The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Nonprofit Business Plan
A business plan can be an invaluable tool for your nonprofit. Even a short business plan pushes you to do research, crystalize your purpose, and polish your messaging. This blog shares what it is and why you need it, ten steps to help you write one, and the dos and don’ts of creating a nonprofit business plan.
Nonprofit business plans are dead — or are they?
For many nonprofit organizations, business plans represent outdated and cumbersome documents that get created “just for the sake of it” or because donors demand it.
But these plans are vital to organizing your nonprofit and making your dreams a reality! Furthermore, without a nonprofit business plan, you’ll have a harder time obtaining loans and grants , attracting corporate donors, meeting qualified board members, and keeping your nonprofit on track.
Even excellent ideas can be totally useless if you cannot formulate, execute, and implement a strategic plan to make your idea work. In this article, we share exactly what your plan needs and provide a nonprofit business plan template to help you create one of your own.

What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan describes your nonprofit as it currently is and sets up a roadmap for the next three to five years. It also lays out your goals and plans for meeting your goals. Your nonprofit business plan is a living document that should be updated frequently to reflect your evolving goals and circumstances.
A business plan is the foundation of your organization — the who, what, when, where, and how you’re going to make a positive impact.
The best nonprofit business plans aren’t unnecessarily long. They include only as much information as necessary. They may be as short as seven pages long, one for each of the essential sections you will read about below and see in our template, or up to 30 pages long if your organization grows.
Why do we need a Nonprofit Business Plan?
Regardless of whether your nonprofit is small and barely making it or if your nonprofit has been successfully running for years, you need a nonprofit business plan. Why?
When you create a nonprofit business plan, you are effectively creating a blueprint for how your nonprofit will be run, who will be responsible for what, and how you plan to achieve your goals.
Your nonprofit organization also needs a business plan if you plan to secure support of any kind, be it monetary, in-kind , or even just support from volunteers. You need a business plan to convey your nonprofit’s purpose and goals.
It sometimes also happens that the board, or the administration under which a nonprofit operates, requires a nonprofit business plan.
To sum it all up, write a nonprofit business plan to:
- Layout your goals and establish milestones.
- Better understand your beneficiaries, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Assess the feasibility of your nonprofit and document your fundraising/financing model.
- Attract investment and prove that you’re serious about your nonprofit.
- Attract a board and volunteers.
- Position your nonprofit and get clear about your message.
- Force you to research and uncover new opportunities.
- Iron out all the kinks in your plan and hold yourself accountable.
Before starting your nonprofit business plan, it is important to consider the following:
- Who is your audience? E.g. If you are interested in fundraising, donors will be your audience. If you are interested in partnerships, potential partners will be your audience.
- What do you want their response to be? Depending on your target audience, you should focus on the key message you want them to receive to get the response that you want.
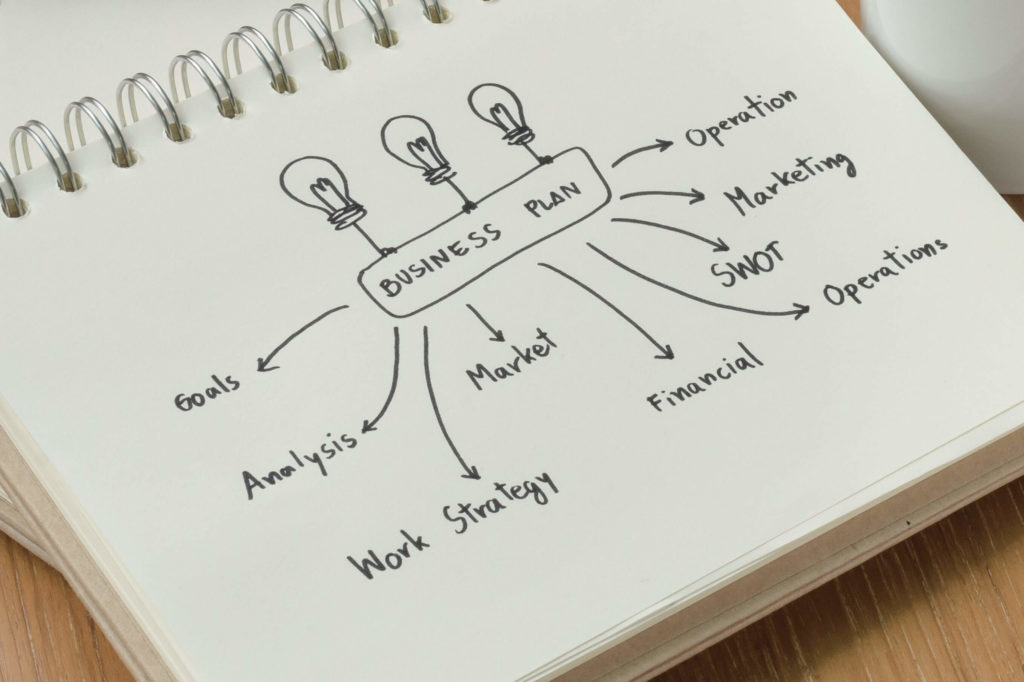
10-Step Guide on Writing a Business Plan for Nonprofits
Note: Steps 1, 2, and 3 are in preparation for writing your nonprofit business plan.
Step 1: Data Collection
Before even getting started with the writing, collect financial, operating, and other relevant data. If your nonprofit is already in operation, this should at the very least include financial statements detailing operating expense reports and a spreadsheet that indicates funding sources.
If your nonprofit is new, compile materials related to any secured funding sources and operational funding projections, including anticipated costs.
Step 2: Heart of the Matter
You are a nonprofit after all! Your nonprofit business plan should start with an articulation of the core values and your mission statement . Outline your vision, your guiding philosophy, and any other principles that provide the purpose behind the work. This will help you to refine and communicate your nonprofit message clearly.
Your nonprofit mission statement can also help establish your milestones, the problems your organization seeks to solve, who your organization serves, and its future goals.
Check out these great mission statement examples for some inspiration. For help writing your statement, download our free Mission & Vision Statements Worksheet .
Step 3: Outline
Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets).
An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end. Outlining actually helps us write more quickly and more effectively.
An outline will help you understand what you need to tell your audience, whether it’s in the right order, and whether the right amount of emphasis is placed on each topic.
Pro tip: Use our Nonprofit Business Plan Outline to help with this step! More on that later.
Step 4: Products, Programs, and Services
In this section, provide more information on exactly what your nonprofit organization does.
- What products, programs, or services do you provide?
- How does your nonprofit benefit the community?
- What need does your nonprofit meet and what are your plans for meeting that need?
E.g. The American Red Cross carries out its mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.
Don’t skimp out on program details, including the functions and beneficiaries. This is generally what most readers will care most about.
However, don’t overload the reader with technical jargon. Try to present some clear examples. Include photographs, brochures, and other promotional materials.
Step 5: Marketing Plan
A marketing plan is essential for a nonprofit to reach its goals. If your nonprofit is already in operation, describe in detail all current marketing activities: any outreach activities, campaigns, and other initiatives. Be specific about outcomes, activities, and costs.
If your nonprofit is new, outline projections based on specific data you gathered about your market.
This will frequently be your most detailed section because it spells out precisely how you intend to carry out your business plan.
- Describe your market. This includes your target audience, competitors, beneficiaries, donors, and potential partners.
- Include any market analyses and tests you’ve done.
- Outline your plan for reaching your beneficiaries.
- Outline your marketing activities, highlighting specific outcomes.
Step 6: Operational Plan
An operational plan describes how your nonprofit plans to deliver activities. In the operational plan, it is important to explain how you plan to maintain your operations and how you will evaluate the impact of your programs.
The operational plan should give an overview of the day-to-day operations of your organization such as the people and organizations you work with (e.g. partners and suppliers), any legal requirements that your organization needs to meet (e.g. if you distribute food, you’ll need appropriate licenses and certifications), any insurance you have or will need, etc.
In the operational plan, also include a section on the people or your team. Describe the people who are crucial to your organization and any staff changes you plan as part of your business plan.
Pro tip: If you have an organizational chart, you can include it in the appendix to help illustrate how your organization operates. Learn more about the six types of nonprofit organizational charts and see them in action in this free e-book .
Step 7: Impact Plan
For a nonprofit, an impact plan is as important as a financial plan. A nonprofit seeks to create social change and a social return on investment, not just a financial return on investment.
Your impact plan should be precise about how your nonprofit will achieve this step. It should include details on what change you’re seeking to make, how you’re going to make it, and how you’re going to measure it.
This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives.
These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.
Answer these in the impact plan section of your business plan:
- What goals are most meaningful to the people you serve or the cause you’re fighting for?
- How can you best achieve those goals through a series of specific objectives?
E.g. “Finding jobs for an additional 200 unemployed people in the coming year.”
Step 8: Financial Plan
This is one of the most important parts of your nonprofit business plan. Creating a financial plan will allow you to make sure that your nonprofit has its basic financial needs covered.
Every nonprofit needs a certain level of funding to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will meet at least that threshold.
To craft your financial plan:
- Outline your nonprofit’s current and projected financial status.
- Include an income statement, balance sheet , cash flow statement, and financial projections.
- List any grants you’ve received, significant contributions, and in-kind support.
- Include your fundraising plan .
- Identify gaps in your funding, and how you will manage them.
- Plan for what will be done with a potential surplus.
- Include startup costs, if necessary.
If your nonprofit is already operational, use established accounting records to complete this section of the business plan.
Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public demands transparency about where their donations are going.
Pro tip : Leverage startup accelerators dedicated to nonprofits that can help you with funding, sponsorship, networking, and much more.
Step 9: Executive Summary
Normally written last but placed first in your business plan, your nonprofit executive summary provides an introduction to your entire business plan. The first page should describe your non-profit’s mission and purpose, summarize your market analysis that proves an identifiable need, and explain how your non-profit will meet that need.
The Executive Summary is where you sell your nonprofit and its ideas. Here you need to describe your organization clearly and concisely.
Make sure to customize your executive summary depending on your audience (i.e. your executive summary page will look different if your main goal is to win a grant or hire a board member).
Step 10: Appendix
Include extra documents in the section that are pertinent to your nonprofit: organizational chart , current fiscal year budget, a list of the board of directors, your IRS status letter, balance sheets, and so forth.
The appendix contains helpful additional information that might not be suitable for the format of your business plan (i.e. it might unnecessarily make it less readable or more lengthy).

Do’s and Dont’s of Nonprofit Business Plans – Tips
- Write clearly, using simple and easy-to-understand language.
- Get to the point, support it with facts, and then move on.
- Include relevant graphs and program descriptions.
- Include an executive summary.
- Provide sufficient financial information.
- Customize your business plan to different audiences.
- Stay authentic and show enthusiasm.
- Make the business plan too long.
- Use too much technical jargon.
- Overload the plan with text.
- Rush the process of writing, but don’t drag it either.
- Gush about the cause without providing a clear understanding of how you will help the cause through your activities.
- Keep your formatting consistent.
- Use standard 1-inch margins.
- Use a reasonable font size for the body.
- For print, use a serif font like Times New Roman or Courier. For digital, use sans serifs like Verdana or Arial.
- Start a new page before each section.
- Don’t allow your plan to print and leave a single line on an otherwise blank page.
- Have several people read over the plan before it is printed to make sure it’s free of errors.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
To help you get started we’ve created a nonprofit business plan outline. This business plan outline will work as a framework regardless of your nonprofit’s area of focus. With it, you’ll have a better idea of how to lay out your nonprofit business plan and what to include. We have also provided several questions and examples to help you create a detailed nonprofit business plan.
Download Your Free Outline

At Donorbox, we strive to make your nonprofit experience as productive as possible, whether through our donation software or through our advice and guides on the Nonprofit Blog . Find more free, downloadable resources in our Library .
Many nonprofits start with passion and enthusiasm but without a proper business plan. It’s a common misconception that just because an organization is labeled a “nonprofit,” it does not need to operate in any way like a business.
However, a nonprofit is a type of business, and many of the same rules that apply to a for-profit company also apply to a nonprofit organization.
As outlined above, your nonprofit business plan is a combination of your marketing plan , strategic plan, operational plan, impact plan, and financial plan. Remember, you don’t have to work from scratch. Be sure to use the nonprofit business plan outline we’ve provided to help create one of your own.
It’s important to note that your nonprofit should not be set in stone—it can and should change and evolve. It’s a living organism. While your vision, values, and mission will likely remain the same, your nonprofit business plan may need to be revised from time to time. Keep your audience in mind and adjust your plan as needed.
Finally, don’t let your plan gather dust on a shelf! Print it out, put up posters on your office walls, and read from it during your team meetings. Use all the research, data, and ideas you’ve gathered and put them into action!
If you want more help with nonprofit management tips and fundraising resources, visit our Nonprofit Blog . We also have dedicated articles for starting a nonprofit in different states in the U.S., including Texas , Minnesota , Oregon , Arizona , Illinois , and more.
Learn about our all-in-one online fundraising tool, Donorbox, and its simple-to-use features on the website here .

Raviraj heads the sales and marketing team at Donorbox. His growth-hacking abilities have helped Donorbox boost fundraising efforts for thousands of nonprofit organizations.
Join the fundraising movement!
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to receive the latest blogs, news, and more in your inbox.

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan ensures your organization’s fundraising and activities align with your core mission.

Every nonprofit needs a mission statement that demonstrates how the organization will support a social cause and provide a public benefit. A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your organization off the ground successfully.
Start with your mission statement
The mission statement is foundational for your nonprofit organization. The IRS will review your mission statement in determining whether to grant you tax-exempt status. This statement also helps you recruit volunteers and staff, fundraise, and plan activities for the year.
[Read more: Writing a Mission Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide ]
Therefore, you should start your business plan with a clear mission statement in the executive summary. The executive summary can also cover, at a high level, the goals, vision, and unique strengths of your nonprofit organization. Keep this section brief, since you will be going into greater detail in later sections.
Identify a board of directors
Many business plans include a section identifying the people behind the operation: your key leaders, volunteers, and full-time employees. For nonprofits, it’s also important to identify your board of directors. The board of directors is ultimately responsible for hiring and managing the CEO of your nonprofit.
“Board members are the fiduciaries who steer the organization towards a sustainable future by adopting sound, ethical, and legal governance and financial management policies, as well as by making sure the nonprofit has adequate resources to advance its mission,” wrote the Council of Nonprofits.
As such, identify members of your board in your business plan to give potential donors confidence in the management of your nonprofit.
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain.
Describe your organization’s activities
In this section, provide more information about what your nonprofit does on a day-to-day basis. What products, training, education, or other services do you provide? What does your organization do to benefit the constituents identified in your mission statement? Here’s an example from the American Red Cross, courtesy of DonorBox :
“The American Red Cross carries out their mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.”
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Write a fundraising plan
This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind support. If you are planning to host a fundraising event, put together a budget for that event and demonstrate the anticipated impact that event will have on your budget.
Create an impact plan
An impact plan ties everything together. It demonstrates how your fundraising and day-to-day activities will further your mission. For potential donors, it can make a very convincing case for why they should invest in your nonprofit.
“This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives,” wrote DonorBox . “These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.”
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain. Revisit your business plan as your organization grows to make sure the goals you’ve set both align with your mission and continue to be within reach.
[Read more: 8 Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Plan ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How to build a manufacturing business plan, what 'feature creep' teaches small businesses about marketing messaging, sole proprietorship vs. llc: which structure should you choose.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Raise More & Grow Your Nonprofit.
The complete guide to writing a nonprofit business plan.
August 14, 2019
Leadership & Management
July 7, 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Statistics from the National Center for Charitable Statistics (NCCS) show that there are over 1.5 million nonprofit organizations currently operating in the U.S. alone. Many of these organizations are hard at work helping people in need and addressing the great issues of our time. However, doing good work doesn’t necessarily translate into long-term success and financial stability. Other information has shown that around 12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark, and this number expands to 17% at the 10-year mark.
12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark and 17% at the 10-year mark
There are a variety of challenges behind these sobering statistics. In many cases, a nonprofit can be sunk before it starts due to a lack of a strong nonprofit business plan. Below is a complete guide to understanding why a nonprofit needs a business plan in place, and how to construct one, piece by piece.
The purpose of a nonprofit business plan
A business plan for a nonprofit is similar to that of a for-profit business plan, in that you want it to serve as a clear, complete roadmap for your organization. When your plan is complete, questions such as "what goals are we trying to accomplish?" or "what is the true purpose of our organization?" should be clear and simple to answer.

Your nonprofit business plan should provide answers to the following questions:
1. What activities do you plan to pursue in order to meet the organization’s high level goals?
2. What's your plan on getting revenue to fund these activities?
3. What are your operating costs and specifically how do these break down?
Note that there’s a difference between a business plan and a strategic plan, though there may be some overlap. A strategic plan is more conceptual, with different ideas you have in place to try and meet the organization’s greater vision (such as fighting homelessness or raising climate change awareness). A business plan serves as an action plan because it provides, in as much detail as possible, the specifics on how you’re going to execute your strategy.
More Reading
- What is the Difference Between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan?
- Business Planning for Nonprofits
Creating a nonprofit business plan
With this in mind, it’s important to discuss the individual sections of a nonprofit business plan. Having a proper plan in a recognizable format is essential for a variety of reasons. On your business’s end, it makes sure that as many issues or questions you may encounter are addressed up front. For outside entities, such as potential volunteers or donors, it shows that their time and energy will be managed well and put to good use. So, how do you go from conceptual to concrete?
Step 1: Write a mission statement
Having a mission statement is essential for any company, but even more so for nonprofits. Your markers of success are not just how the organization performs financially, but the impact it makes for your cause.
One of the easiest ways to do this is by creating a mission statement. A strong mission statement clarifies why your organization exists and determines the direction of activities.

At the head of their ethics page , NPR has a mission statement that clearly and concisely explains why they exist. From this you learn:
- The key point of their mission: creating a more informed public that understands new ideas and cultures
- Their mechanism of executing that vision: providing and reporting news/info that meets top journalistic standards
- Other essential details: their partnership with their membership statement
You should aim for the same level of clarity and brevity in your own mission statement.
The goal of a mission statement isn’t just about being able to showcase things externally, but also giving your internal team something to realign them if they get off track.
For example, if you're considering a new program or services, you can always check the idea against the mission statement. Does it align with your higher level goal and what your organization is ultimately trying to achieve? A mission statement is a compass to guide your team and keep the organization aligned and focused.
Step 2: Collect the data
You can’t prepare for the future without some data from the past and present. This can range from financial data if you’re already in operation to secured funding if you’re getting ready to start.
Data related to operations and finances (such as revenue, expenses, taxes, etc.) is crucial for budgeting and organizational decisions.
You'll also want to collect data about your target donor. Who are they in terms of their income, demographics, location, etc. and what is the best way to reach them? Every business needs to market, and answering these demographic questions are crucial to targeting the right audience in a marketing campaign. You'll also need data about marketing costs collected from your fundraising, marketing, and CRM software and tools. This data can be extremely important for demonstrating the effectiveness of a given fundraising campaign or the organization as a whole.
Then there is data that nonprofits collect from third-party sources as to how to effectively address their cause, such as shared data from other nonprofits and data from governments.
By properly collecting and interpreting the above data, you can build your nonprofit to not only make an impact, but also ensure the organization is financially sustainable.
Step 3: Create an outline
Before you begin writing your plan, it’s important to have an outline of the sections of your plan. Just like an academic essay, it’s easier to make sure all the points are addressed by taking inventory of high level topics first. If you create an outline and find you don’t have all the materials you need to fill it, you may need to go back to the data collection stage.
Writing an outline gives you something simple to read that can easily be circulated to your team for input. Maybe some of your partners will want to emphasize an area that you missed or an area that needs more substance.
Having an outline makes it easier for you to create an organized, well-flowing piece. Each section needs to be clear on its own, but you also don’t want to be overly repetitive.
As a side-note, one area where a lot of business novices stall in terms of getting their plans off the ground is not knowing what format to choose or start with. The good news is there are a lot of resources available online for you to draw templates for from your plan, or just inspire one of your own.
Using a business plan template
You may want to use a template as a starting point for your business plan. The major benefit here is that a lot of the outlining work that we mentioned is already done for you. However, you may not want to follow the template word for word. A nonprofit business plan may require additional sections or parts that aren’t included in a conventional business plan template.
The best way to go about this is to try and focus less on copying the template, and more about copying the spirit of the template. For example, if you see a template that you like, you can keep the outline, but you may want to change the color scheme and font to better reflect your brand. And of course, all your text should be unique.
When it comes to adding a new section to a business plan template, for the most part, you can use your judgment. We will get into specific sections in a bit, but generally, you just want to pair your new section with the existing section that makes the most sense. For example, if your non-profit has retail sales as a part of a financial plan, you can include that along with the products, services and programs section.
- Free Nonprofit Sample Business Plans - Bplans
- Non-Profit Business Plan Template - Growthink
- Sample Nonprofit Business Plans - Bridgespan
- Nonprofit Business Plan Template - Slidebean
- 23+ Non Profit Business Plan Templates - Template.net
Nonprofit business plan sections
The exact content is going to vary based on the size, purpose, and nature of your nonprofit. However, there are certain sections that every business plan will need to have for investors, donors, and lenders to take you seriously. Generally, your outline will be built around the following main sections:
1. Executive summary
Many people write this last, even though it comes first in a business plan. This is because the executive summary is designed to be a general summary of the business plan as a whole. Naturally, it may be easier to write this after the rest of the business plan has been completed.
After reading your executive summary a person should ideally have a general idea of what the entire plan covers. Sometimes, a person may be interested in learning about your non-profit, but doesn’t have time to read a 20+ page document. In this case, the executive summary could be the difference between whether or not you land a major donor.
As a start, you want to cover the basic need your nonprofit services, why that need exists, and the way you plan to address that need. The goal here is to tell the story as clearly and and concisely as possible. If the person is sold and wants more details, they can read through the rest of your business plan.
2. Products/Services/Programs
This is the space where you can clarify exactly what your non-profit does. Think of it as explaining the way your nonprofit addresses that base need you laid out earlier. This can vary a lot based on what type of non-profit you’re running.

This page gives us some insight into the mechanisms Bucks County Historical Society uses to further their mission, which is “to educate and engage its many audiences in appreciating the past and to help people find stories and meanings relevant to their lives—both today and in the future.”
They accomplish this goal through putting together both permanent exhibits as well as regular events at their primary museum. However, in a non-profit business plan, you need to go further.
It’s important here not only to clearly explain who benefits from your services, but also the specific details how those services are provided. For example, saying you “help inner-city school children” isn’t specific enough. Are you providing education or material support? Your non-profit business plan readers need as much detail as possible using simple and clear language.
3. Marketing
For a non-profit to succeed, it needs to have a steady stream of both donors and volunteers. Marketing plays a key role here as it does in a conventional business. This section should outline who your target audience is, and what you’ve already done/plan on doing to reach this audience. How you explain this is going to vary based on what stage your non-profit is in. We’ll split this section to make it more clear.
Nonprofits not in operation
Obviously, it’s difficult to market an idea effectively if you’re not in operation, but you still need to have a marketing plan in place. People who want to support your non-profit need to understand your marketing plan to attract donors. You need to profile all the data you have about your target market and outline how you plan to reach this audience.
Nonprofits already in operation
Marketing plans differ greatly for nonprofits already in operation. If your nonprofit is off the ground, you want to include data about your target market as well, along with other key details. Describe all your current marketing efforts, from events to general outreach, to conventional types of marketing like advertisements and email plans. Specific details are important. By the end of this, the reader should know:
- What type of marketing methods your organization prefers
- Why you’ve chosen these methods
- The track record of success using these methods
- What the costs and ROI of a marketing campaign
4. Operations
This is designed to serve as the “how” of your Products/Services/Programs section.
For example, if your goal is to provide school supplies for inner-city schoolchildren, you’ll need to explain how you will procure the supplies and distribute them to kids in need. Again, detail is essential. A reader should be able to understand not only how your non-profit operates on a daily basis, but also how it executes any task in the rest of the plan.
If your marketing plan says that you hold community events monthly to drum up interest. Who is in charge of the event? How are they run? How much do they cost? What personnel or volunteers are needed for each event? Where are the venues?
This is also a good place to cover additional certifications or insurance that your non-profit needs in order to execute these operations, and your current progress towards obtaining them.
Your operations section should also have a space dedicated to your team. The reason for this is, just like any other business plan, is that the strength of an organization lies in the people running it.

