age. Thus, it becomes easier to analyze small data buckets rather than deal with the massive data pile.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
Methods used for data analysis in quantitative research
After the data is prepared for analysis, researchers are open to using different research and data analysis methods to derive meaningful insights. For sure, statistical analysis plans are the most favored to analyze numerical data. In statistical analysis, distinguishing between categorical data and numerical data is essential, as categorical data involves distinct categories or labels, while numerical data consists of measurable quantities. The method is again classified into two groups. First, ‘Descriptive Statistics’ used to describe data. Second, ‘Inferential statistics’ that helps in comparing the data .

Descriptive statistics
This method is used to describe the basic features of versatile types of data in research. It presents the data in such a meaningful way that pattern in the data starts making sense. Nevertheless, the descriptive analysis does not go beyond making conclusions. The conclusions are again based on the hypothesis researchers have formulated so far. Here are a few major types of descriptive analysis methods.
Measures of Frequency
- Count, Percent, Frequency
- It is used to denote home often a particular event occurs.
- Researchers use it when they want to showcase how often a response is given.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean, Median, Mode
- The method is widely used to demonstrate distribution by various points.
- Researchers use this method when they want to showcase the most commonly or averagely indicated response.
Measures of Dispersion or Variation
- Range, Variance, Standard deviation
- Here the field equals high/low points.
- Variance standard deviation = difference between the observed score and mean
- It is used to identify the spread of scores by stating intervals.
- Researchers use this method to showcase data spread out. It helps them identify the depth until which the data is spread out that it directly affects the mean.
Measures of Position
- Percentile ranks, Quartile ranks
- It relies on standardized scores helping researchers to identify the relationship between different scores.
- It is often used when researchers want to compare scores with the average count.
For quantitative research use of descriptive analysis often give absolute numbers, but the in-depth analysis is never sufficient to demonstrate the rationale behind those numbers. Nevertheless, it is necessary to think of the best method for research and data analysis suiting your survey questionnaire and what story researchers want to tell. For example, the mean is the best way to demonstrate the students’ average scores in schools. It is better to rely on the descriptive statistics when the researchers intend to keep the research or outcome limited to the provided sample without generalizing it. For example, when you want to compare average voting done in two different cities, differential statistics are enough.
Descriptive analysis is also called a ‘univariate analysis’ since it is commonly used to analyze a single variable.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about a larger population after research and data analysis of the representing population’s collected sample. For example, you can ask some odd 100 audiences at a movie theater if they like the movie they are watching. Researchers then use inferential statistics on the collected sample to reason that about 80-90% of people like the movie.
Here are two significant areas of inferential statistics.
- Estimating parameters: It takes statistics from the sample research data and demonstrates something about the population parameter.
- Hypothesis test: I t’s about sampling research data to answer the survey research questions. For example, researchers might be interested to understand if the new shade of lipstick recently launched is good or not, or if the multivitamin capsules help children to perform better at games.
These are sophisticated analysis methods used to showcase the relationship between different variables instead of describing a single variable. It is often used when researchers want something beyond absolute numbers to understand the relationship between variables.
Here are some of the commonly used methods for data analysis in research.
- Correlation: When researchers are not conducting experimental research or quasi-experimental research wherein the researchers are interested to understand the relationship between two or more variables, they opt for correlational research methods.
- Cross-tabulation: Also called contingency tables, cross-tabulation is used to analyze the relationship between multiple variables. Suppose provided data has age and gender categories presented in rows and columns. A two-dimensional cross-tabulation helps for seamless data analysis and research by showing the number of males and females in each age category.
- Regression analysis: For understanding the strong relationship between two variables, researchers do not look beyond the primary and commonly used regression analysis method, which is also a type of predictive analysis used. In this method, you have an essential factor called the dependent variable. You also have multiple independent variables in regression analysis. You undertake efforts to find out the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable. The values of both independent and dependent variables are assumed as being ascertained in an error-free random manner.
- Frequency tables: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Analysis of variance: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
Considerations in research data analysis
- Researchers must have the necessary research skills to analyze and manipulation the data , Getting trained to demonstrate a high standard of research practice. Ideally, researchers must possess more than a basic understanding of the rationale of selecting one statistical method over the other to obtain better data insights.