For example, let’s look at this profile from The Nature Conservancy . The main points of the biography are to showcase Chief Development Officer Jim Asp’s work history as it is relevant to his job. You’ll want to do something similar in your business plan’s team section.
Equally important is making sure that you cover any staff changes that you plan to implement in the near future in your business plan. The reason for this is that investors/partners may not want to sign on assuming that one leadership team is in place, only for it to change when the business reaches a certain stage.
The sections we’ve been talking about would also be in a traditional for profit business plan. We start to deviate a bit at this point. The impact section is designed to outline the social change you plan to make with your organization, and how your choices factor into those goals.
Remember the thoughts that go into that mission statement we mentioned before? This is your chance to show how you plan to address that mission with your actions, and how you plan to track your progress.
Let’s revisit the idea of helping inner-city school children by providing school supplies. What exactly is the metric you’re going to use to determine your success? For-profit businesses can have their finances as their primary KPI, but it’s not that easy for non-profits. Let’s say that your mission is to provide 1,000 schoolchildren in an underserved school district supplies for their classes. Your impact plan could cover two metrics:
- How many supplies are distributed
- Secondary impact (improved grades, classwork completed, etc).
The primary goal of this section is to transform that vision into concrete, measurable goals and objectives. A great acronym to help you create these are S.M.A.R.T. goals which stands for: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely.

Vitamin Angels does a good job of showing how their action supports the mission. Their goal of providing vitamins to mothers and children in developing countries has a concrete impact when we look at the numbers of how many children they service as well as how many countries they deliver to. As a non-profit business plan, it’s a good idea to include statistics like these to show exactly how close you are to your planned goals.
6. Finances
Every non-profit needs funding to operate, and this all-important section details exactly how you plan to cover these financial needs. Your business plan can be strong in every other section, but if your financial planning is flimsy, it’s going to prove difficult to gather believers to your cause.
It's important to paint a complete, positive picture of your fundraising plans and ambitions. Generally, this entails the following parts:
- Current financial status, such as current assets, cash on hand, liabilities
- Projections based off of your existing financial data and forms
- Key financial documents, such as a balance sheet, income statements, and cash flow sheet
- Any grants or major contributions received
- Your plan for fundraising (this may overlap with your marketing section which is okay)
- Potential issues and hurdles to your funding plan
- Your plans to address those issues
- How you'll utilize surplus donations
- Startup costs (if your non-profit is not established yet)
In general, if you see something else that isn’t accounted for here, it’s better to be safe than sorry, and put the relevant information in. It’s better to have too much information than too little when it comes to finances, especially since there is usually a clear preference for transparent business culture.
- How to Make a Five-Year Budget Plan for a Nonprofit
- Financial Transparency - National Council of Nonprofits
7. Appendix
Generally, this serves as a space to attach additional documents and elements that you may find useful for your business plan. This can include things like supplementary charts or a list of your board of directors.
This is also a good place to put text or technical information that you think may be relevant to your business plan, but might be long-winded or difficult to read. A lot of the flow and structure concerns you have for a plan don’t really apply with an appendix.
In summary, while a non-profit may have very different goals than your average business, the ways that they reach those goals do have a lot of similarities with for-profit businesses. The best way to ensure your success is to have a clear, concrete vision and path to different milestones along the way. A solid, in-depth business plan also gives you something to refer back to when you are struggling and not sure where to turn.
Alongside your business plan, you also want to use tools and resources that promote efficiency at all levels. For example, every non-profit needs a consistent stream of donations to survive, so consider using a program like GiveForms that creates simple, accessible forms for your donors to easily make donations. Accounting and budgeting for these in your plans can pay dividends later on.
Share this Article
Related articles, start fundraising today.
- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs
Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.

Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Cookie settings

We use cookies
We use cookies to improve your experience on our platform. By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage and assist in our marketing efforts.
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Nonprofit Business Plan
https://home.simplyk.io/blog/nonprofit-business-plan
What is a nonprofit business plan?
In simple terms, a nonprofit business plan is your organization’s roadmap to success. It’s a comprehensive document that outlines your nonprofit’s goals, strategies, and action plans for achieving its mission. Just like a GPS guides you to your destination, a well-crafted business plan guides your nonprofit toward its vision of a better world.
Do I need a nonprofit business plan?
A nonprofit business plan is more than just an additional tool—it’s an essential part of any nonprofit. A business plan:
Guides your organization: A nonprofit business plan serves as your organization’s compass, guiding you toward your goals. It provides clarity on what you want to achieve and how you’ll get there. Without a plan, you’re like a ship adrift at sea—directionless and vulnerable to the whims of the waves.
Facilitates strategy: A well-crafted plan helps you make informed decisions about resource allocation, program development, fundraising strategies, and more.
Promotes accountability: When donors, volunteers, and community members invest their time, money, and trust in your organization, they want to know their efforts aren’t going to waste. A nonprofit business plan demonstrates your commitment to achieving results and holds you accountable to stakeholders. It’s your promise to deliver on your mission and make a meaningful impact in the world.
Supports sustainability: Economic downturns, shifts in public opinion, and evolving community needs can all impact your organization’s ability to thrive. A nonprofit business plan helps you anticipate and navigate these challenges, ensuring your organization remains resilient and sustainable for the long haul.
The 10-Step guide on writing a business plan for nonprofits
Crafting a business plan for your nonprofit organization is a crucial step toward success. This comprehensive guide will walk you through each step, providing actionable insights and tips to help you create a robust plan that sets your nonprofit up for success.
Step 1: Clarify your mission
Your mission and vision are the heart and soul of your nonprofit. Start by defining your mission statement—what you do and why it matters. Then, articulate your vision statement, outlining the future you aspire to create. Be concise, compelling, and specific.
Gather your team and brainstorm ideas to refine your mission and vision statements. Consider what sets your organization apart and how you envision making a difference.
Step 2: Conduct a needs assessment
Understanding the needs of your community or target audience is essential for designing effective programs and services. Conduct thorough research, engage with stakeholders, and gather data to identify the most pressing issues you aim to address.
To do this, create a needs assessment survey or conduct interviews with community members, partners, and experts. Analyze the data to prioritize the most significant needs your organization can address.
Step 3: Define your goals
Set clear, measurable goals that align with your mission and address the identified needs. Break down each goal into specific objectives, outlining the steps you’ll take to achieve them. Use the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—to ensure your goals are realistic and actionable.
Host a goal-setting workshop with your team to brainstorm and prioritize objectives. Use a goal-setting framework like OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) to ensure alignment and accountability.
Step 4: Outline your programs
Describe the programs and services your nonprofit will offer to address the identified needs. Define the goals, activities, target audience, and expected outcomes of each program. Consider how your programs will complement each other and work together to achieve your overall mission.
Step 5: Develop a marketing and outreach plan
Create a marketing and outreach plan to raise awareness about your organization and attract supporters, volunteers, and beneficiaries. Define your target audience, messaging, channels, and tactics for reaching and engaging key stakeholders.
To do this, conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to assess your organization’s marketing and outreach capabilities. Develop a marketing calendar with key milestones and campaigns to guide your efforts.
Step 6: Create a financial plan
Develop a detailed budget and financial projections for your nonprofit. Identify potential revenue streams, such as grants, donations, fundraising events, membership fees, and earned income. Estimate expenses for staffing, programs, operations, and overhead costs.
Step 7: Establish governance and management structure
Define your nonprofit's organizational structure, including leadership roles, board of directors, staff positions, and volunteer management. Clarify responsibilities, decision-making processes, and lines of authority to ensure effective governance and management.
Action: Review and update your bylaws, policies, and procedures to reflect your organization’s current needs and goals. Provide board orientation and training to ensure board members understand their roles and responsibilities.
Step 8: Consider risks
Identify potential risks and challenges that could impact your organization’s ability to achieve its goals. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks and ensure the sustainability of your nonprofit. Consider risks related to funding, operations, legal compliance, reputation, and external factors.
Step 9: Monitor and evaluate
Establish systems for monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of your programs and operations. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track progress towards your goals. Regularly review and update your business plan based on feedback and results.
Step 10: Communicate your plan
Share your business plan with stakeholders, including board members, staff, volunteers, donors, partners, and the community. Solicit feedback, build buy-in, and encourage collaboration toward achieving your nonprofit’s mission and vision. Use various communication channels and platforms to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
To do this, you might host a launch event or town hall meeting to present your business plan to stakeholders and answer questions. Develop a communications plan to ensure consistent messaging and updates across all channels.
Essential nonprofit business plan elements
- Mission and vision : Clearly define the nonprofit's purpose and long-term goals.
- Needs assessment : Identify the needs of the community or target audience your nonprofit serves.
- Programs and services : Describe the programs and services your nonprofit offers to address identified needs.
- Marketing and outreach : Develop strategies to raise awareness and attract supporters, volunteers, and beneficiaries.
- Financial plan : Create a budget and financial projections, outlining revenue sources and expenses.
- Governance and management : Establish the organizational structure and define roles and responsibilities.
- Risk management : Identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
- Monitoring and evaluation : Set up systems to track progress and evaluate program effectiveness.
- Communication and engagement : Share your business plan with stakeholders and engage them in your nonprofit's work.
- Executive summary : Provide a concise overview of the nonprofit and its key objectives.
Nonprofit business plan template
1. executive summary.
- Mission Statement: [Briefly describe your nonprofit's mission and vision.]
- Objectives: [List the key objectives your nonprofit aims to achieve.]
- Strategies: [Summarize the strategies and tactics your nonprofit will use to achieve its objectives.]
- Financial Overview: [Provide an overview of your nonprofit's financial projections and funding needs.]
2. Organization Description
- Mission Statement: [State your nonprofit's mission.]
- Vision Statement: [Outline your nonprofit's vision for the future.]
- History: [Briefly describe the history and background of your nonprofit.]
- Legal Structure: [Specify the legal structure of your nonprofit (e.g., 501(c)(3) status).]
- Governance: [Describe the governance structure of your nonprofit, including the board of directors and leadership team.]
3. Needs Assessment
- Community Needs: [Identify the needs of the community or target audience your nonprofit serves.]
- Data and Research: [Provide data and research supporting the identified needs.]
- Program Impact: [Explain how your nonprofit addresses the identified needs and the impact of its programs.]
4. Programs and Services
- Program Descriptions: [Describe the programs and services your nonprofit offers, including goals, objectives, and outcomes.]
- Logic Models: [Include logic models or theory of change diagrams for each program.]
5. Marketing and Outreach Plan
- Target Audience: [Define your nonprofit's target audience.]
- Messaging: [Outline the messaging and branding strategies for your nonprofit.]
- Marketing Channels: [List the marketing channels and tactics you will use to reach your target audience.]
6. Financial Plan
- Budget: [Provide a detailed budget for your nonprofit, including income and expenses.]
- Financial Projections: [Include financial projections for the next three to five years.]
- Revenue Streams: [Identify potential revenue streams, such as grants, donations, and fundraising events.]
7. Governance and Management
- Organizational Structure: [Describe the organizational structure of your nonprofit, including the board of directors, staff positions, and volunteer management.]
- Roles and Responsibilities: [Clarify the roles and responsibilities of board members, staff, and volunteers.]
8. Risk Management
- Risk Identification: [Identify potential risks and challenges that could impact your nonprofit's operations.]
- Risk Mitigation: [Develop strategies to mitigate the identified risks and ensure the sustainability of your nonprofit.]
9. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Key Performance Indicators: [Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track progress toward your nonprofit's objectives.]
- Evaluation Framework: [Establish an evaluation framework for assessing program effectiveness and impact.]
10. Communication and Engagement
- Stakeholder Communication: [Develop a stakeholder communication plan to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.]
- Engagement Strategies: [Outline strategies for engaging board members, staff, volunteers, donors, and the community in your nonprofit's work.]
Add free fundraising to your nonprofit business plan
Whether you’re a brand new nonprofit looking to get your fundraising up and running, or an established one looking for new tools and features to make even more impact, Zeffy is one of the best all-in-one solutions for all of your nonprofit needs.
From event tracking and management to marketing and engagement tools, custom donation forms, and even the ability to create an online shop or nonprofit membership association, Zeffy offers everything you need without charging a single fee.
Simple and powerful — and packed with free support whenever you need it — Zeffy ensures that your donor’s gifts are going right to the cause, and nowhere else.
Nonprofit Business Plan FAQS
Starting a nonprofit organization with no money requires strategic planning. To cut down on costs, consider:
- Using volunteers: Leverage volunteers for administrative, fundraising, or program work, to reduce the need for paid staff.
- Seeking out in-kind donations and grants: Ask for donations of goods and services from businesses, individuals, or other organizations to support your nonprofit's activities (think office space or equipment). And, research grant opportunities to generate free financial support for your nonprofit's mission.
- Leveraging partnerships: Look for potential partners, such as other nonprofits or community organizations, who might want to collaborate on shared goals.
- Taking advantage of free tools and platforms: Be sure to use fundraising and donor engagement tools that are completely free to use, like Zeffy. That way, you’ll never have to worry about hidden fees and can get started making an impact right away — without paying a cent.
Start fundraising with Zeffy for free
Here are some ways nonprofit founders can pay themselves:
- Salary or wages: Nonprofit founders can receive a salary or hourly wages for their services, similar to employees of the organization.
- Reimbursement for expenses: Nonprofit founders can be reimbursed for reasonable and necessary expenses incurred in the course of their duties, such as travel expenses, office supplies, and professional development costs.
- Consulting or contractual arrangements: Nonprofit founders may enter into consulting or contractual agreements with the organization to provide specific services or expertise on a project basis.
Donor management and fundraising software can support strategic planning in a few ways:
- Data centralization: Donor management software centralizes donor information for analysis and insights.
- Targeted engagement: Software enables personalized communication and engagement strategies.
- Campaign management: Facilitates planning, execution, and tracking of fundraising campaigns.
- Donor retention: Supports cultivation and stewardship efforts to retain donors.
More articles
How to start a school in 10 steps: a guide for nonprofits, the essential nonprofit capacity building guide for growth, keep reading :.

Everything you need to know about creating a nonprofit annual report. Learn what to include, best practices, and annual report examples.

Learn how to start a nonprofit with our comprehensive guide. Ready to make a difference ? Discover the 9 steps to transform your passion into action.

Maximize your nonprofit's impact with our 7-step guide to creating an effective strategic plan. Learn how to set SMART goals, engage stakeholders, and align your fundraising efforts.