- Usually, research and data analytics projects differ by scientific discipline; therefore, getting statistical advice at the beginning of analysis helps design a survey questionnaire, select data collection methods , and choose samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- The primary aim of data research and analysis is to derive ultimate insights that are unbiased. Any mistake in or keeping a biased mind to collect data, selecting an analysis method, or choosing audience sample il to draw a biased inference.
- Irrelevant to the sophistication used in research data and analysis is enough to rectify the poorly defined objective outcome measurements. It does not matter if the design is at fault or intentions are not clear, but lack of clarity might mislead readers, so avoid the practice.
- The motive behind data analysis in research is to present accurate and reliable data. As far as possible, avoid statistical errors, and find a way to deal with everyday challenges like outliers, missing data, data altering, data mining , or developing graphical representation.
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research The sheer amount of data generated daily is frightening. Especially when data analysis has taken center stage. in 2018. In last year, the total data supply amounted to 2.8 trillion gigabytes. Hence, it is clear that the enterprises willing to survive in the hypercompetitive world must possess an excellent capability to analyze complex research data, derive actionable insights, and adapt to the new market needs.
LEARN ABOUT: Average Order Value
QuestionPro is an online survey platform that empowers organizations in data analysis and research and provides them a medium to collect data by creating appealing surveys.
MORE LIKE THIS

Qualtrics Employee Experience Alternatives: The 6 Best in 2024
Nov 19, 2024

Reputation Management: How to Protect Your Brand Reputation?

Reference Bias: Identifying and Reducing in Surveys and Research

Maximize Employee Feedback with QuestionPro Workforce’s Slack Integration
Nov 6, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Why might you need to analyze research? First of all, when you analyze a research article, you begin to understand your assigned reading better. It is also the first step toward learning how to write your own research articles and literature reviews. However, if you have never written a research paper before, it may be difficult for you to analyze one. After all, you may not know what criteria to use to evaluate it. But don’t panic! We will help you figure it out!
In this article, our team has explained how to analyze research papers quickly and effectively. At the end, you will also find a research analysis paper example to see how everything works in practice.
- 🔤 Research Analysis Definition
📊 How to Analyze a Research Article
✍️ how to write a research analysis.
- 📝 Analysis Example
- 🔎 More Examples
🔗 References
🔤 research paper analysis: what is it.
A research paper analysis is an academic writing assignment in which you analyze a scholarly article’s methodology, data, and findings. In essence, “to analyze” means to break something down into components and assess each of them individually and in relation to each other. The goal of an analysis is to gain a deeper understanding of a subject. So, when you analyze a research article, you dissect it into elements like data sources , research methods, and results and evaluate how they contribute to the study’s strengths and weaknesses.
📋 Research Analysis Format
A research analysis paper has a pretty straightforward structure. Check it out below!
Research articles usually include the following sections: introduction, methods, results, and discussion. In the following paragraphs, we will discuss how to analyze a scientific article with a focus on each of its parts.

How to Analyze a Research Paper: Purpose
The purpose of the study is usually outlined in the introductory section of the article. Analyzing the research paper’s objectives is critical to establish the context for the rest of your analysis.
When analyzing the research aim, you should evaluate whether it was justified for the researchers to conduct the study. In other words, you should assess whether their research question was significant and whether it arose from existing literature on the topic.
Here are some questions that may help you analyze a research paper’s purpose:
- Why was the research carried out?
- What gaps does it try to fill, or what controversies to settle?
- How does the study contribute to its field?
- Do you agree with the author’s justification for approaching this particular question in this way?
How to Analyze a Paper: Methods
When analyzing the methodology section , you should indicate the study’s research design (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed) and methods used (for example, experiment, case study, correlational research, survey, etc.). After that, you should assess whether these methods suit the research purpose. In other words, do the chosen methods allow scholars to answer their research questions within the scope of their study?
For example, if scholars wanted to study US students’ average satisfaction with their higher education experience, they could conduct a quantitative survey . However, if they wanted to gain an in-depth understanding of the factors influencing US students’ satisfaction with higher education, qualitative interviews would be more appropriate.
When analyzing methods, you should also look at the research sample . Did the scholars use randomization to select study participants? Was the sample big enough for the results to be generalizable to a larger population?
You can also answer the following questions in your methodology analysis:
- Is the methodology valid? In other words, did the researchers use methods that accurately measure the variables of interest?
- Is the research methodology reliable? A research method is reliable if it can produce stable and consistent results under the same circumstances.
- Is the study biased in any way?
- What are the limitations of the chosen methodology?
How to Analyze Research Articles’ Results
You should start the analysis of the article results by carefully reading the tables, figures, and text. Check whether the findings correspond to the initial research purpose. See whether the results answered the author’s research questions or supported the hypotheses stated in the introduction.
To analyze the results section effectively, answer the following questions:
- What are the major findings of the study?
- Did the author present the results clearly and unambiguously?
- Are the findings statistically significant ?
- Does the author provide sufficient information on the validity and reliability of the results?
- Have you noticed any trends or patterns in the data that the author did not mention?
How to Analyze Research: Discussion
Finally, you should analyze the authors’ interpretation of results and its connection with research objectives. Examine what conclusions the authors drew from their study and whether these conclusions answer the original question.
You should also pay attention to how the authors used findings to support their conclusions. For example, you can reflect on why their findings support that particular inference and not another one. Moreover, more than one conclusion can sometimes be made based on the same set of results. If that’s the case with your article, you should analyze whether the authors addressed other interpretations of their findings .
Here are some useful questions you can use to analyze the discussion section:
- What findings did the authors use to support their conclusions?
- How do the researchers’ conclusions compare to other studies’ findings?
- How does this study contribute to its field?
- What future research directions do the authors suggest?
- What additional insights can you share regarding this article? For example, do you agree with the results? What other questions could the researchers have answered?

Now, you know how to analyze an article that presents research findings. However, it’s just a part of the work you have to do to complete your paper. So, it’s time to learn how to write research analysis! Check out the steps below!
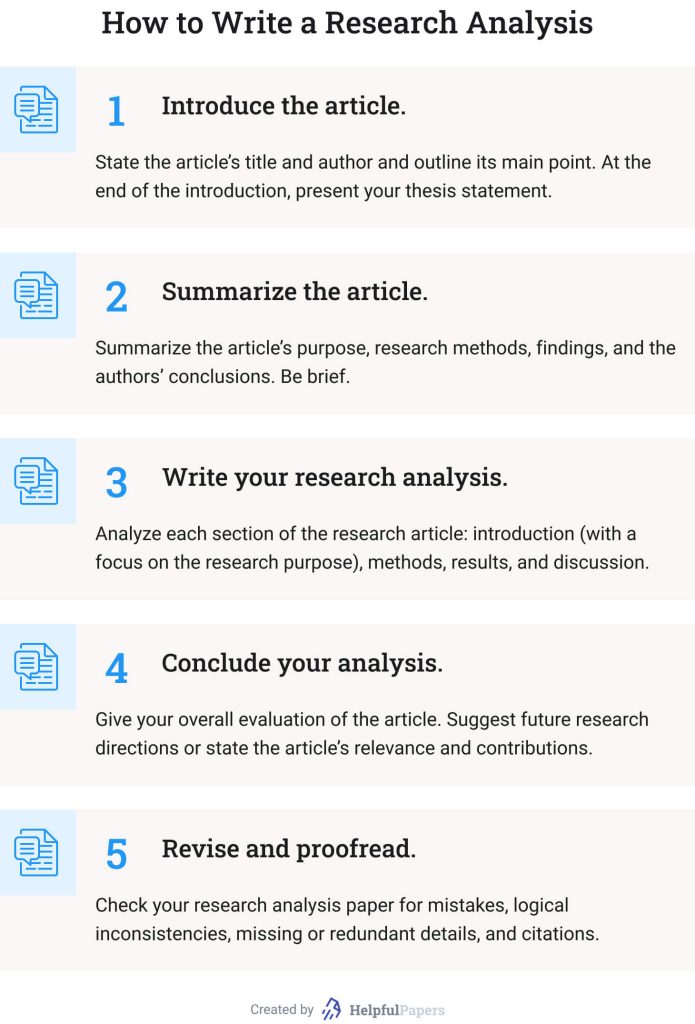
1. Introduce the Article
As with most academic assignments, you should start your research article analysis with an introduction. Here’s what it should include:
- The article’s publication details . Specify the title of the scholarly work you are analyzing, its authors, and publication date. Remember to enclose the article’s title in quotation marks and write it in title case .