Free Nonprofit Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | September 18, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up the most useful list of nonprofit business plan templates, all free to download in Word, PDF, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page nonprofit business plan template , a fill-in-the-blank nonprofit business plan template , a startup nonprofit business planning timeline template , and more. Plus, we provide helpful tips for creating your nonprofit business plan .
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
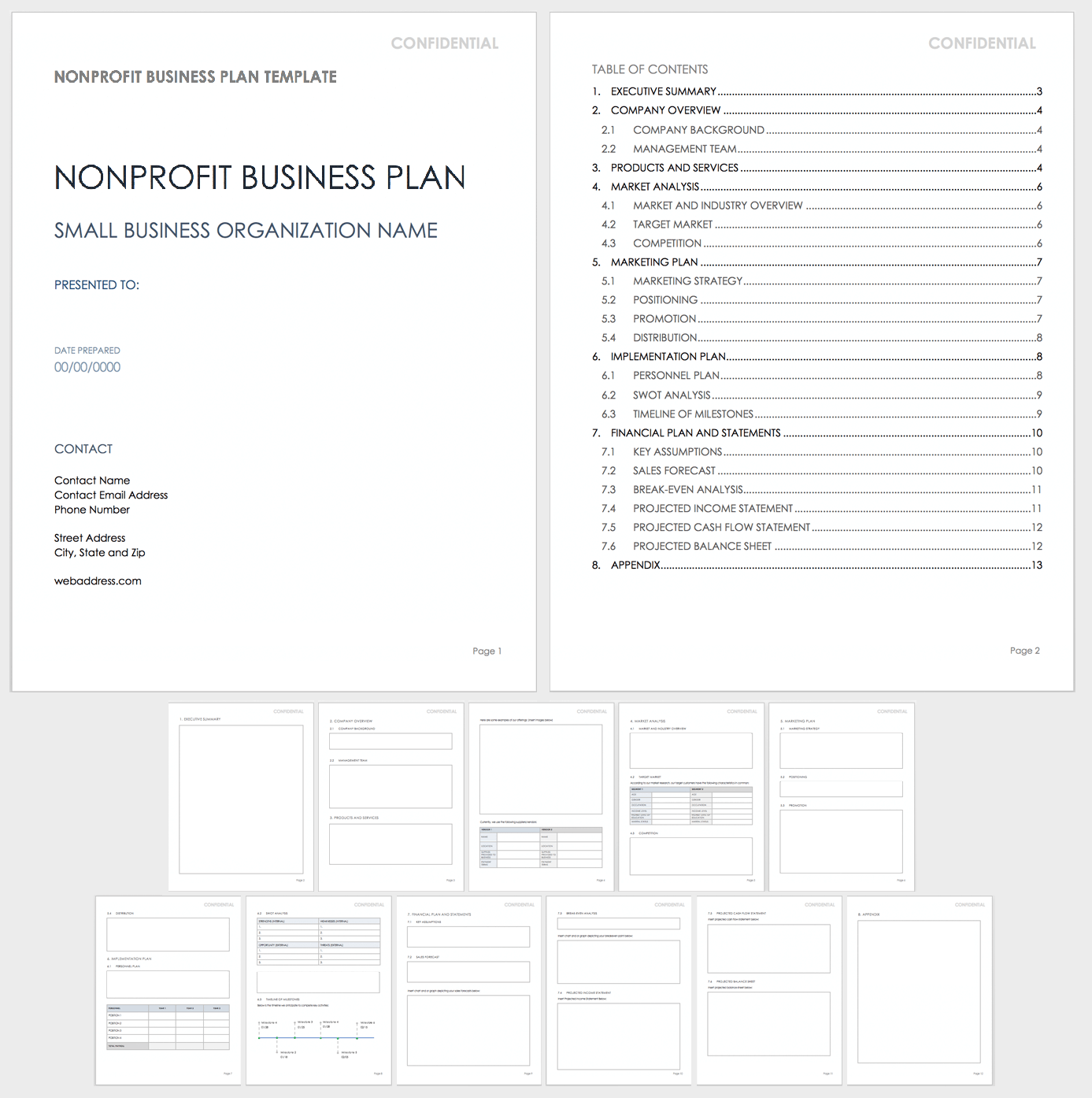
Use this customizable nonprofit business plan template to organize your nonprofit organization’s mission and goals and convey them to stakeholders. This template includes space for information about your nonprofit’s background, objectives, management team, program offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, funding sources, fundraising methods, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
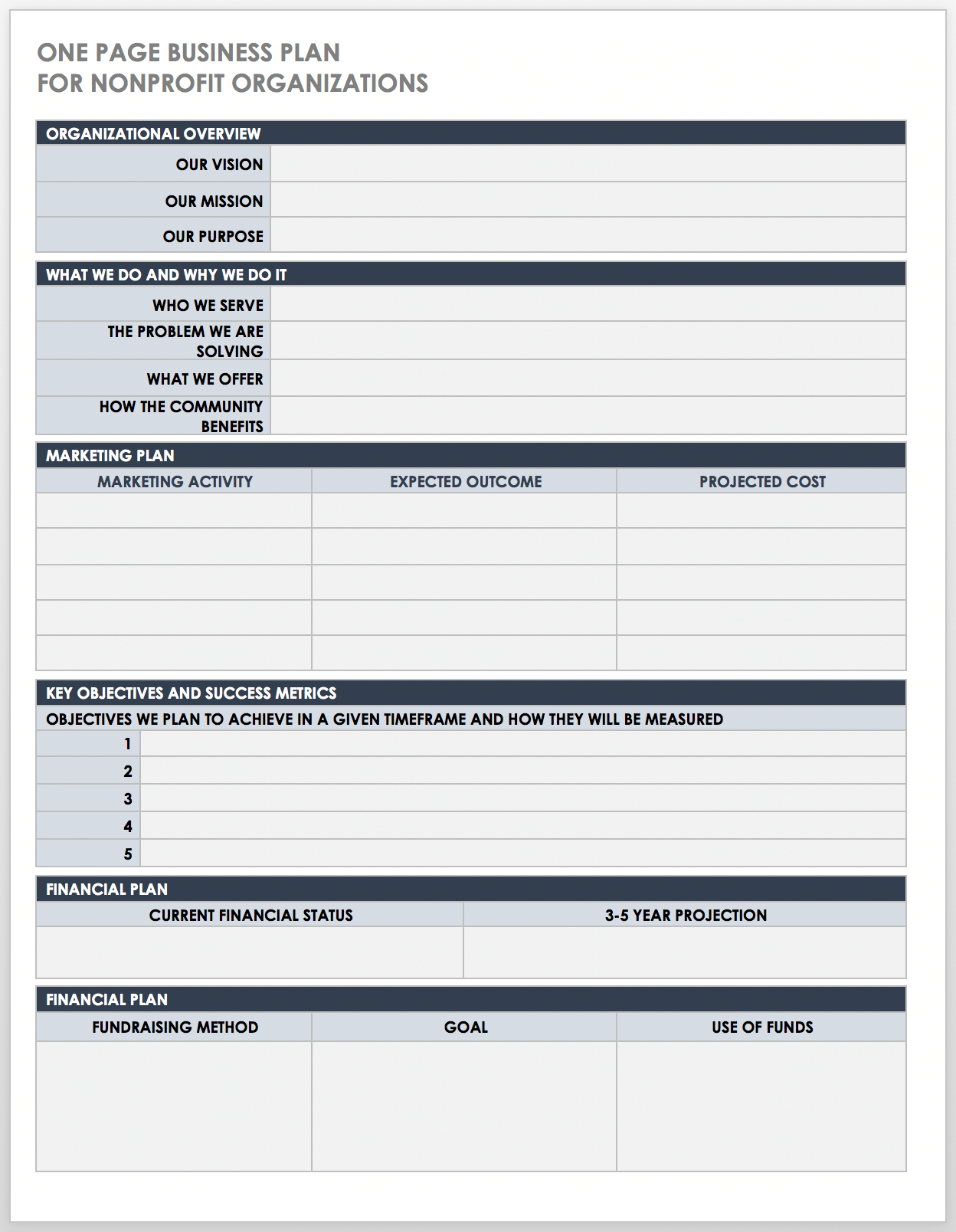
This one-page nonprofit business plan template has a simple and scannable design to outline the key details of your organization’s strategy. This template includes space to detail your mission, vision, and purpose statements, as well as the problems you aim to solve in your community, the people who benefit from your program offerings, your key marketing activities, your financial goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
Excel | Word | PDF
For additional resources, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit “ One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide .”
Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
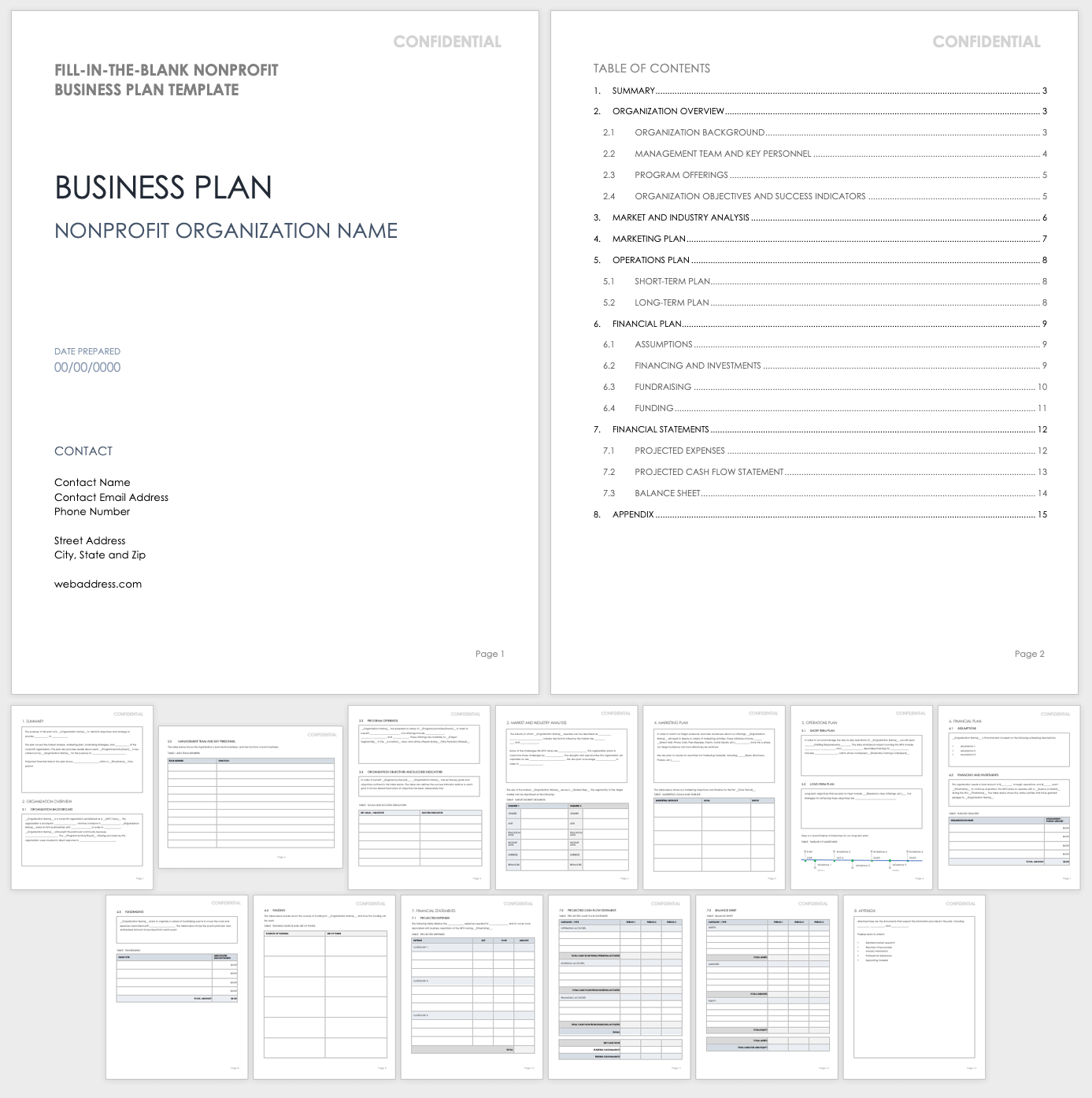
Use this fill-in-the-blank template as the basis for building a thorough business plan for a nonprofit organization. This template includes space to describe your organization’s background, purpose, and main objectives, as well as key personnel, program and service offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, fundraising methods, and more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
For additional resources that cater to a wide variety of organizations, visit “ Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates .”
Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
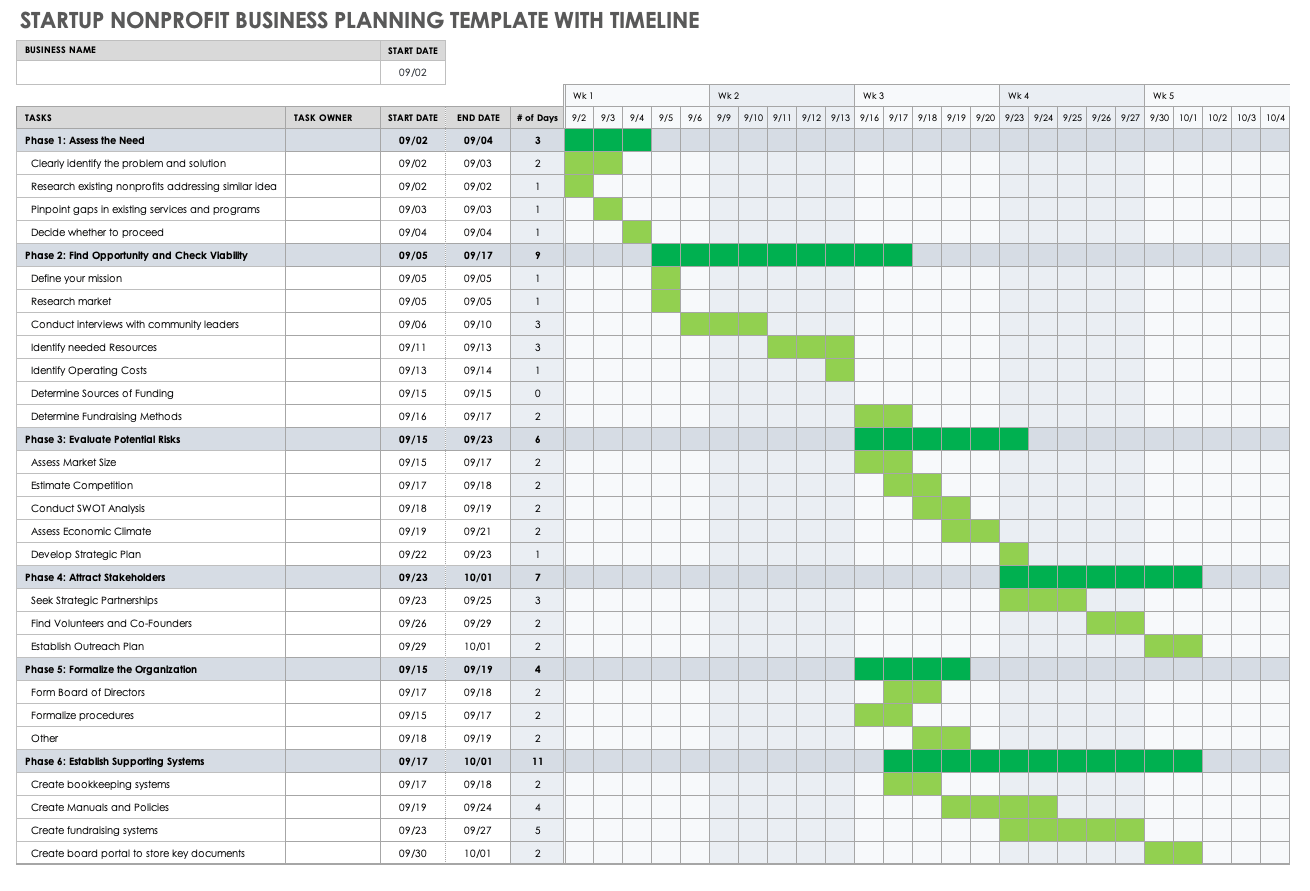
Use this business planning template to organize and schedule key activities for your business. Fill in the cells according to the due dates, and color-code the cells by phase, owner, or category to provide a visual timeline of progress.
Download Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Use this template as a foundation for building a powerful and attractive nonprofit business plan for youth programs and services. This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization’s background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Word | PDF | Google Doc
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
You can customize this sample nonprofit business plan outline to fit the specific needs of your organization. To ensure that you don’t miss any essential details, use this outline to help you prepare and organize the elements of your plan before filling in each section.
Download Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
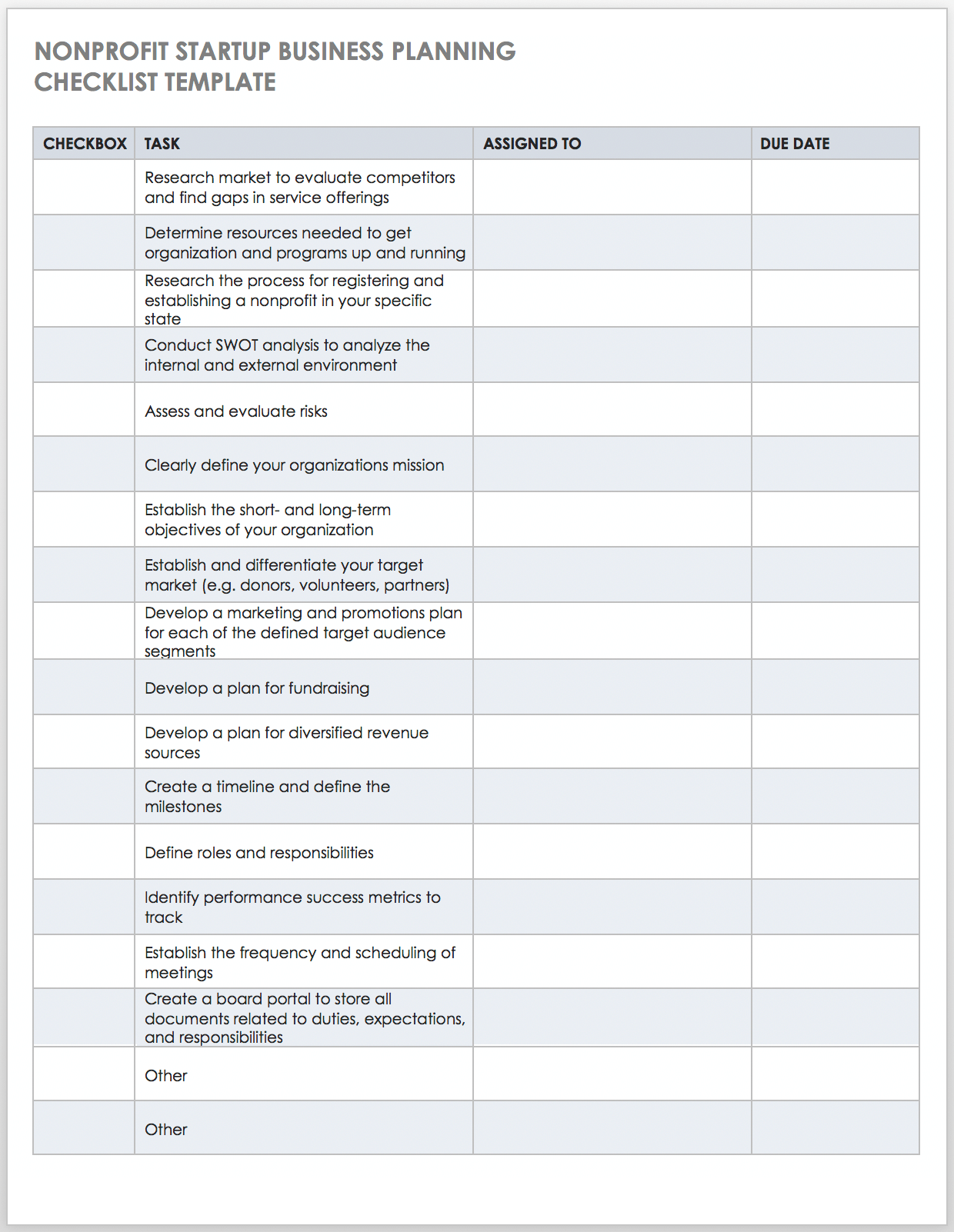
Use this customizable business planning checklist as the basis for outlining the necessary steps to get your nonprofit organization up and running. You can customize this checklist to fit your individual needs. It includes essential steps, such as conducting a SWOT analysis , fulfilling the research requirements specific to your state, conducting a risk assessment , defining roles and responsibilities, creating a portal for board members, and other tasks to keep your plan on track.
Download Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Tips to Create Your Nonprofit Business Plan
Your nonprofit business plan should provide your donors, volunteers, and other key stakeholders with a clear picture of your overarching mission and objectives. Below, we share our top tips for ensuring that your plan is attractive and thorough.
- Develop a Strategy First: You must aim before you fire if you want to be effective. In other words, develop a strategic plan for your nonprofit in order to provide your team with direction and a roadmap before you build your business plan.
- Save Time with a Template: No need to start from scratch when you can use a customizable nonprofit business plan template to get started. (Download one of the options above.)
- Start with What You Have: With the exception of completing the executive summary, which you must do last, you aren’t obligated to fill in each section of the plan in order. Use the information you have on hand to begin filling in the various parts of your business plan, then conduct additional research to fill in the gaps.
- Ensure Your Information Is Credible: Back up all the details in your plan with reputable sources that stakeholders can easily reference.
- Be Realistic: Use realistic assumptions and numbers in your financial statements and forecasts. Avoid the use of overly lofty or low-lying projections, so stakeholders feel more confident about your plan.
- Strive for Scannability: Keep each section clear and concise. Use bullet points where appropriate, and avoid large walls of text.
- Use Visuals: Add tables, charts, and other graphics to draw the eye and support key points in the plan.
- Be Consistent: Keep the voice and formatting (e.g., font style and size) consistent throughout the plan to maintain a sense of continuity.
- Stay True to Your Brand: Make sure that the tone, colors, and overall style of the business plan are a true reflection of your organization’s brand.
- Proofread Before Distribution: Prior to distributing the plan to stakeholders, have a colleague proofread the rough version to check for errors and ensure that the plan is polished.
- Don’t Set It and Forget It: You should treat your nonprofit business plan as a living document that you need to review and update on a regular basis — as objectives change and your organization grows.
- Use an Effective Collaboration Tool: Use an online tool to accomplish the following: collaborate with key personnel on all components of the business plan; enable version control for all documents; and keep resources in one accessible place.
Improve Your Nonprofit Business Planning Efforts with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Nonprofit Business Plan Template & Guide [Updated 2024]
Nonprofit business plan template.
Are you passionate about making a positive impact in your community? Are you part of a nonprofit organization or considering starting one? If so, you need a business plan and you’re in the right place to do that!
Below, we’ll guide you through the essential elements of a nonprofit business plan, sharing valuable insights and a user-friendly template to set you on the path to success.
- How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
Growthink’s nonprofit business plan template below is the result of 20+ years of research into the types of business plans that help nonprofit organizations (NPOs) to secure funding and achieve their goals.
Follow the links to each section of our non-profit business plan template:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary will provide a brief overview of each section of your nonprofit business plan including your mission statement, goals and objectives, key achievements, and financial highlights.
- Organization Overview – The Organization Overview which should include a description of your organization, its guiding philosophy, and the programs and services it provides.
- Products, Programs, and Services – In the Products, Programs and Services section, you will describe in detail the services or products your nonprofit provides to its target audience.
- Industry Analysis – The Industry Analysis section should provide an overview of the market in which your organization operates, including key trends, competitors, and potential opportunities for growth.
- Customer Analysis – The Customer Analysis section will identify the key customer segment(s) your NPO serves and then provide demographics and psychographic details about them.
- Marketing Plan – In the Marketing Plan section, you will outline how you plan to reach and engage with your target audience through various marketing and communication strategies.
- Operational Plan – The Operational Plan will include all the details of your day-to-day operations, including staffing, facilities, and any necessary equipment or technology.
- Management Team – The Management Team section will describe the organizational structure of your NPO, including key personnel, board members, and their roles and responsibilities.
- Financial Plan – The Financial Plan section will include a detailed budget, financial projections and analysis, as well as information on how your organization plans to generate revenue and manage expenses.
- Appendix – In the Appendix, you will include supporting documents and research for your business plan which may include the IRS status letter, financial statements, market research, and any additional information to support your organization’s financial goals and specific objectives.
NPO Planning Resources & FAQs
Below are answers to the most common questions asked by nonprofits:
Is there a nonprofit business plan template I can download?
Where can i download a nonprofit business plan pdf, what is a nonprofit business plan.
A non-profit business plan describes your organization as it currently exists (which could be just an idea) and presents a road map for the next three to five years. It lays out your goals, challenges, and plans for meeting your goals. Your business plan should be updated frequently, as it is not meant to be stagnant. It is particularly important to create/update your business plan annually to make sure your nonprofit remains on track towards successfully fulfilling its mission.
A nonprofit business plan template is a tool used to help your nonprofit business quickly develop a roadmap for your business.
Why do you need a business plan for your nonprofit?
What are the types of nonprofit organizations (npos).
There are several types of nonprofits. These are categorized by section 500(c) by the IRS for tax exempt purposes. Listed below, are some of the frequently filed sections:
Corporations formed under Act of Congress. An example is Federal Credit Unions.
Holding corporations for tax exempt organizations. This group holds title to the property for the exempt group.
This is the most popular type of NPO. Examples include educational, literary, charitable, religious, public safety, international and national amateur sports competitions, organizations committed to the prevention of cruelty towards animals or children, etc. Organizations that fall into this category are either a private foundation or a public charity. Examples include Getty Foundation, Red Cross, Easter Seals, etc.
Examples include social welfare groups, civil leagues, employee associations, etc. This category promotes charity, community welfare and recreational/educational goals.
Horticultural, labor and agricultural organizations get classified under this section. These organizations are instructive or educational and work to improve products, working conditions and efficiency.
Examples include real estate boards, business leagues, etc. They work to ameliorate business conditions.
Recreation and social clubs that promote pleasure and activities fall into this category.
Fraternal beneficiary associations and societies belong to this section.
Voluntary Employees’ beneficiary associations which provide benefits, accidents and life payments to members are a part of this section.
When filling in your nonprofit business plan template, include the type of nonprofit business you intend to be.
What are the primary sources of funding for nonprofit business plans?
The primary funding sources for most nonprofit organizations are donors, grants and bank loans. Donors are individuals that provide capital to start and grow your nonprofit. Major donors, as the name implies, write large checks and are often instrumental in launching nonprofits. Grants are given by organizations and others to achieve specific goals and often nonprofits qualify for them. Business loans, particularly for asset purchases like buildings and equipment, are also typically used by nonprofits.
NPOs may also sell products or services, work with investors or develop their own investments. The expertise of the non-profit staff, members and board of directors will impact funding options for a nonprofit organization. The nonprofit’s mission, resources, goals and vision will all impact the funding sources a nonprofit business will place in it’s business plan as well.
How do you write a nonprofit business plan?
How do you start a nonprofit, how many nonprofit organizations are in the us.
According to the National Center for Charitable Statistics , there are approximately 1.54 million nonprofits registered in the United States (data pulled from registrations with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS)).
The nonprofit sector has annual expenses exceeding 2.46 trillion U.S dollars.
Does your action plan and fundraising plan belong in your plan?
Yes, both belong in your plan.
Include your action plan in the operations plan section.
Your fundraising plan goes in your financial plan section. Here you will discuss how much money you must raise and from whom you plan to solicit these funds, as well as outlines your fundraising events. It should clearly outline your fundraising goals and potential donors.
Where do you include your non profit mission in your plan?
What do you include in a nonprofit’s financial projections.
Your financial projections must include an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. These statements within your business plan show how much money your organization will bring in from donors and customers/clients and how much your organization will spend.
The key purpose of your these projections is to ensure you have enough money to keep your organization operating. They also can be an important component of your nonprofit business plan template, as donors, your board of directors, and others may review to understand financial requirements of your nonprofit.
How do nonprofit owners get paid?
How much does it cost to start a nonprofit business.
NPOs must complete Form 1023 with the IRS in order to get exemption status. The filing fee for this form is $600. If neither actual nor projected annual income for the organization exceeds $50,000, you can file form Form 1023-EZ which costs just $275.
In addition to the filing fee, there are other costs associated with starting a nonprofit organization based on the type of organization you are developing (for example, if you require buildings and equipment). Gathering information through the business planning process will help you accurately estimate costs for your nonprofit business plan template.
Where can I download a nonprofit business plan template doc?
Additional nonprofit resources.
- How to Start a Non-Profit Organization
- Sample Nonprofit Business Plan
- Nonprofit Marketing Plan + Template
- How to Write a Mission Statement for Your Nonprofit Organization
- NonProfit Business Plan PDF
- National Council of Nonprofits
- Nonprofit Quarterly
- The Fundraising Authority
Helpful Video Tips for Nonprofit Business Plans
Below are tips to create select sections of your nonprofit business plan:
How to Write Your Nonprofit Business Plan’s Executive Summary
Writing the management team section of your nonprofit business plan, how to write the operations plan of your nonprofit business plan, writing the customer analysis section of your nonprofit business plan, finish your non profit business plan in 1 day.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your Nonprofit business plan today.
NONPROFIT BUSINESS PLAN OUTLINE
- Nonprofit Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Organization Overview
- 3. Products, Programs, and Services
- 4. Industry Analysis
- 5. Customer Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Nonprofit Business Plan Summary