- The article’s main point . State what the paper is about. What did the authors study, and what was their major finding?
- Your thesis statement . End your introduction with a strong claim summarizing your evaluation of the article. Consider briefly outlining the research paper’s strengths, weaknesses, and significance in your thesis.
Keep your introduction brief. Save the word count for the “meat” of your paper — that is, for the analysis.
2. Summarize the Article
Now, you should write a brief and focused summary of the scientific article. It should be shorter than your analysis section and contain all the relevant details about the research paper.
Here’s what you should include in your summary:
- The research purpose . Briefly explain why the research was done. Identify the authors’ purpose and research questions or hypotheses .
- Methods and results . Summarize what happened in the study. State only facts, without the authors’ interpretations of them. Avoid using too many numbers and details; instead, include only the information that will help readers understand what happened.
- The authors’ conclusions . Outline what conclusions the researchers made from their study. In other words, describe how the authors explained the meaning of their findings.
If you need help summarizing an article, you can use our free summary generator .
3. Write Your Research Analysis
The analysis of the study is the most crucial part of this assignment type. Its key goal is to evaluate the article critically and demonstrate your understanding of it.
We’ve already covered how to analyze a research article in the section above. Here’s a quick recap:
- Analyze whether the study’s purpose is significant and relevant.
- Examine whether the chosen methodology allows for answering the research questions.
- Evaluate how the authors presented the results.
- Assess whether the authors’ conclusions are grounded in findings and answer the original research questions.
Although you should analyze the article critically, it doesn’t mean you only should criticize it. If the authors did a good job designing and conducting their study, be sure to explain why you think their work is well done. Also, it is a great idea to provide examples from the article to support your analysis.
4. Conclude Your Analysis of Research Paper
A conclusion is your chance to reflect on the study’s relevance and importance. Explain how the analyzed paper can contribute to the existing knowledge or lead to future research. Also, you need to summarize your thoughts on the article as a whole. Avoid making value judgments — saying that the paper is “good” or “bad.” Instead, use more descriptive words and phrases such as “This paper effectively showed…”
Need help writing a compelling conclusion? Try our free essay conclusion generator !
5. Revise and Proofread
Last but not least, you should carefully proofread your paper to find any punctuation, grammar, and spelling mistakes. Start by reading your work out loud to ensure that your sentences fit together and sound cohesive. Also, it can be helpful to ask your professor or peer to read your work and highlight possible weaknesses or typos.
📝 Research Paper Analysis Example
We have prepared an analysis of a research paper example to show how everything works in practice.
No Homework Policy: Research Article Analysis Example
This paper aims to analyze the research article entitled “No Assignment: A Boon or a Bane?” by Cordova, Pagtulon-an, and Tan (2019). This study examined the effects of having and not having assignments on weekends on high school students’ performance and transmuted mean scores. This article effectively shows the value of homework for students, but larger studies are needed to support its findings.
Cordova et al. (2019) conducted a descriptive quantitative study using a sample of 115 Grade 11 students of the Central Mindanao University Laboratory High School in the Philippines. The sample was divided into two groups: the first received homework on weekends, while the second didn’t. The researchers compared students’ performance records made by teachers and found that students who received assignments performed better than their counterparts without homework.
The purpose of this study is highly relevant and justified as this research was conducted in response to the debates about the “No Homework Policy” in the Philippines. Although the descriptive research design used by the authors allows to answer the research question, the study could benefit from an experimental design. This way, the authors would have firm control over variables. Additionally, the study’s sample size was not large enough for the findings to be generalized to a larger population.
The study results are presented clearly, logically, and comprehensively and correspond to the research objectives. The researchers found that students’ mean grades decreased in the group without homework and increased in the group with homework. Based on these findings, the authors concluded that homework positively affected students’ performance. This conclusion is logical and grounded in data.
This research effectively showed the importance of homework for students’ performance. Yet, since the sample size was relatively small, larger studies are needed to ensure the authors’ conclusions can be generalized to a larger population.