How to Write a Business Plan For a Nonprofit Organization + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for nonprofits. A nonprofit business plan allows you to set goals and track progress over time. It can also help you secure funding from investors or grant-making organizations.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines your vision for the organization but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. In order to create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components that are essential to its success.
This article will provide an overview of the key elements that every nonprofit founder should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template
What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is a formal written document that describes your organization’s purpose, structure, and operations. It is used to communicate your vision to potential investors or donors and convince them to support your cause.
The business plan should include information about your target market, financial projections, and marketing strategy. It should also outline the organization’s mission statement and goals.
Why Write a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors.
A well-crafted business plan will help you:
- Define your organization’s purpose and goals
- Articulate your vision for the future
- Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals
- Secure funding from investors or donors
- Convince potential supporters to invest in your cause
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting your new nonprofit organization, especially if you are inexperienced in starting a nonprofit.
Writing an Effective Nonprofit Business Plan
The key is to tailor your business plan to the specific needs of your nonprofit. Here’s a quick overview of what to include:
Executive Summary
Organization overview, products, programs, and services, industry analysis, customer analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team.
- Financial Plan
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is a one-to-two page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your nonprofit organization
- Provide a short summary of the key points of each section of your business plan.
- Organize your thoughts in a logical sequence that is easy for the reader to follow.
- Include information about your organization’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast.
This section should include a brief history of your nonprofit organization. Include a short description of how and why you started it and provide a timeline of milestones the organization has achieved.
If you are just starting your nonprofit, you may not have a long history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in the industry and how and why you conceived your new nonprofit idea. If you have worked for a similar organization before or have been involved in a nonprofit before starting your own, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen n onprofit business model and how it is different from other nonprofits in your target market.
This section is all about what your nonprofit organization offers. Include information about your programs, services, and any products you may sell.
Describe the products or services you offer and how they benefit your target market. Examples might include:
- A food bank that provides healthy meals to low-income families
- A job training program that helps unemployed adults find jobs
- An after-school program that helps kids stay out of gangs
- An adult literacy program that helps adults learn to read and write
Include information about your pricing strategy and any discounts or promotions you offer. Examples might include membership benefits, free shipping, or volume discounts.
If you offer more than one product or service, describe each one in detail. Include information about who uses each product or service and how it helps them achieve their goals.
If you offer any programs, describe them in detail. Include information about how often they are offered and the eligibility requirements for participants. For example, if you offer a job training program, you might include information about how often the program is offered, how long it lasts, and what kinds of jobs participants can expect to find after completing the program.
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a nonprofit business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends, identify your potential customers, and the potential size of this market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the nonprofit industry are you targeting?
- Who are your competitors?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now?
You should also include information about your research methodology and sources of information, including company reports and expert opinions.
As an example, if you are starting a food bank, your industry analysis might include information about the number of people in your community who are considered “food insecure” (they don’t have regular access to enough nutritious food). You would also include information about other food banks in your area, how they are funded, and the services they offer.
For each of your competitors, you should include a brief description of their organization, their target market, and their competitive advantage. To do this, you should complete a SWOT analysis.
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a helpful tool to assess your nonprofit’s current position and identify areas where you can improve.
Some questions to consider when conducting a SWOT analysis include:
- Strengths : What does your nonprofit do well?
- Weaknesses : What areas could your nonprofit improve?
- Opportunities : What trends or changes in the industry could you take advantage of?
- Threats : What trends or changes in the industry could hurt your nonprofit’s chances of success?
After you have identified your nonprofit’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can develop strategies to improve your organization.
For example, if you are starting a food bank, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more food banks in your community. You could use this information to develop a marketing strategy to reach potential donors who might be interested in supporting your organization.
If you are starting a job training program, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more programs like yours in the community. You could use this information to develop a business plan and marketing strategy to reach potential participants who might be interested in enrolling in your program.
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your target audience might be low-income adults between the ages of 18 and 35. Your customer analysis would include information about their needs (e.g., transportation, childcare, job readiness skills) and wants (e.g., good pay, flexible hours, benefits).
If you have more than one target audience, you will need to provide a separate customer analysis for each one.
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy your product or use your service. For example, if you are starting an after-school program, you might include information about how parents research and compare programs before making a decision.
You should also include information about your marketing strategy and how you plan to reach your target market. For example, if you are starting a food bank, you might include information about how you will promote the food bank to the community and how you will get the word out about your services.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to use your program, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or nonprofit services with the right marketing.
This part of the business plan is where you determine how you are going to reach your target market. This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your marketing goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your marketing goals? Include information about what you hope to achieve with your marketing efforts, as well as when and how you will achieve it.
- What marketing strategies will you use? Include information about public relations, advertising, social media, and other marketing tactics you will use to reach your target market.
- What tactics will you use? Include information about specific actions you will take to execute your marketing strategy. For example, if you are using social media to reach your target market, include information about which platforms you will use and how often you will post.
Your marketing strategy should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Make sure your product, service, and/or program offering is clearly defined and differentiated from your competitors, including the benefits of using your service.
- Price : How do you determine the price for your product, services, and/or programs? You should also include a pricing strategy that takes into account what your target market will be willing to pay and how much the competition within your market charges.
- Place : Where will your target market find you? What channels of distribution will you use to reach them?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target market? You can use social media or write a blog, create an email marketing campaign, post flyers, pay for advertising, launch a direct mail campaign, etc.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your marketing strategy might include partnering with local job centers and adult education programs to reach potential participants. You might also promote the program through local media outlets and community organizations.
Your marketing plan should also include a sales strategy, which includes information about how you will generate leads and convert them into customers.
You should also include information about your paid advertising budget, including an estimate of expenses and sales projections.
This part of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your products, services and/or programs to your target market? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for collecting and storing food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- How will your nonprofit be structured? For example, will you have paid staff or volunteers? How many employees will you need? What skills and experience will they need to have?
- What kind of facilities and equipment will you need to operate your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need space to hold classes, as well as computers and other office equipment.
- What are the day-to-day operations of your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for accepting and sorting food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- Who will be responsible for each task? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need to identify who will be responsible for recruiting participants, teaching classes, and placing graduates in jobs.
- What are your policies and procedures? You will want to establish policies related to everything from employee conduct to how you will handle donations.
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is the section of the business plan where you elaborate on the day-to-day execution of your nonprofit. This is where you really get into the nitty-gritty of how your organization will function on a day-to-day basis.
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about the individuals who will be running your organization.
- Who is on your team? Include biographies of your executive director, board of directors, and key staff members.
- What are their qualifications? Include information about their education, work experience, and skills.
- What are their roles and responsibilities? Include information about what each team member will be responsible for, as well as their decision-making authority.
- What is their experience in the nonprofit sector? Include information about their work with other nonprofits, as well as their volunteer experiences.
This section of your plan is important because it shows that you have a team of qualified individuals who are committed to the success of your nonprofit.
Nonprofit Financial Plan
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- Your budget. Include information about your income and expenses, as well as your fundraising goals.
- Your sources of funding. Include information about your grants, donations, and other sources of income.
- Use of funds. Include information about how you will use your income to support your programs and operations.
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your organization’s finances. It also shows that you have a plan for raising and managing your funds.
Now, include a complete and detailed financial plan. This is where you will need to break down your expenses and revenue projections for the first 5 years of operation. This includes the following financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how will you generate revenue?
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, what is the net income or loss?
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Revenues | $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 |
| $ 336,090 | $ 450,940 | $ 605,000 | $ 811,730 | $ 1,089,100 | |
| Direct Cost | |||||
| Direct Costs | $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 |
| $ 67,210 | $ 90,190 | $ 121,000 | $ 162,340 | $ 217,820 | |
| $ 268,880 | $ 360,750 | $ 484,000 | $ 649,390 | $ 871,280 | |
| Salaries | $ 96,000 | $ 99,840 | $ 105,371 | $ 110,639 | $ 116,171 |
| Marketing Expenses | $ 61,200 | $ 64,400 | $ 67,600 | $ 71,000 | $ 74,600 |
| Rent/Utility Expenses | $ 36,400 | $ 37,500 | $ 38,700 | $ 39,800 | $ 41,000 |
| Other Expenses | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,200 | $ 9,400 | $ 9,500 |
| $ 202,800 | $ 210,940 | $ 220,871 | $ 230,839 | $ 241,271 | |
| EBITDA | $ 66,080 | $ 149,810 | $ 263,129 | $ 418,551 | $ 630,009 |
| Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| EBIT | $ 60,880 | $ 144,610 | $ 257,929 | $ 413,351 | $ 625,809 |
| Interest Expense | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 | $ 7,600 |
| $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 | |
| Taxable Income | $ 53,280 | $ 137,010 | $ 250,329 | $ 405,751 | $ 618,209 |
| Income Tax Expense | $ 18,700 | $ 47,900 | $ 87,600 | $ 142,000 | $ 216,400 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 | |
| 10% | 20% | 27% | 32% | 37% | |
Balance Sheet
Include a balance sheet that shows what you have in terms of assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Cash | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
| Other Current Assets | $ 41,600 | $ 55,800 | $ 74,800 | $ 90,200 | $ 121,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $ 146,942 | $ 244,052 | $ 415,681 | $ 687,631 | $ 990,278 |
| Fixed Assets | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 25,000 |
| Accum Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 10,400 | $ 15,600 | $ 20,800 | $ 25,000 |
| Net fixed assets | $ 19,800 | $ 14,600 | $ 9,400 | $ 4,200 | $ 0 |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
| Current Liabilities | $ 23,300 | $ 26,100 | $ 29,800 | $ 32,800 | $ 38,300 |
| Debt outstanding | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 108,862 | $ 0 |
| $ 132,162 | $ 134,962 | $ 138,662 | $ 141,662 | $ 38,300 | |
| Share Capital | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Retained earnings | $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 |
| $ 34,580 | $ 123,690 | $ 286,419 | $ 550,170 | $ 951,978 | |
| $ 166,742 | $ 258,652 | $ 425,081 | $ 691,831 | $ 990,278 | |
Cash Flow Statement
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include:
- Income : All of the revenue coming in from clients.
- Expenses : All of your monthly bills and expenses. Include operating, marketing and capital expenditures.
- Net Cash Flow : The difference between income and expenses for each month after they are totaled and deducted from each other. This number is the net cash flow for each month.
Using your total income and expenses, you can project an annual cash flow statement. Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup nonprofit.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
| Net Income (Loss) | $ 34,580 | $ 89,110 | $ 162,729 | $ 263,751 | $ 401,809 |
| Change in Working Capital | $ (18,300) | $ (11,400) | $ (15,300) | $ (12,400) | $ (25,300) |
| Plus Depreciation | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 5,200 | $ 4,200 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $ 21,480 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 380,709 |
| Fixed Assets | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | $ (25,000) | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Equity | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 |
| Cash from Debt financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $ 108,862 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ (108,862) |
| Net Cash Flow | $ 105,342 | $ 82,910 | $ 152,629 | $ 256,551 | $ 271,847 |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $ 0 | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 |
| Cash at End of Period | $ 105,342 | $ 188,252 | $ 340,881 | $ 597,431 | $ 869,278 |
Fundraising Plan
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your fundraising goals? Include information about how much money you hope to raise, as well as when and how you will raise it.
- What fundraising strategies will you use? Include information about special events, direct mail campaigns, online giving, and grant writing.
- What fundraising tactics will you use? Include information about volunteer recruitment, donor cultivation, and stewardship.
Now include specific fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics. These could be annual or multi-year goals. Below are some examples:
Goal : To raise $50,000 in the next 12 months.
Strategy : Direct mail campaign
- Create a mailing list of potential donors
- Develop a direct mail piece
- Mail the direct mail piece to potential donors
Goal : To raise $100,000 in the next 24 months.
Strategy : Special event
- Identify potential special event sponsors
- Recruit volunteers to help with the event
- Plan and execute the special event
Goal : To raise $250,000 in the next 36 months.
Strategy : Grant writing
- Research potential grant opportunities
- Write and submit grant proposals
- Follow up on submitted grants
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your fundraising goals and how you will achieve them.
You will also want to include an appendix section which may include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your nonprofit’s policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- A list of your hard assets and equipment with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- A list of your soft assets with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- Biographies and/or resumes of the key members of your organization
- Your nonprofit’s bylaws
- Your nonprofit’s articles of incorporation
- Your nonprofit’s most recent IRS Form 990
- Any other relevant information that may be helpful in understanding your organization
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and grow your nonprofit organization. It not only outlines your vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. Sometimes it may be difficult to get started, but once you get the hang of it, writing a business plan becomes easier and will give you a sense of direction and clarity about your nonprofit organization.
Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Other helpful articles.
How to Write a Grant Proposal for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template & Examples
How To Create the Articles of Incorporation for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template
How to Develop a Nonprofit Communications Plan + Template
How to Write a Stand-Out Purpose Statement + Examples
Charitable Blog
Everything you need to know about Charitable and our team.

How to Write a Non-Profit Business Plan
Last updated on
So you’ve got a big idea and an even bigger heart, and you’re eager to get your non-profit started ASAP. Not so fast! Without a plan, it’ll be tough to gain momentum for your mission. Before you start printing out flyers and soliciting donors, take the time to learn how to write a non-profit business plan that will set you up for success.
What is a business plan?
Before we get into the details of how to write a business plan, let’s define what it is. A business plan details the services or products your non-profit provides, the people on your team, the community you serve, your non-profit’s financials, the goals you plan to achieve, and how you’re going to achieve them.
But wait … is a non-profit a business?
“But my non-profit doesn’t sell anything!” you might object. While that may be true if you rely strictly on grants or donations, non-profits can and do sell goods and services. And a non-profit is still considered a type of business. Here’s how Investopedia defines a business :
“An organization or enterprising entity engaged in commercial, industrial, or professional activities. Businesses can be for-profit entities or non-profit organizations that operate to fulfill a charitable mission or further a social cause.”
Why does my non-profit need a business plan?
There are several reasons why a non-profit needs a business plan, including:
- It increases your chances of success. Research shows that businesses with a plan grow faster and are less likely to fail.
- It can help you reach your goals. One study found you are more likely to achieve your goals when you write them down.
- It helps you get a business loan. Getting a business loan as a non-profit is hard enough as it is. Boost your chances of getting approved by showing that you have a plan in place for paying that loan back.
- It helps you win grants. Many non-profits rely on grants to make an impact. Having a business plan will show that you’re a legitimate non-profit with a strategy to achieve your goals.
- It can attract board members. Before anyone comes on board, they want to make sure they’re getting into something stable and primed for growth. Hand a potential board member your business plan to reassure them that you’ve carefully thought through every aspect of your organization.

The parts of a non-profit business plan, with examples of each
Before you begin writing any sections of your business plan, ask yourself this: “Who is my audience?” If you’re writing a business plan to keep you on track to reach your goals, that’s one thing. But if you’re writing a business plan to persuade a banker to give you a business loan, that’s another. For the latter, for example, you might want to have a more detailed financial section that makes a strong case for your solvency. It’s good to have more than one version of your business plan, each catering to a specific audience.
Executive Summary
Think of it as the who, what, when, where, how, and why of your nonprofit. Start by answering the following questions:
- Who is on your non-profit’s team? Who does your non-profit serve?
- What does your non-profit do? What does it provide or sell? What are its goals?
- When was it established?
- Where is it located?
- How do you plan to reach your goals? How do you plan to get funding/donations?
- Why does your non-profit exist? This is the perfect place for your mission statement.
Below is an excerpt from the executive summary of Culina’s business plan . It does a great job of answering all of the above questions concisely.
“Fast Facts: Founded: 2013 Headquarters: San Francisco, CA Founder: Kent McClure Market Size: $12.5 billion Target Audience: Homeowners; property managers; insurance providers.
Quick Description: Culina is a San Francisco-based IoT and home automation company. We design an advanced smart hub technology that enables users to interconnect and remotely monitor all of their cooking devices and kitchen appliances through a single user-friendly platform.
Our Mission: To make homes smarter, more connected, and safer for families while helping them save money and conserve energy through the power of affordable, automated technology.”
Products, Programs, and Services
In this section, describe the ways you’ll raise money and serve your community. Be as detailed as possible. Below is an example from Bplans’ nonprofit catering business template for a fictional business called Catering for Kids. Notice how it details every menu item, instead of keeping it general.
“Food Product Descriptions
Boxed lunches: a sandwich or salad with dressing packet, deli salad (i.e. pasta salad or cottage cheese, cinnamon and fresh fruit), fresh seasonal fruit, chips and a cookie. Sandwich or salad options will include:
- Roast beef and havarti dill sandwich;
- Avocado, smoked turkey, lettuce and tomato sandwich;
- Chicken caesar salad sandwich;
- Chicken salad with red grapes croissant sandwich;
- Garden hummus and provolone sandwich;
- Hawaiian sunrise with turkey ham;
- Pear, walnut and goat cheese salad.”
Customer and Market Analysis
As with any business, you need to prove that there is a market for your non-profit.
In this section, describe the customers you serve, including demographics such as income, location, and education level. How many potential customers are there? What are their needs? And how will you meet them?
This is where you prove there is a big enough pool of people and a big enough need so that you can make revenue and make a difference.
For inspiration, here’s an excerpt from a children’s non-profit in Mozambique :
“Seed of Hope’s program reaches around 100 children, boys and girls ages 3 to 18 years old, from three neighboring communities of Maputo. Many of these children are workers in the dump, leaving them without the economic means to go to school. The project also reaches about 25 adults and youth who are workers of Hulene Dumps, of which some are homeless.”
Organizational/Team
This is where you list and describe the important members of your team and their roles. Make sure to include details that highlight how their experience will help your non-profit achieve its goals.
Here’s an example:
“ Mary Johnson has been appointed as the events coordinator for [Non-profit Name]. With more than 10 years of experience planning fundraising events in the mental health space, Mrs. Johnson has the skills and network to help us end mental illness stigma and reach our goal of $250,000 in donations within the next 12 months. She is already responsible for helping us reach 30% of that goal thus far.”
Operational Plan
As its name suggests, this section will describe how your non-profit will operate, including the legal structure, organizational structure, management team, location, product development, inventory, and any other processes you have in place for the products, programs, or services you’ll provide.
Here’s an example from Way to Work’s business plan :
“Goodwill will hire a full-time program manager whose sole responsibility is the day-to-day management of the Way to Work direct services and its three member staff. The Way to Work program manager and staff will be located in Elizabethtown at a location yet to be determined. The program manager will report directly to Goodwill’s regional manager of Program Services.”
Marketing Plan
Marketing will be crucial to achieving your non-profit’s mission because it’s how customers and donors alike will learn about what you do and how you help the community. In this section, come up with a detailed plan for how you will get the word out about your non-profit and how you will attract customers and donors to your cause.
Here’s an example from Bplans’ non-profit law business plan , written for a fictional law firm called Advocates for Legal Equal Access:
“Al will use his marketing skills learned in his MBA studies to market Advocates as an organization that offers public interest support for the greater Portland community. Approximately 40% of Al’s time will be spent fundraising/marketing. A lot of this time will be spent traveling around and meeting with the different leaders of the organizations and convincing them that Advocates is a well run organization, deserving of the company’s support.”
Notice how granular it gets, even specifying the percentage of time Al will spend on fundraising and marketing.
Email marketing is a critical part of any modern non-profit’s marketing strategy. Find out why with our non-profit email marketing guide .
Impact Plan
Unlike for-profit business plans, your non-profit business plan will have a section on impact. This is where you will talk about your overall vision. How do you hope to change your community for the better? And get specific: What does “better” look like?
A great example of a detailed impact plan is from Kroger’s Zero Hunger | Zero Waste social impact plan . Though not part of a business plan, it features precisely the kind of detail needed in a nonprofit business plan. It begins with a clear, concise goal: “Kroger’s plan: To end hunger in our communities and eliminate waste in our company by 2025.” And it’s backed up by specific action steps, such as:
- “Establish a $10 million innovation fund through The Kroger Co. Foundation
- Accelerate food donations to give 3 billion meals by 2025
- Donate not just more food, more balanced meals”
Financial Plan
Here, you will include your current funding, revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. You can add graphs to make it more comprehensive, as well as include financial projections. This section is especially important if you’re soliciting donors or trying to get a bank loan.
If you have additional supporting documents you’d like to add to your non-profit business plan, you can add it at the end in the appendix. Here, you can insert brochures, annual reports, or strategic plans.
Free non-profit business plan templates
If you need more inspiration for your non-profit business plan, check out some of these free samples and templates:
- Google Doc template – To edit this, go to File > Make a copy.
- Bplans non-profit sample business plans
- Upmetrics nonprofit business plan templates
- Turning Stones Coaching business plan templates
For success in the future, get started on your non-profit business plan today
Having a business plan for your non-profit comes with a ton of benefits, including keeping you aligned with your mission, increasing your chances for success, and attracting major donors.
And now that you know how to write a business plan, you can see it doesn’t have to be a tedious, drawn-out process! In fact, the simpler, the better. Start with one of the free templates recommended above, and soon, you’ll be well on your way to a complete roadmap to success.
Start collecting donations with WordPress today
Join 10,000+ non-profits raising more money online with Charitable.
Disclosure: Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. We only recommend products that we believe will add value to our readers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get free tips and resources right in your inbox, along with 60,000+ others
Join our newsletter.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Popular Resources
Recurring Donations
Donor Management
Peer-to-Peer Fundraising
Integrations
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

Angelique O'Rourke
13 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024

Believe it or not, creating a business plan for a nonprofit organization is not that different from planning for a traditional business.
Nonprofits sometimes shy away from using the words “business planning,” preferring to use terms like “strategic plan” or “operating plan.” But, the fact is that preparing a plan for a for-profit business and a nonprofit organization are actually pretty similar processes. Both types of organizations need to create forecasts for revenue and plan how they’re going to spend the money they bring in. They also need to manage their cash and ensure that they can stay solvent to accomplish their goals.
In this guide, I’ll explain how to create a plan for your organization that will impress your board of directors, facilitate fundraising, and ensures that you deliver on your mission.
- Why does a nonprofit need a business plan?
Good business planning is about setting goals, getting everyone on the same page, tracking performance metrics, and improving over time. Even when your goal isn’t to increase profits, you still need to be able to run a fiscally healthy organization.
Business planning creates an opportunity to examine the heart of your mission , the financing you’ll need to bring that mission to fruition, and your plan to sustain your operations into the future.
Nonprofits are also responsible for meeting regularly with a board of directors and reporting on your organization’s finances is a critical part of that meeting. As part of your regular financial review with the board, you can compare your actual results to your financial forecast in your business plan. Are you meeting fundraising goals and keeping spending on track? Is the financial position of the organization where you wanted it to be?
In addition to internal use, a solid business plan can help you court major donors who will be interested in having a deeper understanding of how your organization works and your fiscal health and accountability. And you’ll definitely need a formal business plan if you intend to seek outside funding for capital expenses—it’s required by lenders.
Creating a business plan for your organization is a great way to get your management team or board to connect over your vision, goals, and trajectory. Even just going through the planning process with your colleagues will help you take a step back and get some high-level perspective .
- A nonprofit business plan outline
Keep in mind that developing a business plan is an ongoing process. It isn’t about just writing a physical document that is static, but a continually evolving strategy and action plan as your organization progresses over time. It’s essential that you run regular plan review meetings to track your progress against your plan. For most nonprofits, this will coincide with regular reports and meetings with the board of directors.
A nonprofit business plan will include many of the same sections of a standard business plan outline . If you’d like to start simple, you can download our free business plan template as a Word document, and adjust it according to the nonprofit plan outline below.
Executive summary
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That’s because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan – the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization.
Write it as though you might share with a prospective donor, or someone unfamiliar with your organization: avoid internal jargon or acronyms, and write it so that someone who has never heard of you would understand what you’re doing.
Your executive summary should provide a very brief overview of your organization’s mission. It should describe who you serve, how you provide the services that you offer, and how you fundraise.
If you are putting together a plan to share with potential donors, you should include an overview of what you are asking for and how you intend to use the funds raised.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Opportunity
Start this section of your nonprofit plan by describing the problem that you are solving for your clients or your community at large. Then say how your organization solves the problem.
A great way to present your opportunity is with a positioning statement . Here’s a formula you can use to define your positioning:
For [target market description] who [target market need], [this product] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [key competition], it [most important distinguishing feature].
And here’s an example of a positioning statement using the formula:
For children, ages five to 12 (target market) who are struggling with reading (their need), Tutors Changing Lives (your organization or program name) helps them get up to grade-level reading through a once a week class (your solution).
Unlike the school district’s general after-school homework lab (your state-funded competition), our program specifically helps children learn to read within six months (how you’re different).
Your organization is special or you wouldn’t spend so much time devoted to it. Layout some of the nuts and bolts about what makes it great in this opening section of your business plan. Your nonprofit probably changes lives, changes your community, or maybe even changes the world. Explain how it does this.
This is where you really go into detail about the programs you’re offering. You’ll want to describe how many people you serve and how you serve them.
Target audience
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be used to define your target market . For nonprofit organizations, it’s basically the same thing but framed as who you’re serving with your organization. Who benefits from your services?
Not all organizations have clients that they serve directly, so you might exclude this section if that’s the case. For example, an environmental preservation organization might have a goal of acquiring land to preserve natural habitats. The organization isn’t directly serving individual groups of people and is instead trying to benefit the environment as a whole.
Similar organizations
Everyone has competition —nonprofits, too. You’re competing with other nonprofits for donor attention and support, and you’re competing with other organizations serving your target population. Even if your program is the only one in your area providing a specific service, you still have competition.
Think about what your prospective clients were doing about their problem (the one your organization is solving) before you came on this scene. If you’re running an after-school tutoring organization, you might be competing with after school sports programs for clients. Even though your organizations have fundamentally different missions.
For many nonprofit organizations, competing for funding is an important issue. You’ll want to use this section of your plan to explain who donors would choose your organization instead of similar organizations for their donations.
Future services and programs
If you’re running a regional nonprofit, do you want to be national in five years? If you’re currently serving children ages two to four, do you want to expand to ages five to 12? Use this section to talk about your long-term goals.
Just like a traditional business, you’ll benefit by laying out a long-term plan. Not only does it help guide your nonprofit, but it also provides a roadmap for the board as well as potential investors.
Promotion and outreach strategies
In a for-profit business plan, this section would be about marketing and sales strategies. For nonprofits, you’re going to talk about how you’re going to reach your target client population.
You’ll probably do some combination of:
- Advertising: print and direct mail, television, radio, and so on.
- Public relations: press releases, activities to promote brand awareness, and so on.
- Digital marketing: website, email, blog, social media, and so on.
Similar to the “target audience” section above, you may remove this section if you don’t promote your organization to clients and others who use your services.
Costs and fees
Instead of including a pricing section, a nonprofit business plan should include a costs or fees section.
Talk about how your program is funded, and whether the costs your clients pay are the same for everyone, or based on income level, or something else. If your clients pay less for your service than it costs to run the program, how will you make up the difference?
If you don’t charge for your services and programs, you can state that here or remove this section.
Fundraising sources
Fundraising is critical for most nonprofit organizations. This portion of your business plan will detail who your key fundraising sources are.
Similar to understanding who your target audience for your services is, you’ll also want to know who your target market is for fundraising. Who are your supporters? What kind of person donates to your organization? Creating a “donor persona” could be a useful exercise to help you reflect on this subject and streamline your fundraising approach.
You’ll also want to define different tiers of prospective donors and how you plan on connecting with them. You’re probably going to include information about your annual giving program (usually lower-tier donors) and your major gifts program (folks who give larger amounts).
If you’re a private school, for example, you might think of your main target market as alumni who graduated during a certain year, at a certain income level. If you’re building a bequest program to build your endowment, your target market might be a specific population with interest in your cause who is at retirement age.
Do some research. The key here is not to report your target donors as everyone in a 3,000-mile radius with a wallet. The more specific you can be about your prospective donors —their demographics, income level, and interests, the more targeted (and less costly) your outreach can be.
Fundraising activities
How will you reach your donors with your message? Use this section of your business plan to explain how you will market your organization to potential donors and generate revenue.
You might use a combination of direct mail, advertising, and fundraising events. Detail the key activities and programs that you’ll use to reach your donors and raise money.
Strategic alliances and partnerships
Use this section to talk about how you’ll work with other organizations. Maybe you need to use a room in the local public library to run your program for the first year. Maybe your organization provides mental health counselors in local schools, so you partner with your school district.
In some instances, you might also be relying on public health programs like Medicaid to fund your program costs. Mention all those strategic partnerships here, especially if your program would have trouble existing without the partnership.
Milestones and metrics
Without milestones and metrics for your nonprofit, it will be more difficult to execute on your mission. Milestones and metrics are guideposts along the way that are indicators that your program is working and that your organization is healthy.
They might include elements of your fundraising goals—like monthly or quarterly donation goals, or it might be more about your participation metrics. Since most nonprofits working with foundations for grants do complex reporting on some of these, don’t feel like you have to re-write every single goal and metric for your organization here. Think about your bigger goals, and if you need to, include more information in your business plan’s appendix.
If you’re revisiting your plan on a monthly basis, and we recommend that you do, the items here might speak directly to the questions you know your board will ask in your monthly trustee meeting. The point is to avoid surprises by having eyes on your organization’s performance. Having these goals, and being able to change course if you’re not meeting them, will help your organization avoid falling into a budget deficit.
Key assumptions and risks
Your nonprofit exists to serve a particular population or cause. Before you designed your key programs or services, you probably did some research to validate that there’s a need for what you’re offering.
But you probably are also taking some calculated risks. In this section, talk about the unknowns for your organization. If you name them, you can address them.
For example, if you think there’s a need for a children’s literacy program, maybe you surveyed teachers or parents in your area to verify the need. But because you haven’t launched the program yet, one of your unknowns might be whether the kids will actually show up.
Management team and company
Who is going to be involved and what are their duties? What do these individuals bring to the table?
Include both the management team of the day-to-day aspects of your nonprofit as well as board members and mention those who may overlap between the two roles. Highlight their qualifications: titles, degrees, relevant past accomplishments, and designated responsibilities should be included in this section. It adds a personal touch to mention team members who are especially qualified because they’re close to the cause or have special first-hand experience with or knowledge of the population you’re serving.
There are probably some amazing, dedicated people with stellar qualifications on your team—this is the place to feature them (and don’t forget to include yourself!).
Financial plan
The financial plan is essential to any organization that’s seeking funding, but also incredibly useful internally to keep track of what you’ve done so far financially and where you’d like to see the organization go in the future.
The financial section of your business plan should include a long-term budget and cash flow statement with a three to five-year forecast. This will allow you to see that the organization has its basic financial needs covered. Any nonprofit has its standard level of funding required to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will consistently maintain at least that much in the coffers.
From that point, it’s all about future planning: If you exceed your fundraising goals, what will be done with the surplus? What will you do if you don’t meet your fundraising goals? Are you accounting for appropriate amounts going to payroll and administrative costs over time? Thinking through a forecast of your financial plan over the next several years will help ensure that your organization is sustainable.
Money management skills are just as important in a nonprofit as they are in a for-profit business. Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public is ranking the credibility of charities based on what percentage of donations makes it to the programs and services. As a nonprofit, people are interested in the details of how money is being dispersed within organizations, with this information often being posted online on sites like Charity Navigator, so the public can make informed decisions about donating.
Potential contributors will do their research—so make sure you do too. No matter who your donors are, they will want to know they can trust your organization with their money. A robust financial plan is a solid foundation for reference that your nonprofit is on the right track.
- Business planning is ongoing
It’s important to remember that a business plan doesn’t have to be set in stone. It acts as a roadmap, something that you can come back to as a guide, then revise and edit to suit your purpose at a given time.
I recommend that you review your financial plan once a month to see if your organization is on track, and then revise your plan as necessary .
Angelique is a skilled writer, editor, and social media specialist, as well as an actor and model with a demonstrated history of theater, film, commercial and print work.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

11 Min. Read
Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

14 Min. Read
How to Write a Five-Year Business Plan

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Write a Nonprofit Business Plan (2024)
Learn how to write nonprofit business plans with detailed sections and examples. Use this nonprofit business plan template to get it done faster.

While businesses exist primarily to make a profit, nonprofits instead serve the public good for charitable, religious, educational, or other public service reasons. Starting a business as a nonprofit organization is an excellent way to impact positive change for a cause you care about. Plus, nonprofits are exempt from federal and state taxes on any income earned, unlike for-profit corporations. So there are also financial benefits.
If you’re just getting started with your nonprofit idea, one of the first things you’ll want to document is your nonprofit business plan. Below, we’ll take you through your nonprofit business plan, section by section, using this business plan template and guide as a base.
What is a nonprofit business plan?
A nonprofit needs a plan, just like any other business. But there’s a big difference: while most businesses aim to make profits for their owners or shareholders, a nonprofit’s main goal is to make a positive impact on a particular cause or in the community. The nonprofit business plan aims to achieve that mission while keeping the organization running and paying its bills.
Why do you need a nonprofit business plan
At its core, a nonprofit business plan provides a clear mission and vision for the organization. It lays out where the organization is headed and the steps to get there. Some other benefits of a nonprofit business plan include:
- Helping to set priorities and allocate resources to reach the nonprofit’s goals.
- Deciding where funds will come from, be it donors, sponsors, or grant-making institutions.
- Outlining the operational details, from roles and responsibilities to day-to-day activities.
- Identifying risks and highlighting strategies to mitigate them.
For a nonprofit to have a lasting impact, it needs to outline strategies for long-term funding and growth. You want to make sure the organization has a clear direction, works efficiently, communicates well with stakeholders, and stays adaptable and sustainable—all of which you can find in a nonprofit business plan.
How to write a nonprofit business plan
- Create an executive summary
- Write an organization description
- Conduct market analysis
- Outline management and organization
- Describe programs, products, and services
- Document customer segmentation
- Create a marketing plan
- Create a logistics and operations plan
- Write an impact plan
- Outline the financial plan
1. Create an executive summary
The first section of nonprofit business plans is the executive summary . The executive summary should describe your organization and the contents of your nonprofit business plan. This section should be no more than a page, briefly covering the following:
- Concept. What does your nonprofit organization do?
- Goals and vision. What does your nonprofit want to do?
- Product description and differentiation. What do you sell, and why is it different?
- Target market. Who do you sell to and raise money from? Who do you serve?
- Marketing strategy. How do you plan on reaching your audience?
- Current and projected financial state. What do you currently earn through fundraising? What do you foresee earning through fundraising?
- The ask. How much money are you asking for?
- The team. Who’s involved in the organization?
- The document. What can your audience expect from the following sections of your nonprofit business plan? Which highlights should they be excited about?

2. Write an organization description
The second section of your nonprofit business plan is the description of your organization. While the executive summary sets the stage for the business plan document, the organization description is a summary focused on your organization and what it does and aspires to do. Use this section to identify the industry or niche your organization operates in.
Here, you’ll want to identify the structure of your organization. A nonprofit is a tax-exempt, non-business entity that invests excess funds back into the mission. For nonprofits, you’ll typically register as a 501(c)(3), but you’ll also need to choose your business structure from the following list:
- Unincorporated association. This is the S corporation for nonprofits—you don’t need to file any paperwork. Many nonprofits start out as unincorporated associations.
- Trust. The first structure for nonprofits, this mandates all the organization’s assets be given to charitable use.
- Corporation. This structure offers the most protection from liabilities but also comes with some extra paperwork and fees.
- Limited liability company (LLC) . LLCs offer both tax benefits and limited fees, but not as much protection as a corporation. All members of the LLC must be 501(c)(3) organizations. See our state specific guides for California LLC , Texas LLC and Florida LLC .
The organization description should also include the following elements:
Mission and vision statement
Your mission and vision statement serve as the foundation for why your nonprofit exists, and this “why” influences your decision making. It’s also an effective tool for connecting with your audience and reaching your organization’s full potential.
Outdoor brand Cotopaxi also has a nonprofit arm— the Cotopaxi Foundation . The brand and nonprofit each have their own mission statements, published boldly on the company’s website:
Keep your mission statement on the shorter side (one to two sentences) and use your vision statement to expand on the ideas.
Value proposition
Your value proposition tells people why they should choose to support your nonprofit over other ones. It essentially outlines your unique selling proposition , or competitive advantage for what sets you apart from the competition.
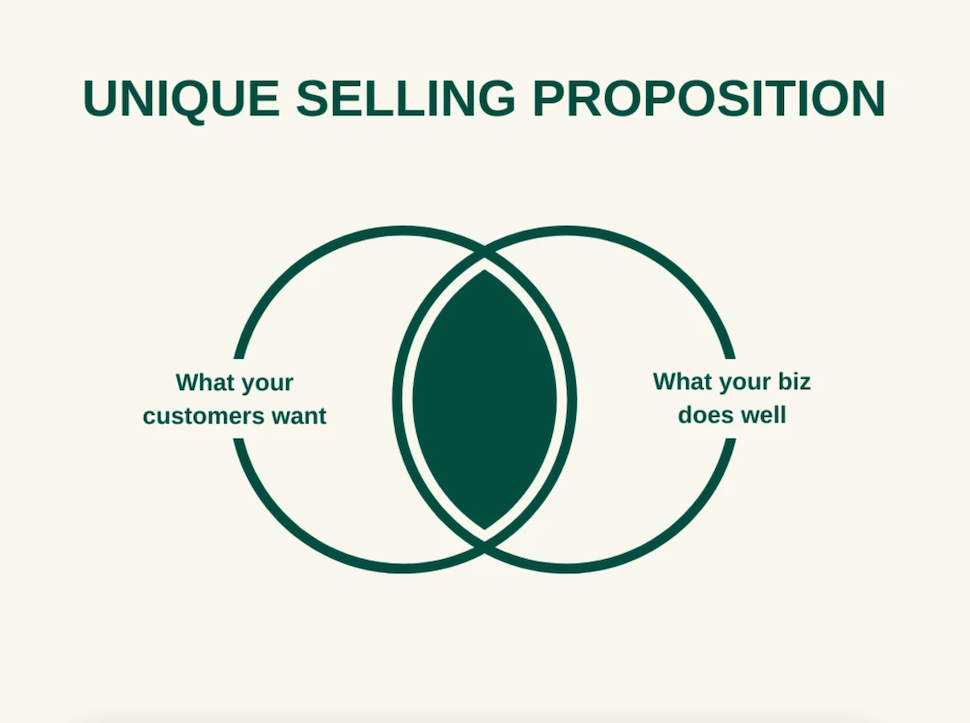
Short- and long-term goals
Your nonprofit business plan should also include measurable short- and long-term goals. Cotopaxi, for example, makes no secret of both its socially driven and business-minded goals through the Cotopaxi Foundation:
You’ll also want to highlight the people behind your organization. This information shows you have enough people to make the nonprofit a success. Nonprofits typically have a few different “teams,” including a board of directors, paid staff, and maybe even volunteers. There may also be key donors who are worth noting here, as well as key people who you plan to help through your organization.
Re:new is a community of refugee artisans and students, volunteers, staff, and board members. It raises money by selling handcrafted products made by refugees from around the world. On its website, Re:new shares information about some of the people behind the organization, including board members, artisans, and paid staff.

For your business plan, outline how those board members are chosen and what their involvement is, salaries and roles for paid staff members, and payment information for the artisans. Remember to note this information in your nonprofit business plan as well.
3. Conduct market analysis
The market analysis section of your nonprofit business plan demonstrates that you’ve done research to determine there is a need for your services and people who will potentially support your mission. Here, you’re essentially determining how big your potential market is.
There are a few key ways to get information about your market:
- Check government census data. Visit official websites such as the US Census Bureau to get the latest statistics. Filter the data to match your nonprofit’s target demographic. For example, if your nonprofit is aiming to help homeless youth, determine how many young people are homeless or at risk in your region.
- Conduct a competitive analysis . Identify similar nonprofits or organizations in your area. Study their services, target audience, and how they communicate their mission, and include your findings in the business plan.
- Research industry trends and trajectory. Subscribe to newsletters, join nonprofit forums, and attend seminars or webinars focused on your sector. Stay updated on the latest trends.
- Make educated guesses based on your experience and research. While hard data is important, there will be times where you have to rely on intuition. Ensure these guesses are always grounded in some form of research or past experience.
Organize a brainstorming session with your team to map out the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) . Make sure it’s comprehensive and considers both internal and external factors.
4. Outline management and organization
Every organization needs people to run it. When it comes to nonprofits, this typically involves the following groups of people:
- Board of directors. Nonprofits typically have a board of directors or leadership team. Give Merit, for example, might include its leadership team in this section.
- Staff. These people are your paid employees. Include roles, responsibilities, salaries, etc.
- Volunteers. You may or may not have specific people in mind for these volunteer roles. Some nonprofits have different tiers of volunteers—maybe lead volunteers or volunteer coordinators. Make note of these individuals, if relevant.
- Donors/customers. If you have any significant or notable donors who plan to make sizable contributions, include them in this section of your nonprofit business plan.
- Recipients. These are the people who you’re planning to help. This may not always be a person (as is the case with environmentally driven nonprofits, for example). Sometimes this is a group of people and sometimes this is a specific person.
Sometimes these groups overlap. The Empowerment Plan, for example, actually hires the people it helps—one of the organization’s main pillars.
5. Describe programs, products, and services
Your programs, products, and services section sums up what your organization offers. These offerings include everything for customers, donors, volunteers, and recipients.
For example, Merit sells products as a brand on its website and then donates the proceeds of its sales to its nonprofit, Give Merit . So Merit would note all of these things in this section of its nonprofit business plan.
If you operate like Merit, consider diversifying how you generate funds. Selling products and then donating the proceeds is one method. You can also explore direct donations, sponsorship deals, and grants.

6. Document customer segmentation
You can pull from your management and organization section for your customer segmentation, as some of these groups represent your customers as well.
For example, your volunteers are one key customer segment and your donors are another. Within each of these segments, you’ll want to drill down further into smaller segments so you can build targeted campaigns to recruit volunteers and/or donors when needed.
When documenting your customer segments in your nonprofit business plan, add the following information:
- Where they live
- Level of education
- How they spend their free time
- Where they work
- How much they earn
- What technology they use
- Their values, beliefs, and opinions
- Common behavior patterns
7. Create a marketing plan
Your marketing plan outlines how you plan to spread the word about your nonprofit organization. Marketing may include attracting donors, volunteers, and/or customers, depending how your nonprofit operates.
The four main components of this section of your nonprofit business plan are:
- Price. How much do your products cost, and why have you made that decision? If you don’t sell products, you might outline different tiers of donorship.
- Product. What are you selling and how do you differentiate it in the market? Again, if you don’t plan to sell products, outline what you plan to provide to both donors and recipients.
- Promotion. How will you get your cause in front of your ideal customer? How will you connect with recipients?
- Place. Where will you sell your products or share information about your organization? Will this be online, in person, or both?
8. Create a logistics and operations plan
The logistics and operations section of your nonprofit business plan outlines how you plan to raise money and execute your mission. Add a few key sections:
- Suppliers. This could refer to the suppliers for products you sell, as well as donors who contribute financially. You might also include fundraising organizers. One Tree Planted , for example, allows volunteers to run their own independent fundraisers .
- Production. If you’re selling products to raise money for your nonprofit, this part outlines whether you manufacture yourself, purchase wholesale, or use a dropshipping company.
- Facilities. Where will your organization operate? You might outline where headquarters is, as well as any sites or locations. This may also include storage and warehousing facilities.
- Equipment. List which tools and technology you need for your nonprofit. Remember to include everything from phones and computers to vehicles and machinery.
- Shipping and fulfillment. If you need to ship any packages, determine how you’ll do this. You may ship yourself or work with a third-party fulfillment partner.
- Inventory. Determine how much stock you’ll keep on hand (if any) and where you’ll store it, as well as how you’ll approach inventory management .
9. Write an impact plan
The impact plan is an important part of your nonprofit business plan because it outlines the change you’ll inspire in regards to your mission.
Many companies with a strong commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR) publish their own impact plans as well. Though these impact plans aren’t part of a nonprofit business plan, they serve as great reference points for drafting this section of your plan.
Sustainable clothing and shoe brand Allbirds uses its annual sustainability report to show how the company has followed through on its own environmentally conscious CSR initiatives.
For your impact plan:
- Start by clearly stating what you hope to achieve.
- Detail the actions and initiatives you’ll undertake to achieve your objectives.
- Develop indicators for each output, outcome, and impact.
Before starting your project, determine the current state or level of the issue you’re addressing. For each indicator, establish targets that you aim to achieve by specific timeframes.
10. Outline the financial plan
Every nonprofit organization needs a financial plan. This includes how you’ll collect funds, as well as how those funds will be distributed. The financial plan typically includes the following financial statements :
- Income statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
As far as potential sources of funding, you may consider the following for your nonprofit business plan:
- Self-funding. If you have the means, you may support your nonprofit organization financially yourself. You can do this personally or through a business—like how ecommerce brand Merit donates 20% of all purchases to its organization Give Merit , which funds college scholarships for underserved youth.
- Donors. You may seek financial support from organizations, businesses, and individuals. You may also use crowdfunding sites to raise funds and build buzz for your cause.
- Investors. The downside here is that you have to pay the money back, which isn’t ideal for nonprofits in particular.
- Loans . Loans also require repayment. Check with your lender to see if it offers lower interest rates or other benefits to nonprofits. Nonprofits with a Shopify store can leverage simple loans based on sales history, which may be a more hassle-free option.
- Credit cards. Credit cards typically come with high interest rates and lower limits, so be wary about the terms before you fund your organization this way.
Use this spreadsheet template , which includes everything you’ll need to create an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, including some sample numbers. You can edit it to reflect projections for your specific organization.

Make a positive change with your nonprofit business plan
Starting a nonprofit organization is an excellent way to make a difference for a cause you’re passionate about. The best way to kickstart your nonprofit organization is with a well-formulated business plan. Your nonprofit business plan will help you secure funding and build excitement for your organization.
- How to Start a Business in Texas- 8 Easy Steps
- How To Write the Perfect Business Plan in 9 Steps (2024)
- Trimming It Down- How to Create a Lean Business Plan
- 4 Major Advantages of a Sole Proprietorship
- 6 Types of Corporations- A Comparison of Business Structures
- Moving From Etsy to Shopify- An Ecommerce Migration Story
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
- Domain History - How To Check the History of a Domain Name
- How to Buy a Domain Name- Domain Registration Guide
- How to Form a Single-Member LLC
Nonprofit business plan FAQ
What should be in a nonprofit business plan.
- Executive summary
- Organization description
- Market analysis
- Management and organization
- Programs, products, and services
- Customer segmentation
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Impact plan
- Financial plan
What are the 4 types of nonprofit organizations?
- Unincorporated association
- Corporation
- Limited liability company (LLC)
How do you start a nonprofit with no money?
It doesn’t cost anything to start a nonprofit. You can start a nonprofit with no money by securing donations from external sources. You can raise money to start your nonprofit from businesses, organizations, individuals, and crowdfunding.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 28, 2024
Aug 27, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
The best nonprofit business plan template
If you’re looking to start a new charity but don’t know where to start, a nonprofit business plan template can help. There are more than 1.5 million nonprofit organizations registered in the US. While it’s awesome that there are so many charitable orgs, unfortunately, many of them struggle to keep their doors open.
Like any other business, a nonprofit needs to prepare for the unexpected. Even without a global pandemic, strategic planning is crucial for a nonprofit to succeed.
In this article, we’ll look at why a business plan is important for nonprofit organizations and what details to include in your business plan. To get you started, our versatile nonprofit business plan template is ready for you to download to turn your nonprofit dreams into a reality.
Get the template
What is a nonprofit business plan template?
A nonprofit business plan template is not that different from a regular, profit-oriented business plan template. It can even focus on financial gain — as long as it specifies how to use that excess for the greater good.
A nonprofit business plan template includes fields that cover the foundational elements of a business plan, including:
- The overarching purpose of your nonprofit
- Its long and short-term goals
- An outline of how you’ll achieve these goals
The template also controls the general layout of the business plan, like recommended headings, sub-headings, and questions. But what’s the point? Let’s dive into the benefits a business plan template offers nonprofits.
Download Excel template
Why use a nonprofit business plan template?
To get your nonprofit business plans in motion, templates can:
Provide direction
If you’ve decided to start a nonprofit, you’re likely driven by passion and purpose. Although nonprofits are generally mission-driven, they’re still businesses. And that means you need to have a working business model. A template will give your ideas direction and encourage you to put your strategic thinking cap on.
Help you secure funding
One of the biggest reasons for writing a nonprofit business plan is to attract investment. After all, without enough funding , it’s nearly impossible to get your business off the ground. There’s simply no business without capital investment, and that’s even more true for nonprofits that rarely sell products.
Stakeholders and potential investors will need to assess the feasibility of your nonprofit business. You can encourage them to invest by presenting them with a well-written, well-thought-out business plan with all the necessary details — and a template lays the right foundation.
Facilitate clear messaging
One of the essential characteristics of any business plan — nonprofits included — is transparency around what you want to achieve and how you are going to achieve it. A nebulous statement with grandiose aspirations but no practical plan won’t inspire confidence.
Instead, you should create a clear and concise purpose statement that sums up your goals and planned action steps. A good template will help you maintain a strong purpose statement and use clear messaging throughout.
Of course, there are different types of nonprofit plan templates you can use, depending on the kind of business plan you want to draw up.
What are some examples of a nonprofit business plan template?
From summary nonprofit plans to all encompassing strategies, check out a few sample business plan templates for different nonprofit use cases.

Summary nonprofit business plan template
New nonprofit ventures in the early stages of development can use this business plan template. It’s created to put out feelers to see if investors are interested in your idea. For example, you may want to start an animal shelter in your community, but aren’t sure if it’s a viable option due to a lack of funds. You’d use a summary business plan template to gauge interest in your nonprofit.
Full nonprofit business plan template
In this scenario, you have already laid the foundations for your nonprofit. You’re now at a point where you need financing to get your nonprofit off the ground.
This template is much longer than a summary and includes all the sections of a nonprofit business plan including the:
Executive summary
- Nonprofit description
- Needs analysis
- Product/service
- Marketing strategy
- Management team & board
- Human resource needs
It also typically includes a variety of documents that back up your market research and financial situation.
Operational nonprofit business plan template
This type of business plan template is extremely detail-oriented and outlines your nonprofit’s daily operations. It acts as an in-depth guide for who does what, how they should do it, and when they should do it.
An operational nonprofit business plan is written for your internal team rather than external parties like investors or board members.
Convinced to give a business plan template a go? Lucky for you, our team has created the perfect option for nonprofits.
monday.com’s nonprofit business plan template
At monday.com, we understand that starting a nonprofit business can feel overwhelming — scrambling to line up investors, arranging fundraising events, filing federal forms, and more. Because we want you and your nonprofit to succeed, we’ve created a customizable template to get you started. It’s right inside our Work OS , a digital platform that helps you effectively manage every aspect of your work — from budgets and high-level plans to individual to-do lists.

Here’s what you can do on our template:
Access all your documents from one central location
Besides a business plan, starting a nonprofit requires a lot of other documentation. Supporting documents include a cash flow statement or a general financial statement, resumes of founders, and letters of support.
monday.com’s Work OS lets you store all these essential documents in one centralized location. That means you don’t need to open several tabs or run multiple programs to view your information. On monday.com, you can quickly and easily access documents and share them with potential investors and donors. Security features also help you control access to any board or document, only letting invited people or employees view or edit them. By keeping everything in one place, you save time on tracking down rogue files or statements and can focus on what really matters, such as running your nonprofit.
Turn your business plan into action
With monday.com’s nonprofit business plan template, you can seamlessly transform your plan into actionable tasks. After all, it’s going to take more than some sound strategic planning to bring your nonprofit to life.

Based on your business plan, you have the power to create interactive vision boards, calendars, timelines, cards, charts, and more. Because delegation is key, assign tasks to any of your team members from your main board. You can even set up notification automations so that everyone stays up to date with their responsibilities. Plus, to make sure the team stays on track, you can use the Progress Tracking Column that shows you the percent to completion of tasks based on the different status columns of your board.
Keep your finger on the pulse
From budgets to customer satisfaction, you need to maintain a high-level overview of your nonprofit’s key metrics.
monday.com keeps you well-informed on the status of your nonprofit’s progress, all on one platform. With customizable dashboards — for example, a real-time overview of donations received and projects completed — and visually appealing views, you can make confident decisions on how to take your nonprofit business forward.
Now that you have the template, let’s cover each section and how to fill it out correctly.
Essential sections of a nonprofit business plan template
So what exactly goes into a nonprofit business plan? Let’s take a look at the different sections you’ll find in most templates.
This is a concise summary of your business at the beginning of your plan. It should be both inspired and to the point. The executive summary is typically two pages long and dedicates about two sentences to each section of the plan.
Organization overview
This section gives some background on your company and summarizes the goal of your business. At the same time, it should touch on other important factors like your action plan for attracting potential external stakeholders. You can think of an organization overview as a mission statement and company description rolled into one.
Products, programs, and services
Any business exists to provide products, programs, and services — perhaps with a focus on the latter two for nonprofits. Your business plan should outline what you are bringing to your community. This will influence your target market , potential investors, and marketing strategies.
Marketing plan
An effective marketing strategy is the cornerstone of any successful business. Your marketing plan will identify your target audience and how you plan to reach them. It deals with pricing structures while also assessing customer engagement levels.
Operational plan
The operational plan describes the steps a company will take over a certain period. It focuses on the day-to-day aspects of the business, like what tasks need to be done and who is responsible for what. The operational section of a business plan works closely with strategic planning.
Competitive analysis
Even nonprofits face competition from other nonprofits with similar business profiles. A market analysis looks at the strengths and weaknesses of competing businesses and where you fit in. This section should include a strategy to overtake competitors in the market. There are many formats and templates you can use here, for example, a SWOT analysis .
Financial plan
Your financial plan should be a holistic image of your company’s financial status and financial goals. As well as your fundraising plan , make sure to include details like cash flow, investments, insurance, debt, and savings.
Before we wrap up, we’ll address some commonly asked questions about nonprofit business plan templates.
FAQs about nonprofit business plan templates
How do you write a business plan for a nonprofit.
The best way to write a nonprofit business plan is with a template so that you don’t leave anything out. Our template has all the sections ready for you to fill in, combined with features of a cutting-edge Work OS.
For some extra tips, take a look at our advice on how to write a business plan . We’ve detailed the various elements involved in business planning processes and how these should be structured.
How many pages should a nonprofit business plan be?
Business plans don’t have to be excessively long. Remember that concise communication is optimal. As a rule of thumb — and this will vary depending on the complexity and size of your business plan — a nonprofit business plan is typically between seven and thirty pages long.
What is a nonprofit business plan called?
A nonprofit business plan is called just that — a ‘nonprofit business plan.’ You may think that its nonprofit element makes it very different from a profit-oriented plan. But it is essentially the same type of document.
What is the best business structure for a nonprofit?
The consensus is that a corporation is the most appropriate and effective structure for a nonprofit business.
How do you start a nonprofit with no money?
Creating a business plan and approaching potential investors, aka donators, is the best way to start a nonprofit business if you don’t have the funds yourself.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.

- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Organization Name
[PODCAST] The Recipe for Winning Virtual Meetings
Ten giving ideas more creative than cash, how to create a nonprofit business plan.
The most important thing to remember is that your nonprofit needs to be unique so it stands out from other nonprofits. Secondly, you want to convey the value that those who engage with your organization or donate money will receive. This can be making them feel charitable but also more productive and engaged. Think about the value/emotion you are hoping to evoke and convey it through your business plan.
The following sections should be included in your nonprofit business plan:
Executive Summary
Organization overview.
- Products, Programs, and Services
Industry Analysis
Customer analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team, financial plan.
Let’s break each of these down.
Start your nonprofit business plan by clearly stating your organization’s mission and describing how it plans on reaching its goals. Include a concise description of what makes your organization stand out among competitors (e.g., “We are the only non-profit animal welfare organization in XYZ county” or “Our college student volunteers provide assistance at less than half the cost as our competitors”). Succinctly communicate why people should care about your organization so they will choose to support you. Include other pertinent information about your organization such as the bios of key staff members and the amount of funding you are looking to raise.
The purpose of the executive summary is to convey key information about your organization so readers can decide whether they are interested and willing to read the rest of your plan. Keep the executive summary to one to two pages in length. Create it after completing the other sections so you can simply summarize them. But make sure you do so in an exciting and compelling manner, so readers want to read and learn more about your organization.
This section should include a description of your organization’s overall structure, beginning with who founded it and how it is currently governed. Other important information to provide includes your the nonprofit is located, how many paid/unpaid staff members there are, what facilities are available for use by customers or employees, and what kind of support services are provided (e.g., IT, HR). Lastly, explain any accomplishments your organization has achieved to-date, as the best indicator of future success is past performance.
Products/Services/Programs
In this section, write about your nonprofit’s services or programs in detail. Document the programs you offer and how they function. Provide details, sketches, etc. to clearly communicate the offerings and value your organization provides. If applicable, consider including audience testimonials that express satisfaction with your nonprofit’s offerings.
For industry analysis, address some questions and provide information that supports your answers. Consider this: how big is the industry? For example, if you provide education to high school students, discuss the market size for public and private high school education.
Also answer the following questions:
- What trends are facing the industry (positive or negative)?
- What are some of the industry challenges facing organizations?
- How can your organization help people overcome those problems?
This section should begin with a definition of who the organization considers to be its primary target market (e.g., high school students, working moms, etc.). Based on this group’s needs and wants, prioritize which benefits/offerings from your services or programs are most important to them. This section should also include facts about your supporters’ key needs and pains or other information that might be helpful for your nonprofit’s fundraising efforts.
The marketing plan should discuss how the individuals you serve are likely to find out about your organization’s services and programs along with what promotional activities will be used to reach new audiences . Outline why each activity is beneficial for growing your nonprofit and which demographic it best targets. For strategies that have already been used, provide specific figures on results achieved.
Below are sample promotional activities that many nonprofit organizations use:
Public relations
Developing relationships with the media and utilizing earned media coverage helps with free public exposure. This in turn gets the word out about an organization’s mission. For example, you can create press releases related to new staff additions or upcoming events and share them with your media contacts.
Social media marketing
Social media sites allow organizations to stay connected with supporters and advocates at any time of day. There are different social media platforms that work for different organizations. For example, Twitter is a great way to have quick conversations with people about an issue. Facebook is a good place for sharing more in-depth content and articles on a particular subject area. LinkedIn is a platform where you can build your network of contacts and share information about your organization or topic area.
Blogs and Other Content
Producing great content for blogs or other channels can be an extremely effective way to bring people back to your site or area of social media where they are more likely to donate. A blog can allow you to have conversations with supporters and advocates, answer questions, give more information about your organization or cause, and talk about the issues in your community. In addition, the use of photos, videos, infographics, etc., is a great way to get information across in a compelling manner.
E-newsletters
Sending out an e-newsletter is a great way to engage your supporters. You can include links back to your website, send updates about your organization, share compelling videos or photos from recent events, etc. Just make sure your audience has opted in to hear from you and be sure you don’t spam their inboxes with constant updates every day.
Event marketing
Organizing special events around a particular subject area is a good way to inform the public about an issue or about your organization. Some examples of events are panel discussions about a subject, fundraising dinners, etc. Webinars have grown in popularity with nonprofits in recent years as well. With so many options for virtual, hybrid or in-person gatherings, you’ll be sure to find a way to boost your nonprofit’s audience and growth.
Newspaper/Magazine ads
Just because digital marketing has grown doesn’t mean that traditional media isn’t viable. Unfortunately, this can be one component of advertising that nonprofits often neglect due to lack of funds. Adding an ad to the back of a newspaper with some basic information about what you do, how people can get involved, and what you are looking for in terms of volunteers, donors, etc., is still a great way to spread the word.
PPC advertising
Don’t forget about pay-per-click advertising on search engines like Google. This makes it possible to drive traffic to your website based on specific keywords your target audience searches or pages they visit online. You can write compelling ads that allow you to get the word out about what your organization does.
This section should describe in detail how your nonprofit runs or plans to run its business day-to-day. Outline internal systems that will be used to track and monitor each product, service, or program offered by the organization (e.g., accounting software). Describe what kind of training employees may need to perform their duties effectively. Also include information about whether future hiring plans are scheduled. If so, mention whether all positions will need to be filled immediately or if some can be temporarily contracted out until permanent staff is hired. Finally, create a chart showing the milestones your organization hopes to achieve annually over the next five years.
Provide a list of important management team members within your organization. Make sure to include each person’s title, how long they have been working there, and what responsibilities are part of their role. For each person, include any previous experience they have as well as personal traits that would help them succeed in it. If there are no existing employees with enough business expertise to serve certain roles, list the qualifications the ideal candidate would possess instead.
In this section of your business plan, provide a detailed breakdown of how much funding you are seeking broken down by category (e.g., marketing, staffing, etc.). Provide information about how much revenue is expected from donors and customers compared to funds needed to cover operating costs such as salaries, advertising, and rent. If the organization already has an existing revenue stream, explain how new funding will be used to fund new operations.
The appendix is a good place for any additional information that you would like readers of your nonprofit business plan to have. This includes additional industry research and information on your products, services, or programs. It might also include testimonials from satisfied customers or profiles of board members. Or, it might include architectural designs of a new facility you hope to build.
In summary, a nonprofit business plan is a document that outlines your nonprofit organization’s goals and objectives. A well-written, comprehensive plan can help you attract funding from potential donors or investors. It will also provide clarity to stakeholders by giving them an understanding of your vision for the organization’s future growth.
*This spotlighted blog post is courtesy of Growthink
The post How to Create a Nonprofit Business Plan appeared first on Nonprofit Hub .
Share and Enjoy !
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.
Copy short link
 (1).png)
How to Write a Charity Business Plan in 5 Easy Steps
Read Time: 3 Minutes
Posted: 16 Dec 2020
16 Dec 2020
Starting up your own charity or non-profit organisation can be extremely rewarding, but it’s important to set up a strong foundation before you even think about diving into fundraising. Planning ahead is the best way to ensure you’re having the biggest impact on your cause.
Although not run like a business in the traditional sense, charities definitely benefit from having a sound business plan – plus, it’ll make it easier to launch your charity and secure funding in the long run. Here’s exactly how to write your charity business plan in 5 easy steps.
Why Do Charities Need a Business Plan?
Ultimately, a business plan is an important document for a charity because it sets out your goals and the strategies you’ll be using to achieve these goals. Like a business makes a business plan to ensure it will be profitable, a charity makes a business plan to ensure it can benefit those it sets out to benefit.
Step 1: Say Who You Are
The first two sections of your business plan are your executive summary and charity description. In the executive summary, you’ll need to outline:
- Your personal details
- Your charity idea
- Your mission, goals and aims
- The type of organisation you’d like to set up
You’ll then go into more detail in your charity description, where you can talk about where your charity idea came from and why you believe it’s important to raise funds for this untapped cause.
You’ll also need to think about where you’ll be based and the advantages and disadvantages of this location.
Describe what you hope to achieve in the first, second and third years of your charity running, showing both ambition for your organisation but also that you know what is realistic to be able to achieve.
You may also want to brush on some of your unique selling points (USPs), explaining why your charity is necessary in the current climate and what makes you stand out from similar charities who may be raising awareness and funds for similar or the same cause.
Step 2: Understanding Your Market
It’s important to show that you’ve completed the necessary market research to understand how feasible your goals actually are. As well as knowing that there’s a community or group of people who would benefit from the funds raised for your charity, you also need to know that people will be willing to donate to you to create those funds in the first place.
Use polls or ask people face-to-face about their opinion on your cause, asking how much or how often (if at all) they’d be willing to donate to support you.
Furthermore, it’s important to know who else is raising awareness or funds for the same or a similar cause – in the business world, these would be known as your competitors. Check out what they’re doing and how you could do it better or target a more niche demographic of donors. It’s also great to look at other kinds of successful charities, who may not necessarily be supporting the same cause as you, for inspiration as to what works and what doesn’t.
We recommend completing a SWOT analysis as part of your market research. This helps you to identify yours and your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, giving a well-rounded view on where exactly you’d sit in the current market.
Step 3: Day-to-Day Operations
Next, you’ll need to get into the specifics of the day-to-day running of your charity. For this section, you should outline:
- Any resources you’ll need to run your charity
- Suppliers and other organisations you’ll work with
- Premises of your charity
- Equipment you’ll use
- Your process for taking payments from donors
- Any legal requirements like licenses you’ll need, e.g. for preparing food
- Any insurance you have or will need
You’ll also need to write a small biography for each person who is important to the running of your charity, including their role and their experience showing why they’re perfect for the role. Important people include the management team and any trustees. If this is set to change in the immediate future, make sure to include an overview of any planned changes to your management structure.
Finally, using your SWOT analysis, write down any skills gaps you have in your team and how you plan to fill these gaps.
Step 4: Social Impact
Whereas a regular business would need to see a financial return, a charity also needs to show a social impact. This is the difference you make for the communities and people you work with, and one of the most important parts of your charity business plan.
As well as saying what kind of impact you want to achieve for your chosen cause, you’ll also need to state what you’re going to measure to prove this impact and how you’re going to measure it. And, not forgetting, how you’ll use your learnings to keep adapting your processes.
Another important question to ask yourself for this section is: how are people going to find out about your charity? Luckily, we’ve come up with 20 budget-friendly charity marketing ideas to help give you some inspiration!
Step 5: Finances
In this section, you’ll need to outline your costs and expenditure. As great as your charity idea is, it’s nothing without a well-thought-out financial forecast.
You’ll need to include:
- Predicted costs and expenditure (using research to back this up)
- Main source of income (donors, trustees etc. and what you’d expect them to give)
- Pricing strategy if you plan on selling products or services to fund your charity
- Cash flow forecasts
- Costs table
By preparing for all eventualities with your business plan, you’re turning your charity idea into a reality - and that’s something you should be really proud of. We hope this guide has given you plenty of information to include in your business plan, and you can always view our 10-step checklist for writing a business plan for more information on this.

About the Author
Related posts.
.jpg)
Open Day Transport and Accommodation

How Will the UK General Election Affect My Business?

Battling Hay Fever at Work: How Employers Can Support Affected Employees
Iso certified.
Bluetree Print Limited T/A has been certified to ISO 9001:2015 & ISO 14001:2015 for the following scope:
ISO 9001:2015: The production and supply of digitally, lithographically and nanographically printed products on paper, board and plastic substrates at the Manvers sites.
ISO 14001:2015: The production and supply of digitally, lithographically and nanographically printed products on paper, board and plastic substrates at the Manvers sites.
Certification is subject to periodic surveillance and re-assessment. For further information regarding the validity of the certification please Contact us for Certification Help. Call our helpful team today!
We’re a completely free one-stop-shop to find grant funding, and free help and resources
Fast, simple and very effective, need help ask the ai bunny.

Free Example UK CIC or Charity Business Plan Template
Uk cic and charity business plan template - 3 steps.
I've used the term charity business plan and as an example. Your business plan is what you aim to achieve in the coming year. However, this planning template and checklist will work just as well for fundraising, project and other plans, and will work just as well for your CIC or other not for profit organisation.
The only right way to create a charity business plan is whatever way works for your charity and you can use this simple 3 step process as a template to create your CIC or charity business plan. That could be anything from a one page business plan in Word, for a very small CIC, to a substantial, detailed business plan for a large UK charity.
Don't Let Your Charity Miss Out
Use Funding Finder , to find a huge range of grants and Help Finder to find companies that make product/financial donations, plus lots more.
Find Funding, Free Help & Resources - Everything Is Free
Register Now!
Step 1 - charity business plan goals & objectives.
Your objectives (or goals) are what you must achieve to deliver your charity business plan. These can either be long term (strategic plan)) or nearer term, such as annual business, fundraising and project plans.
Charity Business Plan Objectives - Strategic Plan
Often strategic and business, or other annual plans can be seen as quite separate, but these are not. Next year's business plan, is Year 1 of your strategy. Looking at your strategic plan objectives, what must you achieve in the coming year to deliver these?
| To ensure every homeless person in Aylesbury can have a hot meal each day | To increase the number of meals we deliver to 500 this year | |
Charity Business Plan Objectives - Operations
You also need to ensure that your charity continues to be well run and delivers the high quality support you want it to. Look at your operations, such as delivering services for your beneficiaries, fundraising, finance, people and other activities. What are the key activities and what must you achieve in these areas areas?
| Fundraising | To increase trust fundraising income to fund the provision of additional meals | |
| Facilities | To refurbish the Hall to make it much more welcoming, with better services, including upgrading the kitchen | |
STEP 2 - CHARITY BUSINESS PLAN KPIs (TARGETS)
Trying to measure everything would take a huge amount of time and most won't really matter. Your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the key targets you use to measure and monitor your progress to achieving your business plan objectives.
Measuring Charity KPIs
There are really only 3 things you might want to measure - quality, quantity, time and cost. And, these are interlinked. The public sector is particularly prone to what are called perverse outcomes. Focussing on a single KPI measure, to the exclusion of the others that nobody thought about, but which turn out to be really important.
- Buying higher quality fresh food and/or preparing food from scratch, rather than buying in pre-prepared.
- Preparing more meals and/or extending opening times.
- Using pre-prepared ingredients and buying more equipment/expanding kitchen capacity.
You don't need to measure all of them for everything, if the other factors aren't important, or won't change. I've provided some examples of planning KPIs below.
How To Set Charity Business Plan KPIs
In order to ensure you deliver your charity business plan objectives, you need to be able to measure these and monitor progress.
The first step is to set KPIs for each objective using SMART – that is your KPIs are S imple, M easurable, A chievable, T imely and R elevant.
You then need to decide who will be responsible for delivering and reporting these, any milestones in terms of when activities will be delivered and how and when these will be reported.
| Provide more hot meals | Deliver 500 good quality, hot meals to homeless people | Ian | By year end | To be reported to board in quarterly reports, including stats on beneficiary feedback. Last year 431 meals delivered. |
| Increase fundraising | Submit 10 good quality trust bids for total of £100k, to achieve income of £25k | Ian | By year end | Last year raised £20k from 7 bids. Engage bid writer to submit additional bids, with funding in budget for this. Bid numbers and amounts, actual and forecast in board reports |
| Refurbish Hall | Agreed refurbishment delivered on time and on budget | Jim | April | Contract let Dec, work begins Jan. Funding in budget £10k. Progress updates at board meetings. |
Once you've set your business plan KPIs, ask yourself if these are the key issues you need to monitor and manage to deliver your business plan objective. Are there any KPIs you don't need and is there anything missing that you do? And does each KPI meet the SMART criteria above?
STEP 3 - IMPLEMENTING YOU CHARITY BUSINESS PLAN
The Charity Excellence Data Store tracks sector resilience and a key theme is a lack of realism in charity planning. Ambition is a hallmark of the sector, but 'Aspirational' is the flip side of planning to fail, if that involves committing people and resources to business plans that aren't achievable. Here are my ideas to help you ensure that your business plan will succeed.
Charity Business Plan Reality Checklist
For your charity business plan to work, you need to be able to confidently answer 'yes' to each of the questions below. That's about making an objective assessment of each.
- Our charity business plan includes everything that's important to us that we want to achieve
- Our business plan objectives and targets are realistic and achievable
- We will have enough people, with the necessary skills and experience to deliver our plan
- The key risks have been identified and quantified
- We have taken adequate steps to manage these, to ensure no risk remains unacceptably high
- There is adequate funding in our budget to resource all of our business plan objectives
- Our fundraising targets are realistic and we are confident that these should be achieved
- For example, not launching a project until funding is secured, or having plans to scale back activity
- Our business plan has been communicated to everyone who needs to know about it and it is simple, clear and will be understood by them
- The information reported focusses on the key issues and will enable us to take action in good time, if we need to
Congratulations, you have created a simple, clear and effective business plan. If you are unsure about any of the above, revisit your plan and make any changes you need to.
Communicating Your Charity Business Plan And Making It A Success
The World is full of detailed and beautifully crafted business plans sitting on shelves gathering dust. In any, except the smallest of charities, it is your staff and volunteers who will deliver your business plan, so they need to know what you want them to do and feel motivated to do so. If you e mail a big complicated business plan to everyone, it may not be read and, if it is, may not mean much to its readers.
You need to communicate your plan in a simple, clear way that engages them. It also needs to be reflected in any other plans or procedures. For example, your budget and risk plans, any project plans and, for larger charities, appraisal objectives and departmental work plans.
For reporting, sometimes reports are too 'fluffy' or nor easily understandable, or far too long and complicated. Often these can be simply rubber stamped by boards. Ensure that your reports meet your needs, focus on the key issues, are clear and understandable for trustees, and acted upon. Here's the Charity Excellence guide to making reports more effective and less work.
Access All The Free Charity Resources & Free Funding Database
A registered charity ourselves, the CEF works for any non profit, not just charities.
- Funding Finder - with categories for Core Cost Funding and Small Charities & Community Groups .
- Help Finder – find anything for free, including companies that make financial donations and raffle prizes .
- Data Finder – for fundraising bids & research, impact reporting, planning and campaigning.
Plus, 100+downloadable funder lists , 40+ policies , 8 online health checks and the huge resource base.
Quick, simple and very effective.
Find Funding, Free Help & Resources - Everything Is Free.
To access help and resources on anything to do with running a charity, including funding, click the AI Bunny icon in the bottom right of your screen and ask it short questions, including key words. Register, then login and the in-system AI Bunny is able to write funding bids and download charity policy templates as well.

With 40,000 members, growing by 2000 a month, we are the largest and fastest growing UK charity community. How We Help Charities
Charity excellence framework cio.
CHARITY BUSINESS PLAN: The Ultimate Guide To Writing A Non-Profit Business Plan
- by Kenechukwu Muoghalu
- August 14, 2023

Table of Contents Hide
What is a charity business plan , why do i need a charity business plan, #1. executive summary, #2. present your opportunity, #3. target audience, #4. strategic plan objective, #5. your products and services, #6. operational plan, #7. marketing plan, #8. financial plan, #9. management team and board, #10. appendix, charity business plan template checklist, how many pages should my charity business plan be, how do i start a non-profit with no money, do not let your charity business plan miss out, charity business plan faqs, can i make money owning a charity business, how do charity owners make money, how do i start a small charity.
A lot of charity organizations do not like the idea of having a business plan. This is because they think that creating a business plan for their charity organization is a waste of time. But wait! What makes you think so? Isn’t a charity organization a form of business? Be it a profit or nonprofit, it makes no difference. Learn to accept that it is still in the business genre. This is why we have created an example of what a UK template checklist looks like, just to guide you while writing your charity business plan.
There are lots of benefits to having a business plan for your charity organization. This article will furtherly cover those grounds. Shall we!
A charity business plan isn’t just a document of many pages. When you define it like that, it is said to reduce its actual value. A charitable business plan details the products and services your nonprofit organization provides. A charity business plan also contains the people on your team, the community you work for, your financials, goals, and how to attain those goals. Now, this right here can count as a definition.
Don’t make the mistake of starting that excellent idea of yours without having a charity business plan on standby. Even those dreams and ideas can turn useless if you cannot formulate, execute, and implement a plan that can help you achieve them.
Creating a nonprofit business plan doesn’t have to be long and bulky. Even a short business plan can serve its purpose more than a long one. All it needs to contain is the necessary information about your organization and you are good to go.
Heaven yes! You do need a charity business plan. Having a charity business plan will save you tons of pitfalls. A charity business plan can help you create forecasts for revenue and also help you plan how to utilize any money that comes in. You would have a clear guide on all the activities your organization goes through. You can even measure your growth and denote where changes are needed for more growth.
When you talk about good business planning, you talk about setting goals , carrying your team along, tracking performance, and improving. Every business needs these essentials to grow, no matter the nature of the business. Even if you are not interested in whatever profits the organization will yield due to your large heart, you still need to run a healthy organization. Whichever angle you come from, you can’t run from it.
Read Also: How To Register A Business: Detailed Guide To Business Registration In The Uk
For example, when you run a charity business, you need to always report and plan with the board of directors. Most of the time, the financial status of the organization is mostly what is being discussed. This is where your charity business plan comes in. It can help you compare your actual results to your financial forecasts. It can guide the amount of spending you do while keeping your financial position in check.
Moreover, keeping a charity business plan can also help attract sponsors, donors, or even lenders who want to understand how your organization works and help you achieve your goals.
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Non-profit Business Plan
To create a charitable business plan, you will need to either follow some examples, which can also be accessed in a PDF, or follow these outlines. These outlines should be in check while creating a business plan for your charity organization. Nothing should be left out. This ultimate guide includes:
This is the general overview of the whole business plan. It is usually the first section to read and the last to write. While in this section, avoid jargon and write as though an external eye is going to access it. It should be easily accessible and easy to read. Go ahead to briefly state the overview of your mission. Include the services you provide and how you fundraise.
A great way to do this is by using a positioning statement . In this section, describe the problems people face and how your organization can solve them. It can be giving tutors to kids or providing food to a large number of people. Explain how your organization is different from other, and state what you do to help the community and saves lives.
If you have a specific target audience that your organization caters to, then specify it in this section. State who benefits from the services you render. You should also note that it is possible not to have a particular target market. This means that your product is utilized by all.
In your strategic plan objective , mention those plans and visions you want to observe next in your organization. With those improvements and a project plan, you are ready to take. For example, you feed 300 people per year, but then you are planning on making it 500 this particular year. It can even be about your organization. You can choose to grow from a regional nonprofit to a national nonprofit organization. Talk about those long-term goals in this section and work towards getting them done.
Just like the name implies, you will need to define the products and services you offer. Talk about how you will raise money and serve your community. Detail every item and avoid keeping it general. In this section, you will need to include even the smallest detail that you think no one would notice.
How will your charity organization operate? What are the legal structures, organizational structures, location, and inventory? What about the management team? How would they operate? You will need to answer these questions in this section.
When writing your charity business plan, our marketing strategy is an important factor because you will need to promote your organization. You will need to make it known, and let people know the services you offer and what your charity organization is all about. While at this, you can indirectly attract sponsors or donors that love what you do and will help in any way.
This section will have information on your financial details. You will include all your current funding, expenses, liabilities, revenue, and assets. Add statistics and make it more professional. Add graphs to make it more comprehensive. This section is also the most crucial to loaners and donors. Add expected expenses as well, salaries, utility bills, website hosting, insurance, subscriptions, and anyone expenses that the organization will be running.
List the individuals that will be present in your organization. Clearly, they have different duties and responsibilities. Both your day-to-day team and your board members should not be left out. Feature those capable workers that always put the organization first before any other thing. Indicate their qualifications and degree, and don’t forget to also mention how good you are too.
In this section, you will be free to include anything extra that you wish to. Any special feature that you think shouldn’t be exempted from your charity business plan? It can be the bios of your board members and any other details you feel are relevant for the section. When you follow all these, there shouldn’t be a reason why you will not have a successful charity organization.
To help you get started with your UK charity organization, we have created a business plan example template. This charity business plan template can also be utilized in other locations apart from the UK. So we urge you to explore. Don’t fret. Let’s take a look at our charity business plan example template. They include:
- Define your goals and milestones.
- Understand your team and other stakeholders.
- Assess your financing model.
- Identify your risks and manage them.
- Attract investment and volunteers.
- Research and discover new opportunities.
- Kink your plan.
You can have from seven to thirty pages in your business plan. It must not be made too long before it can serve its purpose in your organization. Just keep it clear and concise for anyone to scale through without difficulty. But why bother when we have an already composed charity business plan that is highly convertible. All you need to do is to get a copy here and start your journey to success.
The best action to take is to approach potential investors or donors for help. While doing this, you will need to explain the nature of your organization and whatever idea you have for its growth. Even with no cash at hand, you can still make this work.
Meanwhile ,
Our main priority is to boost your charity organization and to give you an opportunity that is rare to find.
Have you tried creating a plan and it seems tough? Do you have questions that you don’t have an answer to even after multiple trials? Stop trying!
Your plea has been heard and that is why we will be giving you a uniquely designed charity business plan. A plan that multiple charity organizations have tested and confirmed its productivity. You won’t have to stress more because it is simplified and easy for anyone to access. Take your charity organization to another level now!
Nonprofit organizations have proven to be created out of passion and enthusiasm. But passion without a proper business plan will render your zeal powerless. Imagine being patriotic, going to war without a weapon. How would you win? Just because it is labeled “nonprofit” doesn’t mean that you should operate it like any other business out there. Make a difference with your charity business plan.
A non-profit organization doesn’t earn a taxable profit. But that does not mean that the people that run it can’t receive a taxable salary. The founder can ensure that its workers earn a living, while still running a charity organization.
Charity businesses can earn money through regular activities like using volunteers, hosting fundraising events, sponsoring occasions, selling products, or even running adverts that can bring in donations.
Starting a charity business can be hectic but there are some steps to follow to make it a better experience. Start by defining your mission, picking a name, registering the business, opening a website, raising some cash and staying lean. Don’t forget to also own a Charity Business plan, which you can create using a UK template.
Starting a charity business can be hectic but there are some steps to follow to make it a better experience. Start by defining your mission, picking a name, registering the business, opening a website, raising some cash and staying lean. Don't forget to also own a Charity Business plan, which you can create using a UK template.
Related Articles
- CHILD PROTECTION PLAN: Initiation & Purpose of Section 47
- DIRECT DEBIT GUARANTEE | Detailed Explanation & Guide To The Processes
- BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION APPRENTICESHIP: Definitions, Duration and Levels
- Mortgage Guide: Best Guide For First Timer Buyers In 2023
Kenechukwu Muoghalu
Kenny, an accomplished business writer with a decade of experience, excels in translating intricate industry insights into engaging articles. Her passion revolves around distilling the latest trends, offering actionable advice, and nurturing a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape. With a proven track record of delivering insightful content, Kenny is dedicated to empowering her readers with the knowledge needed to thrive in the dynamic and ever-evolving world of business.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
BRITISH SENIOR LIFE INSURANCE REVIEWS (UPDATED)
Probate house sale: definitive guide to probate house sale.
We noticed you're visiting from Netherlands. We've updated our prices to Euro for your shopping convenience. Use Pound sterling instead. Dismiss
Last Updated on August 15, 2023 by Kenechukwu Muoghalu
- Spend & Save
- Auto & RVs
- Personal Loans
- Equity Loans
- Digital Tools
- Digital Banking & Mobile App
- Mobile Wallet
- Mobile Check Deposit
- Calculators
- Insure & Protect
- Maps Insurance
- Loan Protection
- Wealth Management
- Private Client
- Personal Investments
- Business Checking
- Business Savings
- Business CDs
- Excess Share Insurance
- Digital & Cash Management Tools
- Commercial Insurance
- Employment & Tenant Screening
- Business Loans
- Business Credit Cards
- Business Lines of Credit
- Business Auto Loans
- Commercial Loans
- Multi-Family & Apartment Financing
- Commercial/Industrial
- Commercial Equipment
- Meet Our Team
- Business Investments
- Personal Rates
- Business Rates
- Financial Wellness
- Free Credit Coaching
- Financial Education
- Financial Resources
- For School Employees
- Summer Saver
- Teacher Resources
- Security Centers
- Security Library
- Scam Alerts
- Security Updates
- Events & Education
- Workshops & Webinars
- Maps Community Foundation
- Impact Partnerships
- Events and Fundraisers
- Community Sponsorships
- Education Initiatives
- Teacher Innovation Grants
- Scholarships
- Individual Development Accounts
- Vision and Leadership
- Community Stories
- Credit Union Philosophy
- Guiding Principles
- Core Values
- Executive Team
- Board of Directors
- Annual Report
- Our History
- Why Join Maps?
- Contact Information
- Routing Number & Contact Info
- Branch and ATM Locations
- Branch Services
- Make a Payment
- 503-588-0181
How to Write a Small Business Plan
- Published August 26, 2024 August 26, 2024