🔎 More Research Analysis Paper Examples
Do you want another research analysis example? Check out the best analysis research paper samples below:
- Nursing Practice Issue: Qualitative Research Article Analysis
- Quantitative Article Critique in Nursing
- Evidence-Based Practice Beliefs and Implementation: Article Critique
- “Differential Effectiveness of Placebo Treatments”: Research Paper Analysis
- “Family-Based Childhood Obesity Prevention Interventions”: Analysis Research Paper Example
- Space and the Atom: Article Analysis
- China’s Hegemonic Prospects: Article Review
- Article Analysis: Fear of Missing Out
- Codependence, Narcissism, and Childhood Trauma: Analysis of the Article
- Relationship Between Work Intensity, Workaholism, Burnout, and MSC: Article Review
We hope that our article on research paper analysis has been helpful. If you liked it, please share this article with your friends!
- Analyzing Research Articles: A Guide for Readers and Writers | Sam Mathews
- Summary and Analysis of Scientific Research Articles | San José State University Writing Center
- Analyzing Scholarly Articles | Texas A&M University
- Article Analysis Assignment | University of Wisconsin-Madison
- How to Summarize a Research Article | University of Connecticut
- Critique/Review of Research Articles | University of Calgary
- Art of Reading a Journal Article: Methodically and Effectively | PubMed Central
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article | McLaughlin Library
- How to Read and Understand a Scientific Paper: A Guide for Non-scientists | LSE
- How to Analyze Journal Articles | Classroom
How to Write an Animal Testing Essay: Tips for Argumentative & Persuasive Papers
Descriptive essay topics: examples, outline, & more.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Analysis is a type of primary research that involves finding and interpreting patterns in data, classifying those patterns, and generalizing the results. It is useful when looking at actions, events, or occurrences in different texts, media, or publications. Analysis can usually be done without considering most of the ethical issues discussed in the overview, as you are not working with people but rather publicly accessible documents. Analysis can be done on new documents or performed on raw data that you yourself have collected.
Here are several examples of analysis:
- Recording commercials on three major television networks and analyzing race and gender within the commercials to discover some conclusion.
- Analyzing the historical trends in public laws by looking at the records at a local courthouse.
- Analyzing topics of discussion in chat rooms for patterns based on gender and age.
Analysis research involves several steps:
- Finding and collecting documents.
- Specifying criteria or patterns that you are looking for.
- Analyzing documents for patterns, noting number of occurrences or other factors.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary and Analysis of Scientific Research Articles, Spring 2020. 1 of 5 Summary and Analysis of Scientific Research Articles Being able to summarize and analyze a research article is important not only for showing your professor that you have understood your assigned reading, but it also is the first step to learning
For example, a marketing analysis examines buying patterns, market size, demographics and other variables to develop a targeted marketing plan. Related: How Analyzing Data Can Improve Decision-Making How to write an analysis Writing an analysis requires a particular structure and key components to create a compelling argument.
Learn how to plan, collect, and analyze quantitative data for research using five steps and two examples. Find out how to write hypotheses, choose a research design, measure variables, and interpret results.
Learn how to choose and use research methods for collecting and analyzing data. Find out the pros and cons of different methods, such as qualitative vs. quantitative, primary vs. secondary, descriptive vs. experimental, and more.
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis. Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
Methods used for data analysis in qualitative research. There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods, Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented ...
Content Analysis | Guide, Methods & Examples. Published on July 18, 2019 by Amy Luo.Revised on June 22, 2023. Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: ...
🔤 Research Paper Analysis: What Is It? We'll deliver a custom paper tailored to your requirements. We'll even cut 15% OFF your first order! Use discount. A research paper analysis is an academic writing assignment in which you analyze a scholarly article's methodology, data, and findings. In essence, "to analyze" means to break something down into components and assess each of them ...
Analysis is a type of primary research that involves finding and interpreting patterns in data, classifying those patterns, and generalizing the results. It is useful when looking at actions, events, or occurrences in different texts, media, or publications. ... Here are several examples of analysis:
University and research level data analysis . ... The researcher used the Yamane (1967) formula to determine the sample size of 225 teenagers. Data was collected using a questionnaire. Data was ...