Starting a small business can be both exciting and overwhelming. To set yourself up for success, start by creating a solid small business plan. A business plan not only helps you clarify your ideas but also serves as a roadmap for growth and a tool to attract investors and secure loans.
What is a Small Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how you intend to make money, and what your future strategies will be. According to the U.S. Small Business Association , “Your business plan is the tool you’ll use to convince people that working with you—or investing in your company—is a smart choice.” It often includes a mission statement, details about the products or services offered, and a timeline for achieving goals. They are also living documents, so you can—and should—change your business plan as your business evolves.

What to Include in Your Small Business Plan
As the U.S. Small Business Association notes, there is no right or wrong way to write a business plan. The key is to structure your plan to meet your business’s needs. Here’s a simple guide to help you write a small business plan (along with some essential business banking tips to keep in mind).
1. Executive Summary
What it is: A brief overview of your business, including your mission statement, the products or services you offer, and your business goals.
Why it matters: This section captures the essence of your business and is often the first thing potential investors or lenders will read. Keep it concise and compelling.
2. Business Description
What it is: A detailed description of your business, including its history, the market needs it will meet, and what sets it apart from competitors.
Why it matters: This section shows you have a clear understanding of your industry and your place within it.
3. Market Analysis
What it is: An analysis of your target market, including demographics, buying habits, and market trends.
Why it matters: Demonstrating knowledge of your market can help you craft strategies that resonate with your audience and help you stand out.
4. Organization and Management
What it is: A breakdown of your business’s organizational structure, including the roles of your team members.
Why it matters: This section shows that you have the right people in place to execute your business plan.
5. Product Line or Services
What it is: A detailed description of the products or services your business will offer.
Why it matters: Clearly defining what you’re selling helps investors and customers understand your value proposition.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
What it is: Your plan for attracting and retaining customers, including pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies.
W hy it matters: A strong marketing plan shows that you’re serious about reaching your target audience and generating revenue.
7. Funding Request
What it is: If you’re seeking financing, this section outlines how much money you need, what you’ll use it for, and how you’ll repay it.
Why it matters: Being clear about your financial needs and plans shows lenders that you’re responsible and prepared.
8. Financial Projections
What it is: Forecasts of your business’s future financial performance, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Why it matters: This section shows potential lenders and investors that your business is financially viable.
9. Appendix
What it is: Additional information that supports your business plan, such as resumes, permits, and other legal documents.
Why it matters: The appendix provides credibility and additional context for your business plan.
Writing a small business plan might seem daunting but breaking it down into these sections makes it manageable. Remember, your business plan is a living document—update it regularly as your business grows and changes.
With a well-thought-out business plan and the right banking strategies in place, you’ll be better positioned to navigate the challenges of starting and growing your small business.
Small Business Banking Tips
- When seeking funding, consider opening both business checking and savings accounts to draw a clear line between your personal and business finances. This makes managing your finances easier and more professional.
- Use online business banking tools to monitor your cash flow regularly. Many financial institutions (including Maps) offer budgeting tools that can help you track expenses and income in real time, making it easier to stay on top of your financial projections.
- As your business evolves, your banking needs might change too. Regularly review your business bank account, credit options, and financial services to ensure they align with your current goals.
Want more small business strategies?
- Check out our article on how to minimize small business taxes (coming soon).
- Learn about the business banking tools Maps has to offer .
- Find out whether your side hustle should become a small business .
Open an Account
I'm a maps member.
Login to digital banking and select open/apply from the menu.
I Want to Join
I live or work in the Willamette basin.
You are now leaving Maps Credit Union
Modal called incorrectly.
Give us a call at 855-536-7470 . Book a Sales Call
Call us 855-536-7470. Book a Sales Call
For Business Owners
Power your business with GorillaDesk and grow your revenue.
Review Generation
Turn customers into business advocates with online reviews.
Customer portal
Allow customers to view estimates and appointments and pay invoices.
Get an overview of your core metrics with the reporting dashboard.
API integration
Connect GorillaDesk to the tools you use with an open API integration.
Reach every customer with VoIP and SMS.
Improve business operations and keep customers happy.
Manage all your contacts with one tool.
Invoicing & billing
Automate your entire billing process in minutes.
Scheduling & dispatching
Add customers and book jobs faster.
Route optimization
Plan and dispatch optimized routes in seconds.
For Technicians
Your on-the-go solution to simplify workflows and impress customers.
Prepare for and complete jobs easily with the GorillaDesk mobile app.
Quotes & estimates
Send customized quotes and estimates.
Invoicing & payments
Send professional invoices and get paid faster.
GPS tracking
Cut your route planning time in half.
Tools and insights to manage your sales process end-to-end.
Smart views
Close more deals with customizable inbox filters.
Enhanced follow ups
Enhance customer communication with batched emails and VoIP.
Opportunity pipeline
Track and organize your leads across your sales stages.
Pipeline reporting
Gain visibility into how your sales stages are progressing.
GorillaDesk Pricing
Know exactly how much you'll pay
Why GorillaDesk?
Rated #1 in ease of use, service, & features
Book A Sales Call
Ask us anything during this 15-minute call
Pest & Wildlife
Pest control, wildlife control, mosquito control, termite inspections, landscaping, fertilization, residential cleaning, commercial cleaning, bin cleaning, window washing, pressure washing, maid service, contracting, inspections, pool service, fire safety, snow removal, gorilladesk demo video.
Watch it on-demand right now
Guides & tutorials
Become a GorillaDesk pro in no time
YouTube channel
Learn about our latest products and features
Help center
How to set up and use GorillaDesk
Read what our customers have to say
Book a call
Ask us anything with this 15-minute call
Chat with us
Your support team is ready to help
Digital Business Documents
150+ documents to close more business, faster
How to write a cleaning business plan, with example
GorillaDesk Staff

“If you fail to plan, you plan to fail.” – Benjamin Franklin
A house cleaning service business plan can help you get a loan. It’s also a roadmap to a successful cleaning company. But —
There are seven key elements every business plan must have. It’s not hard to write one, but you’ll need to know the answers to some questions before you start.
See how to write a cleaning business plan below, along with tips, advice, and a sample cleaning business plan to get you off on the right foot.
What is a cleaning business plan?
A cleaning business plan is a document that shows why your business should exist, what it will do, how you’ll do it, and who you’ll do it for. It maps out your path to success, including financial projections, a market analysis, your services, and a description of your organizational structure.
Most banks will want to see a business plan before they’ll lend you money. Even if you don’t need a loan, a plan can guide you as you start and scale your business.
Pro Tip: If you’re just looking for the steps to create a successful cleaning company, one of the most important is to set your prices higher than you think. See our article on how to start a cleaning business for more.
The 7 parts of a cleaning business plan
Each cleaning service business plan has seven important parts. The best way to write your own plan is to read this article, then come back with a pen and notebook and jot down your best answers and to-do items. Writing the plan will be a lot easier if you’ve answered all the questions first.
1. Executive summary
Since you haven’t written your house cleaning business plan yet, you’ll skip this part for now. Then when you’ve finished writing the rest, you’ll come back and summarize your plan at the top.
- Your business name
- A very brief overview of your services
- Your mission and vision statements (see examples here and here )
- Why you’re writing the plan (for example, to get a loan or to increase your odds of success)
2. Company description
What is your company all about, and how will it be structured? Write about 100 words on:
- Your business structure ( LLC , corporation , sole proprietorship )
- The types of consumers you’ll serve
- A complete list of your service offerings (for example, cleaning homes and Airbnbs)
- Your business goals
3. Cleaning services you’ll offer
Re-list your service offerings, and this time, write a short description of each one. Include:
- Benefits to the customer of each service
- Why your services are better than the competition’s
4. Market analysis
This is where you show how much you understand the cleaning industry. Include:
- A list of your different types of customers (like property managers and homeowners)
- How many customers are in your area
- A detailed description of the other cleaning companies near you and their strengths and weaknesses
Pro Tip: Make it easier by introducing yourself to a few cleaning company owners and asking how-to questions. (You can find them by searching “cleaning business owner” on LinkedIn.)
5. Strategy
Describe your sales and marketing plan and how you’ll put it into action, including:
- Your operating hours and locations
- Your service area
- How many employees you’ll have, and where you’ll find them
- How you’ll find and connect with customers
- Your pricing
- Your costs, both fixed and per cleaning
- How the company will function (from getting a new customer to doing a cleaning and invoicing)
6. Leadership
Who’s in charge of your cleaning company, and what are they responsible for? Make:
- A list of your company’s leaders and job descriptions
- Names of the owners, what percent of the business they own, their background, and how much they’ll be involved
- Names and bios of any advisors or mentors who will help, including attorneys or other professionals
7. Financial plan and projections
You’ll most likely need to pay an accountant to help with creating financial projections. Create 3-year projections of:
- P&L statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
You can see examples of all three projections below, at the bottom of the cleaning company business plan template below.
Pro Tip: Writer’s block? Tell ChatGPT the answers to the questions above, then ask it to write your plan up for you. Then read and adjust it to fit it to your business goals.
Example cleaning business plan
You can copy, paste, and edit this sample cleaning service business plan template to get started:
1) Executive Summary
Business Name: [Your Business Name]
Owner: [Your Name]
Location: [City, State]
Business Structure: Sole Proprietorship / LLC
Services Offered: Residential Cleaning, Deep Cleaning, Move-In/Move-Out Cleaning, Seasonal Cleaning
Mission Statement: Our mission is to provide high-quality, reliable, and affordable cleaning services that make our clients’ homes healthier and more comfortable.
2) Business Description
A) Company Overview:
[Your Business Name] is a residential cleaning service committed to offering top-tier cleaning solutions to homeowners. We specialize in maintaining a clean, organized, and hygienic living space that enhances the well-being of our clients. Our services cater to a variety of needs, from regular upkeep to deep cleaning sessions.
B) Target Market:
Our primary target market includes busy professionals, families, and elderly individuals who require assistance with maintaining their homes. Our services are also ideal for property managers and real estate agents in need of cleaning services for move-in/move-out or post-renovation scenarios.
C) Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
We stand out by offering personalized cleaning plans tailored to each client’s specific needs. Our commitment to using eco-friendly products and methods sets us apart, ensuring a safe environment for children, pets, and allergy-sensitive individuals.
3) Market Analysis
A) Industry Overview:
The residential cleaning industry is a growing market with increasing demand due to busy lifestyles, dual-income households, and an aging population. The shift towards eco-friendly cleaning solutions is also driving growth.
B) Competitor Analysis:
- Competitor A: Offers basic cleaning services at low prices but lacks personalized service.
- Competitor B: Focuses on high-end clients with premium pricing but limited availability.
- Competitor C: Uses eco-friendly products but charges extra for this service.
C) Market Trends:
- Increasing demand for green cleaning services.
- Growing preference for personalized and flexible cleaning schedules.
- Rising use of online booking platforms for convenience.
D) Target Customer:
- Demographics: Ages 25-65, middle to upper-middle income, homeowners, renters, and property managers.
- Geographic: Residential areas within [City/Region].
- Psychographics: Value convenience, cleanliness, and a healthy living environment.
4) Services Offered
- Standard Residential Cleaning: Regular cleaning services including dusting, vacuuming, mopping, and bathroom/kitchen cleaning.
- Deep Cleaning: Comprehensive cleaning, including areas not typically covered in standard cleaning, such as baseboards, inside appliances, and behind furniture.
- Move-In/Move-Out Cleaning: Specialized cleaning service for homes being prepared for new occupants or post-move-out.
- Seasonal Cleaning: Deep cleaning services tailored to specific seasonal needs, like spring cleaning or pre-holiday preparation.
- Customized Cleaning Plans: Tailored cleaning schedules and services based on individual client preferences.
5) Marketing Strategy
A) Branding:
Develop a professional brand image with a clean, modern logo, and a user-friendly website. Emphasize your commitment to eco-friendly products and personalized service.
B) Marketing Channels:
- Online Presence: Develop a website with online booking options, service descriptions, and testimonials. Use SEO strategies to increase visibility.
- Social Media: Engage potential clients on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn with before-and-after photos, cleaning tips, and promotions.
- Local Advertising: Distribute flyers, post ads in local newspapers, and participate in community events.
- Referral Program: Offer discounts or free services for clients who refer new customers.
C) Pricing Strategy:
- Competitive Pricing: Set prices based on market research, offering competitive rates that reflect the quality and value of your services.
- Package Deals: Create cleaning packages for regular clients, offering discounted rates for long-term contracts.
6) Operations Plan
A) Location and Equipment:
- Location: Operate from a home office with a storage area for supplies and equipment.
- Equipment: Invest in high-quality cleaning tools, vacuum cleaners, mops, and eco-friendly cleaning products.
B) Staffing Plan:
- Initial Staffing: Start as a sole proprietor or with a small team. As the business grows, hire part-time cleaners or contract workers.
- Training: Provide thorough training in cleaning techniques, customer service, and safety protocols.
C) Operations Workflow:
- Client Consultation: Discuss client needs, schedule, and pricing.
- Service Delivery: Perform the cleaning service based on the agreed plan.
- Quality Control: Conduct follow-up checks to ensure client satisfaction.
- Billing and Payment: Use an invoicing system for easy payment processing.
7) Financial Plan
A) Startup Costs:
- Initial Equipment: $2,000
- Supplies (3 months): $500
- Marketing Materials: $1,000
- Website Development: $1,500
- Legal and Licensing Fees: $500
- Total: $5,500
B) Revenue Projections:
- Year 1: $50,000
- Year 2: $75,000
- Year 3: $100,000
C) Break-Even Analysis:
- Monthly Fixed Costs: $2,000
- Variable Costs per Job: $50
- Average Revenue per Job: $150
- Break-Even Point: 14 jobs per month
D)) Funding Requirements:
Seeking $5,500 in startup funding, which will be used to cover initial costs and establish the business.
- Legal Documents: Business license, insurance, contracts.
- Sample Cleaning Checklist: Detailed checklist for standard and deep cleaning services.
- Client Testimonials: Positive reviews from early clients to build credibility.
This house cleaning business plan template outlines the key steps and strategies for launching and growing [Your Business Name], positioning it as a trusted and reliable cleaning service provider in [City/Region]. With a focus on quality, customer satisfaction, and eco-friendly practices, we aim to build a loyal client base and achieve sustainable growth.
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| Revenue | |||
| Total Cleaning Jobs | $30,000 | $45,000 | $60,000 |
| Package Deals/Recurring Clients | $20,000 | $30,000 | $40,000 |
| Total Revenue | $50,000 | $75,000 | $100,000 |
| Direct Costs | |||
| Cleaning Supplies | $1,500 | $2,250 | $3,000 |
| Equipment Maintenance/Replacement | $500 | $750 | $1,000 |
| Transportation (Fuel, Vehicle) | $2,000 | $3,000 | $4,000 |
| Total Direct Costs | $4,000 | $6,000 | $8,000 |
| Gross Margin | $46,000 | $69,000 | $92,000 |
| Gross Margin % | 92% | 92% | 92% |
| Operating Expenses | |||
| Salaries & Wages | $20,000 | $30,000 | $40,000 |
| Marketing & Advertising | $3,000 | $4,000 | $5,000 |
| Insurance | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Website Hosting/Maintenance | $500 | $500 | $500 |
| Office Supplies | $300 | $400 | $500 |
| Utilities (Phone, Internet) | $600 | $700 | $800 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $25,600 | $36,800 | $48,000 |
| Operating Income | $20,400 | $32,200 | $44,000 |
| Interest Incurred | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Income Taxes | $4,080 | $6,440 | $8,800 |
| Total Expenses | $29,680 | $43,240 | $56,800 |
| Net Profit | $16,320 | $25,760 | $35,200 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 33% | 34% | 35% |
|
| |||
|
|
|
| |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash & Cash Equivalents | $3,000 | $8,000 | $15,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | $5,000 | $7,500 | $10,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses | $500 | $500 | $500 |
| Total Current Assets | $8,500 | $16,000 | $25,500 |
| Fixed Assets | |||
| Equipment (net of depreciation) | $2,000 | $2,500 | $3,000 |
| Total Fixed Assets | $2,000 | $2,500 | $3,000 |
| Total Assets | $10,500 | $18,500 | $28,500 |
| Liabilities & Equity | |||
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $2,000 | $3,000 | $4,000 |
| Wages Payable | $1,500 | $2,000 | $2,500 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $3,500 | $5,000 | $6,500 |
| Long-Term Liabilities | |||
| Loan Payable | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Long-Term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $3,500 | $5,000 | $6,500 |
| Equity | |||
| Owner’s Equity | $7,000 | $13,500 | $22,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Equity | $7,000 | $13,500 | $22,000 |
| Total Liabilities & Equity | $10,500 | $18,500 | $28,500 |
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| Operating Activities | |||
| Net Profit | $16,320 | $25,760 | $35,200 |
| Adjustments for Non-Cash Items | |||
| Depreciation | $500 | $500 | $500 |
| Changes in Working Capital | |||
| Increase in Accounts Receivable | -$5,000 | -$2,500 | -$2,500 |
| Increase in Prepaid Expenses | -$500 | $0 | $0 |
| Increase in Accounts Payable | $2,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 |
| Increase in Wages Payable | $1,500 | $500 | $500 |
| Net Cash from Operating Activities | $14,820 | $25,260 | $34,700 |
| Investing Activities | |||
| Purchase of Equipment | -$2,000 | -$1,000 | -$1,000 |
| Net Cash from Investing Activities | -$2,000 | -$1,000 | -$1,000 |
| Financing Activities | |||
| Owner’s Equity Contribution | $7,000 | $6,500 | $8,500 |
| Repayment of Loans | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Net Cash from Financing Activities | $7,000 | $6,500 | $8,500 |
| Net Increase in Cash & Cash Equivalents | $19,820 | $30,760 | $42,200 |
| Cash & Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Year | $0 | $19,820 | $50,580 |
| Cash & Cash Equivalents at End of Year | $19,820 | $50,580 | $92,780 |
Once you’ve used the cleaning business plan template above to start your company, it’s time to grow it fast. Start by breaking up with bad customers. See our article on how to grow a cleaning business for more tips.
Grow your company with cleaning business software
To grow, you need an efficient system to schedule cleanings, plan your routes so you don’t spend all your time driving from place to place, and create fast quotes and invoices. So —
Use a cleaning business CRM like GorillaDesk to handle it all for you. GorillaDesk is a full-featured field service software tool to trim your workload, tame your schedule, and handle your invoicing.
GorillaDesk is the highest-rated cleaning company software on top review sites like Capterra for good reason. Our exemplary customer service chats with you in three minutes on average, and our interface is legendary for its ease of use and full-featured power. Call for a free demo today.
★★★★★ “Man am I so glad I went with GorillaDesk. Can’t wait to see what this year holds for our company after seeing what the program did for us last year.” -Tawndra F., Business Owner
Try GorillaDesk Now
Other posts to check out

Make the move from paper to digital: A step-by-step guide for field service pros
If your field service business is still doing business on paper, it’s time to make a change. Here’s how to find success with a move to digital.

Pest control marketing: Let’s make that phone ring
With so many other local pest control companies making competition tight, keeping that phone ringing with new customers may not feel as easy as you thought. To keep your pest control business growing takes marketing know-how. Here are our best tips.

How to get more positive customer feedback
Customers trust online reviews just as much as word of mouth from friends and family. The truth is: Online reviews can make or break your local services business. Here’s how to build that glowing reputation your service deserves.

A step-by-step guide to writing a pest control business plan
Learn how to create a pest control business plan that boosts profitability, secures funding, and sets your company up for long-term success and growth.

How To Start A Pool Service Business
If you are thinking about starting a pool service company, and need a one-stop resource to get your questions answered, you are in the right place.

How to craft pest control ads that convert (+10 examples)
Learn how to create paper and digital pest control ads that build trust, attract customers, and grow your business, and discover 10 successful ad examples.
Transform your business
Try it free for 14 days. No credit card required. Instant setup.
We will be customers for life
“I can not say enough good things about GorillaDesk it saves us so much time and money. The customer service is the best. I would recommend GorillaDesk to anyone no matter what industry. I trained my employee in 5 minutes on how to use it. We will be customers for life.”

Ryan Sullivan
Business Owner
Ready to Get Started?
Get all our amazing features and top-rated support, with no credit card required.
Pest Control Pool Service Lawn Care And Many More...
Customer Portal Routing Scheduling Invoicing Review Engine Reporting And More....
Knowledge Base Customer Reviews Customer Success Stories GorillaDesk Blog Small Business Guides Free Tools & Templates Digital Document Library
Get In Touch
(855) 536-7470 Watch a Demo Chat with Support Book a Sales Call Become an Affiliate API Developer Docs
Get it on the App Store

Get it on Google Play
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

Experience Management
A Business and Development Guide for Female Entrepreneurs
Women own about 25% of all small businesses, and that market share is growing. Women-led companies experienced a growth rate of more than 16% between 2010 and 2019, versus a growth rate of only about 5% for companies led by men. Women start businesses for the same reason anyone else does: They want to fulfill their vision and have autonomy over their work. However, women are more likely to start a business based on an idea, skill, or hobby they are passionate about. Women face unique challenges when starting their own company, but there are also a wealth of resources designed to help women build a successful business.
Women's Business Resources
- Association of Women's Business Centers (AWBC) : The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) partners with this nonprofit to operate more than 100 Women's Business Centers around the country to support female entrepreneurs.
- Center for Women & Enterprise (CWE) : Women in Rhode Island, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont can turn to this organization for support, including microloans, for starting or growing their businesses.
- The International Association of Women (IAW) : Professional development is vital for anyone interested in growing their career or business, and this organization offers a plethora of resources and opportunities.
- Ladies Who Launch : Digital platforms offer the chance for women entrepreneurs to network with each other no matter where they are located, and this organization harnesses that power.
- National Association of Mom Entrepreneurs : Moms sometimes need extra support as they start a business while also balancing raising a family, and this organization works to provide that support and understanding.
- National Association of Women Business Owners (NAWBO) : Founded in 1975, this organization offers a variety of resources as well as both in-person and virtual events to help female business owners thrive.
- National Women's Business Council (NWBC) : The mission of this organization is to advocate for female business owners. They lobby Congress, work with the Small Business Association, and also offer webinars for entrepreneurs.
- National Women Business Owners Corporation (NWBOC) : Some opportunities are only available to women-owned or minority-owned businesses. The NWBOC offers certifications that a business is woman-owned, which is a necessary component for applying for some contracts and grants.
How to Start a Business
- Lender Match Program : The Small Business Administration runs this program designed to help potential business owners find lenders for SBA-backed loan programs.
- Choosing the Right Location for Your New Business : SCORE offers guides for every stage of a business, including the planning stages.
- Seven Tips for Women Who Want to Start a Business : Narrow in on the story of the business and its founder to present a compelling story that will catch the attention of investors.
- How to Start a Woman-Owned Business : It's important that all entrepreneurs know what their niche is and what they offer that no one else does.
- Nine Successful Entrepreneurs Share Their Best Business Advice for Women : The best advice comes from those who have already started a business and been successful.
- Tips for Women Wanting to Start a Business From Scratch : Many female business owners have to keep their day job when they first start their business.
- How to Start a Successful Minority-Woman-Owned Small Business : Women of color face some additional challenges when starting businesses.
- Black Female Entrepreneurs Give Their Best Business Advice : Learning how to survey the business landscape and take risks is necessary for anyone starting a business.
Write Your Business Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step : A business plan outlines potential goals, including financial goals, and provides a road map for how the business will reach these goals.
- How to Write the Perfect Business Plan in Nine Steps : Writing a business plan can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into steps makes it a far more manageable task.
- How to Write a Winning Business Plan : Harvard Business School offers expert advice on writing the best possible business plan.
- Guide to Creating a Business Plan With a Template : The included template will help make writing a business plan a more efficient process.
- Sample Business Plan : The University of Vermont published this business plan that other entrepreneurs can use for inspiration.
- Create Your Business With Business Plan Templates : The Tory Burch Foundation offers an interactive business plan builder that starts with the user choosing from one of three template styles.
- Example Business Plan : Penn State offers this business plan written for a fictional nursery to help new business owners understand how to write a compelling plan for their own company.
- How to Write a Business Plan : Women working to start a business need to write a business plan, but so do women trying to grow their current business.
Business Finances
- Small-Business Loans for Women : Some loans are only available to woman-owned companies.
- WomensNet Grants : Almost half a million dollars a year in grants are given out by this organization.
- Assistance for Small Businesses : The United States Treasury offers resources and help for small businesses and startups.
- Managing Your Small Business Finances : The FDIC designed this guide to help entrepreneurs successfully manage their finances.
- Five Simple Tips to Keep Your Small-Business Finances in Order : The first step is to always keep personal and business finances separate.
Miscellaneous Business Resources
- WBENC Annual Conference : The Women's Business Enterprise National Council (WBENC) puts on an annual conference that provides educational opportunities for entrepreneurs along with networking opportunities.
- U.S. Women's Chamber of Commerce : The U.S. Women's Chamber of Commerce advocates for women-owned businesses and offers a certification accepted by federal contractors.
- Milestone Circles : This program is designed to help potential entrepreneurs hone their business plans and grow their network.
- How to Do Social Media Marketing for Small Businesses : Being able to market your business on social media is an essential part of any successful business.
Nandana Guda
Nandana is a digital marketing professional with over nine years of experience working in the SaaS and higher education industries. She is based in Melbourne, Australia and works for Qualtrics Asia Pacific & Japan, focusing on digital campaigns and the company websites for the region.
Related Articles
August 26, 2024
Tree testing 101: Elevating your user experience
5 easy steps to integrate digital channels into your cx program.
August 21, 2024
The 4 keys to driving action with NPS feedback
August 6, 2024
Qualtrics’ commitment to secure and private AI
July 11, 2024
4 takeaways for government leaders from X4 2024
June 25, 2024
Achieving Equity and Enhancing Quality of Life in Healthcare
June 12, 2024
X4 London 2024: The power of humanised intelligence
June 11, 2024
Qualtrics named a Leader in Forrester Customer Journey Orchestration Platforms Wave
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Get Started
Home >> #realtalk Blog >> Manage a business >> How to Open a Busine…
How to Open a Business in Maryland
By Homebase Team

Starting a business in Maryland can feel like a big step, but it’s manageable if you break it down into clear steps. You need to know what to do and when to do it. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you get started.
First, you’ll need to register your business. This involves choosing a structure, checking name availability, and filing the right documents.
Next, you’ll need to get the necessary licenses and permits. This includes getting a federal EIN and any state or local permits you might need.
What are the Steps to Start a Business in Maryland?
Starting your own business can be both exhilarating and nerve-wracking. You’re excited about the possibilities but also worried about missing crucial steps. Let’s break it down to make it easier.
Register Your Business
- Choose a business structure (LLC, corporation, etc.): Decide whether you want to form an LLC, corporation, or another type of business entity. Each structure has its own benefits and drawbacks, so choose the one that best fits your needs.
- Check business name availability: Before you can register your business, you need to make sure your desired business name is available. Use the state’s business entity database to check if the name you want is already taken.
- File formation documents with the state: Once you have a name and a structure, you need to file the necessary formation documents with the Maryland State Department of Assessments and Taxation (SDAT). This will officially register your business with the state.
For a detailed guide on the steps to start a small business, check out this article .
Obtain Licenses and Permits
Securing the right licenses and permits is crucial to avoid any legal hiccups down the line. It can be daunting to figure out exactly what you need, but it’s essential for smooth sailing.
- Get a federal Employer Identification Number (EIN): Apply for an EIN through the IRS. This number is used for tax purposes and is required for most businesses, especially if you plan to hire employees.
- Obtain necessary state and local licenses and permits: Depending on the type of business you’re starting, you may need various licenses and permits. This could include a general business license, professional licenses, or local permits for things like zoning and health. Check with Maryland’s OneStop Portal and your local county clerk for specific requirements.
TIP: Avoid common small business mistakes by ensuring you have all necessary permits. Learn more here .
How to Choose the Right Business Structure in Maryland
Choosing the right business structure is a key step when starting a business in Maryland. The structure you select impacts your taxes, liability, and management flexibility. Here’s a breakdown of the main options:
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest business structure. As the owner, you have full control over the business. You make all decisions and keep all profits. However, there is no separation between you and the business. This means you have unlimited personal liability. If the business incurs debt or faces a lawsuit, your personal assets are at risk. This structure works well for low-risk businesses and those testing their business idea before forming a more formal entity.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC provides a balance between simplicity and protection. It creates a separate legal entity, which means your personal assets are generally protected from business liabilities. This structure offers limited personal liability, shielding your personal assets from business debts and lawsuits. LLCs also benefit from pass-through taxation, where business income passes through to your personal tax return, avoiding double taxation. Management is flexible, allowing you to choose between member-managed or manager-managed structures. This makes LLCs a popular choice for small to medium-sized businesses. If you’re considering starting a retail business, this guide can help you understand the necessary steps.
Corporation
A corporation is a more formal business structure. It is a separate legal entity, providing limited personal liability to its owners. This means your personal assets are protected from business liabilities. Corporations can raise capital by issuing stock, making them attractive to investors. However, they come with more formal structure and reporting requirements. Corporations must hold regular board meetings, keep detailed records, and file annual reports. They also face double taxation, where the corporation pays taxes on profits, and shareholders pay taxes on dividends. This structure suits businesses planning to scale significantly or seek outside investment. Interested in buying a franchise? Learn more about the process here .
What Licenses and Permits are Required in Maryland?
Understanding what licenses and permits you need can be a headache, but it’s a vital step to keep your business compliant and avoid fines or shutdowns.
- General business license from the state: Most businesses in Maryland require a general business license. This license allows you to legally operate your business within the state. You can obtain this license through the Maryland Department of Assessments and Taxation.
- Professional and occupational licenses for certain industries: Depending on your business type, you may need specific professional or occupational licenses. For example, if you’re starting a medical practice, a law firm, or a construction company, you’ll need industry-specific licenses. These licenses ensure that you meet the state’s standards and qualifications for your profession.
- Local permits (zoning, health, building, signage, etc.): Local permits vary by county and city. Zoning permits ensure your business location complies with local zoning laws. Health permits are necessary if your business involves food preparation or health services. Building permits are required for any construction or significant modifications to your business premises. Signage permits regulate the size, location, and type of signs you can display. If you’re managing a bar, this bar management guide can help you navigate the necessary permits and licenses.
- Sales tax license if selling taxable goods: If your business sells goods subject to sales tax, you need a sales tax license. This license allows you to collect sales tax from customers and remit it to the state. You can apply for this license through the Maryland Comptroller’s Office.
- Employer registrations for hiring employees: If you plan to hire employees, you must register with the Maryland Department of Labor. This registration involves obtaining an unemployment insurance account and complying with state labor laws. You’ll also need to register for workers’ compensation insurance to cover any potential workplace injuries.
How to Register Your Business Name in Maryland
Choosing a name is exciting, but you want to make sure it’s legally yours. This step can help you avoid future legal headaches.
Conduct a Name Availability Search
Before you can register your business name in Maryland, you need to ensure that the name you want is available. Start by checking the business entity database on the state’s website. This database will show you if another business has already registered the name you want to use. It’s important to choose a unique name to avoid any legal issues and to ensure that your business stands out.
Next, search both state and federal trademark databases. This step helps you confirm that your chosen name isn’t trademarked by another business. Even if the name isn’t registered in Maryland, it could be trademarked elsewhere, which could lead to legal complications down the road. Taking the time to do thorough searches now can save you a lot of trouble later. Avoid planning fallacies by thoroughly checking for name availability. Learn more here .
Reserve Your Business Name (Optional)
If you find that your desired business name is available, you might want to reserve it. Filing a name reservation application with the state gives you exclusive rights to the name for a specified period. This is particularly useful if you’re not ready to register your business immediately but want to ensure that no one else can take your name in the meantime.
To reserve your business name, submit a name reservation application to the Maryland State Department of Assessments and Taxation (SDAT). This process is straightforward and typically involves a small fee. Once your application is approved, the state will hold the name for you, giving you time to complete the other steps necessary to start your business. This reservation period allows you to move forward with confidence, knowing that your business name is secured.
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Maryland Business
A well-thought-out business plan is your roadmap to success. It helps you clarify your vision and can be crucial for securing funding.
Executive Summary
Start with a brief overview of your business. Include your business name, location, and the products or services you offer. Highlight your mission statement and business goals. This section should capture the reader’s attention and provide a snapshot of what your business aims to achieve.
Company Description
Describe your business in detail. Explain what your business does, the problems it solves, and the market needs it addresses. Include information about your business structure, ownership, and the type of business (e.g., retail, service, manufacturing). This section should give a clear picture of your business’s purpose and how it operates.
Market Analysis
Understanding your market is crucial for success. It helps you identify opportunities and avoid potential pitfalls.
Target Market and Customer Profiles
Identify your target market. Describe the demographics, behaviors, and needs of your ideal customers. Explain why these customers would be interested in your products or services. Provide data and research to support your analysis, showing that there is a demand for what you offer.
Competitive Analysis
Analyze your competition. Identify your main competitors and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. Discuss what sets your business apart and how you plan to compete in the market. This section should show that you understand the competitive landscape and have a strategy to stand out.
Product/Service Offerings
Detail the products or services your business will offer. Explain the benefits and features of each offering. Discuss how your products or services meet the needs of your target market. Include information on pricing, production, and any unique selling points that differentiate your offerings from competitors.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Outline your marketing and sales strategy. Describe how you plan to attract and retain customers. Include details on your marketing channels, such as social media, email marketing, and advertising. Discuss your sales process, from lead generation to closing the sale. This section should show that you have a clear plan to reach your target market and generate revenue.
Management Team
Introduce your management team. Provide brief biographies of key team members, highlighting their experience and expertise. Explain their roles and responsibilities within the business. This section should demonstrate that you have a capable team to execute your business plan and achieve your goals.
Financial Plan and Projections
Present your financial plan and projections. Include detailed financial statements, such as income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. Provide projections for the next three to five years, showing expected revenue, expenses, and profitability. Discuss your funding requirements and how you plan to use the funds. This section should show that you have a solid financial plan to support your business’s growth and sustainability. For more finance tips for new business owners, check out this article .
5 Tips for Growing Your Business in Maryland
Growing your business is the next big step, and it comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Focus on Providing Exceptional Customer Service
Customer service can make or break your business. Prioritize quick responses to inquiries and resolve issues promptly. Train your staff to be knowledgeable and friendly. Implement feedback systems to understand customer needs and improve your services. Happy customers often become repeat customers and can provide valuable word-of-mouth referrals. Prevent time theft to ensure your team is focused on delivering excellent customer service. Learn how here .
Develop Strategic Partnerships
Forming strategic partnerships can help expand your reach and resources. Partner with businesses that complement yours. For example, a bakery could partner with a local coffee shop to offer joint promotions. These partnerships can introduce your business to new customers and create mutually beneficial opportunities.
Joining local business associations and chambers of commerce can also be beneficial. These organizations offer networking opportunities, resources, and support. They can connect you with other business owners and potential partners. Being active in these groups can increase your visibility and credibility in the community. Learn why other Homebase users started their businesses and gain valuable insights here .
Invest in Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is a powerful tool for reaching a wider audience. Start with a professional website that clearly outlines your products or services. Use search engine optimization (SEO) to improve your website’s visibility on search engines. Regularly update your site with fresh content to keep it relevant.
Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn can help you engage with your audience. Share updates, promotions, and behind-the-scenes content to keep followers interested. Paid advertising on these platforms can also target specific demographics, increasing your reach.
Email marketing remains effective for maintaining customer relationships. Send newsletters with updates, promotions, and valuable content. Personalize emails to make customers feel valued. Use analytics to track the performance of your campaigns and adjust your strategies accordingly. Create a marketing plan to rebuild and grow your business. Find out how here .
Secure Necessary Funding for Growth
Expanding your business often requires additional funding. Explore different financing options to find the best fit for your needs. Traditional bank loans offer substantial amounts but require a solid credit history and collateral. Small business loans from alternative lenders may have more flexible requirements.
Consider applying for grants. Various organizations offer grants to support small businesses, especially those in specific industries or owned by underrepresented groups. These funds do not need to be repaid, making them an attractive option. Use a labor forecasting tool to manage costs effectively. Learn more here .
Equity financing is another route. This involves selling a portion of your business to investors in exchange for capital. While this means giving up some control, it can provide significant funding without the burden of debt. Explore startup business loans to secure the necessary funding for your growth. Find out more here .
Hire and Retain Top Talent
Your team plays a crucial role in your business’s success. Attracting and retaining top talent should be a priority. Start by offering competitive salaries and benefits. Health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off can make your business more attractive to potential employees.
Create a positive work environment. Foster a culture of respect, collaboration, and growth. Provide opportunities for professional development through training and workshops. Recognize and reward employees for their hard work and achievements.
Effective communication is key. Keep your team informed about business goals, changes, and expectations. Encourage feedback and be open to suggestions. A transparent and communicative workplace can boost morale and productivity.
Lastly, streamline your hiring process. Use clear job descriptions and efficient interview techniques to find the right candidates. Onboard new hires effectively to ensure they feel welcomed and prepared for their roles. A smooth onboarding process can set the tone for a positive employment experience.
Onboard employees, track their time, and pay them — all in one place.
Is Starting a Business in Maryland Right for You?
Starting a business requires more than just a good idea. You need to evaluate several factors to determine if this path suits you.
First, consider your entrepreneurial drive and risk tolerance. Are you ready to take on the challenges and uncertainties that come with running a business? Entrepreneurship involves making tough decisions and dealing with setbacks. Assess your willingness to navigate these hurdles and your ability to stay motivated through ups and downs.
Next, evaluate the market demand for your offerings. Research your target market to understand if there is a need for your product or service. Look at current trends, customer preferences, and potential competitors. This analysis helps you gauge if your business idea has a viable market and if you can attract enough customers to sustain your operations. For practical advice on evaluating whether starting a business is right for you, check out these starting a business tips .
Assess your financial readiness and funding needs. Starting a business often requires significant investment. Calculate your startup costs, including equipment, inventory, marketing, and operational expenses. Determine if you have the necessary funds or if you need to seek external financing. Understanding your financial situation helps you plan better and avoid potential cash flow issues.
Determine if you have the right skills and experience. Running a business demands a diverse skill set, from management and marketing to finance and customer service. Reflect on your strengths and identify areas where you might need additional training or support. Having the right skills increases your chances of success and helps you manage your business more effectively.
Understand the time commitment of running a business. Owning a business often requires long hours and dedication. Consider if you are prepared to invest the time needed to get your business off the ground and keep it running smoothly. Balancing work and personal life can be challenging, so ensure you are ready for the commitment involved.
- What : How to start a business in Maryland.
- So What : Simplifies the process into clear steps.
- Pros & Cons : Pros: detailed steps; Cons: complexity and legal risks.
- Bottom Line : Follow these steps to start your business smoothly.
Let’s make work easier. Get started today with Homebase’s all-in-one employee management platform designed to simplify your daily operations. Sign up now at Homebase and take the first step towards efficient business management.
Remember: This is not legal advice. If you have questions about your particular situation, please consult a lawyer, CPA, or other appropriate professional advisor or agency.
Related posts
August 27, 2024
What is Compliance in Business?
Running a small business is no small feat. Between managing employees, ensuring top-notch customer service, and keeping the books balanced,…
Taking a Physical Count of Inventory
Running a small business means juggling a million tasks at once, and keeping track of inventory can feel like one…
How to Start a Business in Washington State
Starting a business in Washington can seem overwhelming, but it’s a rewarding journey. You need to understand the steps involved…
How to Open a Store in a Mall
Thinking about opening a store in a mall? You’re not alone. Many entrepreneurs see the potential of setting up shop…
How to Start a Business in Oregon
Starting a business in Oregon offers a unique set of advantages. Whether you’re a first-time entrepreneur or looking to expand,…
How to Start a Business in Missouri
Starting a business in Missouri can seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes the process easier. Whether…
Subscribe to our newsletter
Looking for ways to stay up to date on employment laws and small business news?
Homebase makes managing hourly work easier for over 100,000 local businesses. With free employee scheduling , time tracking , and team communication , managers and employees can spend less time on paperwork and more time on growing their business.
- Hiring & onboarding
- Team communication
- Employee happiness
- HR & compliance
- Integrations
- Food & beverage
- Beauty & wellness
- Medical & veterinary
- Home & repair
- Hospitality & leisure
- Education & caregiving
- Contact sales
- Become a Partner
- Careers – We’re hiring!
- #realtalk Blog

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Step 3: Outline. Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets). An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end.
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. Give a brief overview of the charity business industry. Discuss the type of charity business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
Avoid using jargon, acronyms, or any unfamiliar terms. Write for a general audience, and you'll be more likely to keep the reader engaged. 2. Outline your plan. Make a nonprofit business plan outline. Once you know what information will be put into the plan, you'll understand what data you need to source to write it.
Write a fundraising plan. This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind ...
Step 1: Write a mission statement. Having a mission statement is essential for any company, but even more so for nonprofits. Your markers of success are not just how the organization performs financially, but the impact it makes for your cause. One of the easiest ways to do this is by creating a mission statement.
Operational Plan: Explain the day-to-day operations of your nonprofit and spotlight the people who'll make it happen. Marketing Plan: Outline the channels and methods you use to drive your campaigns. Impact Plan: Describe the impact you'd like your organization to make and include the impact you've already had.
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit's mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising. Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit's operating environment. What if the sources of income that ...
Step 6: Create a financial plan. Develop a detailed budget and financial projections for your nonprofit. Identify potential revenue streams, such as grants, donations, fundraising events, membership fees, and earned income. Estimate expenses for staffing, programs, operations, and overhead costs. .
This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization's background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more. Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program.
To most quickly write a nonprofit business plan, start with a template that lays out a nonprofit business plan outline. Answer the questions provided in the template and discuss them with your co-founders if applicable. A templated financial model will help you more easily complete your financial forecasts.
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors. A well-crafted business plan will help you: Define your organization's purpose and goals. Articulate your vision for the future. Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals. Secure funding from investors or donors.
Writing a charity business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and ...
Before we get into the details of how to write a business plan, let's define what it is. A business plan details the services or products your non-profit provides, the people on your team, the community you serve, your non-profit's financials, the goals you plan to achieve, and how you're going to achieve them.
Executive summary. The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is typically the first section of the plan to be read, but the last to be written. That's because this section is a general overview of everything else in the business plan - the overall snapshot of what your vision is for the organization. Write it as though you might ...
Let's get started and get into the nonprofit business plan outline: 1. Create an executive summary. The executive summary provides a synopsis of the whole business plan. Business people prefer to write this section last, after gaining knowledge of every other section.
Create a logistics and operations plan. Write an impact plan. Outline the financial plan. 1. Create an executive summary. The first section of nonprofit business plans is the executive summary. The executive summary should describe your organization and the contents of your nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan template includes fields that cover the foundational elements of a business plan, including: The overarching purpose of your nonprofit. Its long and short-term goals. An outline of how you'll achieve these goals. The template also controls the general layout of the business plan, like recommended headings, sub ...
Start your nonprofit business plan by clearly stating your organization's mission and describing how it plans on reaching its goals. Include a concise description of what makes your organization stand out among competitors (e.g., "We are the only non-profit animal welfare organization in XYZ county" or "Our college student volunteers ...
Charity Vision & Mission Statement Templates. How to quickly and simply write great charity mission and vision statements, without arguing, with mission vs vision explained, a template and examples. But there's an even easier way to do it. Simply pick up the vision and mission statement prompts, amend to suit your charity, drop these into ChatGPT and it'll generate a whole series of both ...
How to Write a Charity Business Plan. Creating a charity business plan involves several key steps: Mission Statement and Objectives: Clearly define the organization's mission, values, and long ...
Step 1: Say Who You Are. The first two sections of your business plan are your executive summary and charity description. In the executive summary, you'll need to outline: Your personal details. Your charity idea. Your mission, goals and aims. The type of organisation you'd like to set up.
The only right way to create a charity business plan is whatever way works for your charity and you can use this simple 3 step process as a template to create your CIC or charity business plan. That could be anything from a one page business plan in Word, for a very small CIC, to a substantial, detailed business plan for a large UK charity.
Start by defining your mission, picking a name, registering the business, opening a website, raising some cash and staying lean. Don't forget to also own a Charity Business plan, which you can create using a UK template. When writing a charity business plan, the executive summary should come first.
As the U.S. Small Business Association notes, there is no right or wrong way to write a business plan. The key is to structure your plan to meet your business's needs. Here's a simple guide to help you write a small business plan (along with some essential business banking tips to keep in mind). 1. Executive Summary
The 7 parts of a cleaning business plan. Each cleaning service business plan has seven important parts. The best way to write your own plan is to read this article, then come back with a pen and notebook and jot down your best answers and to-do items. Writing the plan will be a lot easier if you've answered all the questions first. 1 ...
5 Tips for Writing a Strong Business Plan. A strong business plan is your roadmap to success. It not only guides your operations but also attracts investors. Here are some tips to make yours stand out. Define Your Business Model and Strategy. Start by clearly defining what your business does and how it will make money.
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step: A business plan outlines potential goals, including financial goals, and provides a road map for how the business will reach these goals. How to Write the Perfect Business Plan in Nine Steps: Writing a business plan can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into steps makes it a far more manageable ...
Benefits of Starting a Business in Arizona. Starting a business is a significant step, and choosing the right location can make all the difference. Arizona offers several compelling benefits that can help your venture succeed. Low Tax Burden. Arizona offers a flat 2.5% individual income tax rate, which is among the lowest in the United States.
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Maryland Business. A well-thought-out business plan is your roadmap to success. It helps you clarify your vision and can be crucial for securing funding. Executive Summary. Start with a brief overview of your business. Include your business name, location, and the products or services you offer.